Corumbá
Corumbá Portuguese pronunciation: [koɾũˈba] is a municipality in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, 425 km northwest of Campo Grande, the state's capital. It has a population of approximately 112,000 inhabitants, and its economy is based mainly on agriculture, animal husbandry, mineral extraction, and tourism, being the gateway to the biggest wetlands of the world, the Pantanal.
- For the mine of the same name and located in the state, see Corumbá (mine).
Corumbá | |
|---|---|
Municipality | |
| The Municipality of Corumbá | |
 View Corumbá from the River Paraguay | |
 Flag  Seal | |
| Nickname(s): | |
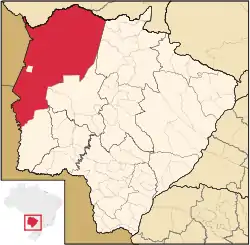 Location in Mato Grosso do Sul | |
 Corumbá Brazil | |
| Coordinates: 19°00′32″S 57°39′10″W | |
| Country | Brazil |
| State | Mato Grosso do Sul |
| Region | Center-West |
| Macroregion | Pantanais Sul-Mato-Grossenses |
| Microregion | Baixo Pantanal |
| Founded | 1778 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Ruiter Cunha (PSDB) |
| Area | |
| • Municipality | 64,960 km2 (25,080 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 21 km2 (8 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 118 m (387 ft) |
| Population (2020 est. [1]) | |
| • Municipality | 112,058 |
| • Density | 16/km2 (40/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC -4 |
| Website | Corumbá Official Website |
Corumbá International Airport connects it to many Brazilian cities and also operates some international flights. There is also another airport serving Corumbá indirectly: the Puerto Suárez International Airport, 20 km away from the center of the city of Corumbá. The city is one of the few Brazilian cities to be served by two international airports
Corumbá is the westernmost and northernmost city in Mato Gosso do Sul, and it is by far the largest municipality by area in that state, composing 18% of its territory. It is also the eleventh largest municipality in Brazil and the largest outside Amazonas and Pará.
The territory of Corumbá has an enclaved municipality within it: Ladário.
History
.jpg.webp)

Founded as a military outpost and colony in 1778 by the Spanish. It became strategically important with the opening of the Paraguay River to international trade after the Paraguayan War (1865–70). Nearby are the buttes of Mt Urucum, which contain vast mineral deposits. In 1878 it was raised to the category of city.
Pantanal
The ecoregion Pantanal is the most important plain of all humid areas in South America. Its large territory meets in the Mato Grosso do Sul, is known as South Pantanal and the city of Corumbá serves as its entrance door. The Pantanal of Mato Grosso do Sul is recognized as one of the most exuberant and diversified natural reserves on the planet.
The great diversity of the fauna is one of its great attractions: caiman, anacondas, fish, capybaras, tapirs, hyacinth macaws, herons, and jabiru storks, among others. The Pantanal received the recognition as National Patrimony in the Constitution of 1988 and as Patrimony of the Humanity and Reserve of the Biosfera from UNESCO.
According to World Wide Fund for Nature (1999), there exist in the Pantanal 650 species of birds, 80 of mammals, 260 of fish and 50 of reptiles. It is a region of great importance for preservation of biodiversity, considered one of the biggest centers of reproduction of fauna of America. Already more than 263 species of fish, 122 species of mammals, 93 species of reptiles, 1,132 species of butterflies, 656 species of birds and 1,700 species of plants have been cataloged there.
Border
The municipality of Corumbá is bordered simultaneously by Bolivia and Paraguay, a situation that is known as tríplice border.
Its urban area borders on the Bolivian cities of Puerto Suárez and Puerto Quijarro, that together make up a Free Zone for purchases of imported products and Bolivian crafts, the limit of which is the end of Ramon Gomes Road. The border with Paraguay is at the south extremity of the municipality in the agricultural zone.
Urbanization
Corumbá consists of two areas. The lower area is where the old village of notable architecture lies, close to the port. The upper area, newer and much bigger, is chessboard-shaped. Its architecture is not like other old Brazilian cities, where the predominant architectural style is the colonial romantic Portuguese. Its architecture is Italian neoclassical, the same as central Asunción, the old suburbs of Buenos Aires, the towns of the countryside of the Uruguay, and the majority of the southwestern Rio Grande do Sul. Its urbanization rate is very high, reaching around 90%. In recent years, due to a better quality of life, the population is aging and the fertility rate is decreasing.
| Population growth | |
|---|---|
| 1970 | 48,600 |
| 1980 | 67,500 |
| 1991 | 88,360 |
| 1993 | 89,585 |
| 1996 | 89,083 |
| 2000 | 95,700 |
| 2004 | 99,441 |
| 2005 | 100,268 |
| 2006 | 101,089 |
| 2010 | 103,772 |
| 2013 | 107,347 |
| 2018 | 110,806 |
References
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Corumbá. |
 Corumbá travel guide from Wikivoyage
Corumbá travel guide from Wikivoyage- Pantanal Escapes - Travel Guide and tourist information for Corumbá
- About the annual Carnaval de Corumbá