South American tapir
The South American tapir (Tapirus terrestris), also commonly called the Brazilian tapir (from the Tupi tapi'ira), the Amazonian tapir, the maned tapir, the lowland tapir, in Portuguese anta, and in mixed Quechua and Spanish sachavaca (literally "bushcow"), is one of the four widely recognized species in the tapir family, along with the mountain tapir, the Malayan tapir, and Baird's tapir.[2] The South American tapir is the largest surviving native terrestrial mammal in the Amazon.[3]
| South American tapir | |
|---|---|
.JPG.webp) | |
| Cristalino River, Brazil | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Perissodactyla |
| Family: | Tapiridae |
| Genus: | Tapirus |
| Species: | T. terrestris |
| Binomial name | |
| Tapirus terrestris | |
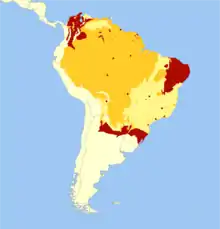 | |
| South American tapir distribution Extinct Extant Probably extant | |
Appearance
T. terrestris is dark brown, paler in the face, and has a low, erect crest running from the crown down the back of the neck. The round, dark ears have distinctive white edges. Newborn tapirs have a dark brown coat, with small white spots and stripes along the body. The South American tapir can attain a body length of 1.8 to 2.5 m (5.9 to 8.2 ft) with a 5 to 10 cm (2.0 to 3.9 in) short stubby tail and an average weight around 225 kg (496 lb). Adult weight has been reported ranging from 150 to 320 kg (330 to 710 lb). It stands somewhere between 77 to 108 cm (30 to 43 in) at the shoulder.[4]

Geographic range
The South American tapir can be found near water in the Amazon Rainforest and River Basin in South America, east of the Andes. Its geographic range stretches from Venezuela, Colombia, and the Guianas in the north to Brazil, Argentina, and Paraguay in the south, to Bolivia, Peru, and Ecuador in the west.[5] On rare occasions, waifs have crossed the narrow sea channel from Venezuela to the southern coast of the island of Trinidad (but no breeding population exists there).
Behavior
T. terrestris is an excellent swimmer and diver, but also moves quickly on land, even over rugged, mountainous terrain. It has a life span of approximately 25 to 30 years. In the wild, its main predators are crocodilians (only the black caiman and Orinoco crocodile, the latter of which is critically endangered, are large enough to take these tapirs, as the American crocodile only exists in the northern part of South America) and large cats, such as the jaguar and cougar, which often attack tapirs at night when tapirs leave the water and sleep on the riverbank. The South American tapir is also attacked by the green anaconda (Eunectes murinus). T. terrestris is known to run to water when scared to take cover.
There is a need for more research to better explore social interactions.[6]
Diet
_browsing_leaves_..._(27931351641).jpg.webp)
The South American tapir is an herbivore. Using its mobile nose, it feeds on leaves, buds, shoots, and small branches it tears from trees, fruit, grasses, and aquatic plants. This is known because the diet is studied through observation of browsing, analysis of feces, and studying stomach contents.[7]
Mating

T. terrestris mates in April, May, or June, reaching sexual maturity in the third year of life. Females go through a gestation period of 13 months (390–395 days) and will typically have one offspring every two years. A newborn South American tapir weighs about 15 pounds (6.8 kilos) and will be weaned in about six months.
Endangered status
The dwindling numbers of the South American tapir are due to poaching for meat and hide, as well as habitat destruction. T. terrestris is generally recognized as an endangered animal species, with the species being designated as endangered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service on June 2, 1970.[8] It has a significantly lower risk of extinction, though, than the other four tapir species.
Gallery
 Young South American tapir at the Dortmund Zoo.
Young South American tapir at the Dortmund Zoo. South American tapir in northern Peru.
South American tapir in northern Peru..jpg.webp) South American tapir heart (Tapirus terrestris).
South American tapir heart (Tapirus terrestris). South American tapir performing the Flehmen response.
South American tapir performing the Flehmen response.
References
- Varela, D.; Flesher, K.; Cartes, J.L.; de Bustos, S.; Chalukian, S.; Ayala, G.; Richard-Hansen, C. (2019). "Tapirus terrestris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21474A45174127. Retrieved 15 February 2020.
- Grubb, P. (2005). "Order Perissodactyla". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 634. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- Montenegro, Olga Lucia. The Behavior of Lowland (Tapirus terrestris) at a Natural Mineral Lick in the Peruvian Amazon. Rep. N.p.: University of Florida, 1998.
- "Tapirus terrestris: Brazilian tapir (Also: South American tapir)". Animal Diversity Web. Ann Arbor, Michigan. Archived from the original on 2014-07-06. Retrieved 2014-08-18.
- "Tapir Specialist Group". Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- Pinho GM, Goncalves da Silva A, Hrbek T, Venticinque EM, Farias IP (2014) Kinship and Social One 9(3): e92507. doi: 10.1371/ journal. pone. 0092507
- Hibert F, Sabatier D, Andrivot J, Scotti-Saintagne C, Gonzalez S, et al. (2011) Botany, Genetics and Ethnobotany: A Crossed Investigation on the Elusive Tapir's Diet in French Guiana. PLoS ONE 6(10): e25850. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025850
- "Endangered and threatened wildlife: Tapir, South American (=Brazilian)" (PDF). 50 CFR §17.11(h). United States Government Printing Office. 2013-10-01. p. 23. Retrieved 2014-08-18.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
- ARKive - images and movies of the lowland tapir (Tapirus terrestris)
- Tapir Specialist Group - Lowland Tapir
Further reading
- Linnaeus C (1758). Systema naturæ per regna tria naturæ, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, diferentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I. Editio Decima, Reformata. Stockholm: L. Salvius. 824 pp. (Hippopotamus terrestris, new species, p. 74). (in Latin).
