Council of Europe Development Bank
The Council of Europe Development Bank (French: CEB, Banque de Développement du Conseil de l'Europe) dates from 1956, when the Council of Europe established the Resettlement Fund for National Refugees and Over-Population in Europe as a Partial Agreement. In 1994, it changed its name to the Council of Europe Social Development Fund, before becoming the Council of Europe Development Bank in 1999.[1]
Situated in Paris, the Bank is a separate legal entity and is autonomous in its decision-making. It has an excellent credit rating from Moody's,[2] Standard and Poor's[3] and Fitch Ratings.[4]
The original aim was to help refugees and other displaced persons after the Second World War. It later expanded its scope of activities to include assistance to disaster victims, help with job creation, and improve social infrastructure. Its aim today is to promote social cohesion in its member states.
The CEB acts as a development bank, granting loans to member states. In 2016, its assets stood at 25.6 billion euros,[5] which it uses to co-finance projects by means of loans of up to 40% of the project cost. The current governor is Rolf Wenzel, born in 1954, of German nationality.
Membership
There are currently 41 member states, as follows:
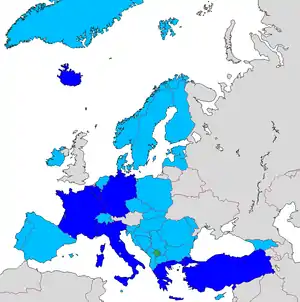
|
The only development bank member states that are not member of the Council of Europe are the Holy See and Kosovo.