DIDS
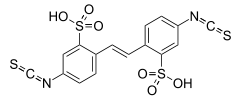
4,4'-Diisothiocyano-2,2'-stilbenedisulfonic acid (DIDS) is an anion exchange inhibitor,[1] blocking reversibly, and later irreversibly, exchangers such as chloride-bicarbonate exchanger.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-Isothiocyanato-2-[2-(4-isothiocyanato-2-sulfophenyl)ethenyl]benzene-1-sulfonic acid | |
| Other names
5-Isothiocyanato-2-[2-(4-isothiocyanato-2-sulfophenyl)ethenyl]benzenesulfonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | DIDS |
| 6543839 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.152.489 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | 4,4'-Diisothiocyanostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic+acid |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H10N2O6S4 | |
| Molar mass | 454.50 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 400 °C (752 °F; 673 K) |
| log P | 4.72 |
| Acidity (pKa) | -3.21, -1.428, -0.37, 0.23 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 13.77, 14.37, 15.425, 17.21 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Jessen, Flemming; Sjøholm, C; Hoffmann, EK (1986), "Identification of the anion exchange protein of ehrlich cells: A kinetic analysis of the inhibitory effects of 4,4′-diisothiocyano-2,2′-stilbene-disulfonic acid (DIDS) and labeling of membrane proteins with3H-DIDS", Journal of Membrane Biology, 92 (3): 195–205, doi:10.1007/BF01869388, PMID 3783658, S2CID 19244281
- Lane, Michelle; Baltz, Jay M.; Bavister, Barry D. (1999), "Bicarbonate/Chloride Exchange Regulates Intracellular pH of Embryos but Not Oocytes of the Hamster", Biology of Reproduction, 61 (2): 452–457, doi:10.1095/biolreprod61.2.452, PMID 10411526
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
