Diplorhynchus
Diplorhynchus is a monotypic genus of plant in the family Apocynaceae native to tropical and southern Africa. As of August 2020, Plants of the World Online recognises the single species Diplorhynchus condylocarpon.[2]
| Diplorhynchus | |
|---|---|
 | |
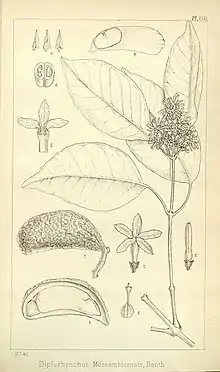 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Gentianales |
| Family: | Apocynaceae |
| Subfamily: | Rauvolfioideae |
| Tribe: | Melodineae |
| Genus: | Diplorhynchus Welw. ex Ficalho & Hiern[2] |
| Species: | D. condylocarpon |
| Binomial name | |
| Diplorhynchus condylocarpon | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
Description
Diplorhynchus condylocarpon grows as a shrub or small tree up to 20 metres (66 ft) tall, with a trunk diameter of up to 2 metres (7 ft). Its fragrant flowers feature a white to creamy corolla. Fruit is green or brown with paired follicles, each up to 6.5 centimetres (2.6 in) long.[4] Vernacular names for the plant include "horn-pod tree" and "wild rubber".[5] The species' local traditional medicinal uses include as a treatment for indigestion, diarrhoea, fever, snakebite, infertility, venereal disease, diabetes, pneumonia and tuberculosis.[4]
Distribution and habitat
Diplorhynchus condylocarpon is native to an area from the Republic of the Congo south and east to Mozambique.[1] Its habitat is dry woodland and hillsides from sea-level to 1,700 metres (5,600 ft) altitude.[4]
References
- Botanic Gardens Conservation International (BGCI) & IUCN SSC Global Tree Specialist Group (2019). "Diplorhynchus condylocarpon". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T146222814A146222816. Retrieved 27 August 2020.
- "Diplorhynchus". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 27 August 2020.
- "Diplorhynchus condylocarpon". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 27 August 2020.
- Medicinal Plants. PROTA. 2008. pp. 229–230. ISBN 978-9-05782-204-9.
- "Diplorhynchus condylocarpon". Flora of Zimbabwe. Retrieved 17 August 2013.
External links
- Dressler, S.; Schmidt, M. & Zizka, G. (2014). "Diplorhynchus condylocarpon". African plants – a Photo Guide. Frankfurt/Main: Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg.
