Elf owl
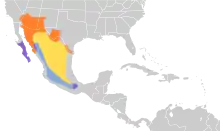
The elf owl (Micrathene whitneyi) is a small grayish brown bird about the size of a sparrow found in the Southwestern United States, central Mexico, and the Baja California peninsula.[2][3] It has pale yellow eyes highlighted by thin white "eyebrows" and a gray bill with a horn-colored tip. The elf owl frequently inhabits woodpecker holes in saguaro cacti; it also nests in natural tree cavities.[4] It is nocturnal and feeds primarily on insects.[5]
| Elf owl | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Strigiformes |
| Family: | Strigidae |
| Genus: | Micrathene Coues, 1866 |
| Species: | M. whitneyi |
| Binomial name | |
| Micrathene whitneyi (J. G. Cooper, 1861) | |
 | |
Reproduction
Elf owls usually choose abandoned, north-facing woodpecker cavities in saguaro cacti, sycamores, cottonwoods, and other hardwood trees, to raise their young. While some cavity nesters utilize vegetation as nesting substrate, elf owls have been observed removing this vegetation and prefer a bare cavity. While elf owls primarily use natural structures for their nesting, they have been known to nest in man-made structures such as telephone poles in urban areas. As populations decrease due to encroachment by urbanization, this may serve elf owls well (for more, see Conservation). [6]
Elf owls generally mate for periods of three months, with male and female birds remaining in close proximity. During this time, females engage in the singing of locational calls (see Appearance and Behavior for more information on elf owl vocalizations), and males respond with mating rituals of their own. Males and female forage independently during this time, but the male elf owl will often hunt for the female as she remains in the pairs' chosen habitat for the mating season. [7]
While three eggs is a very common clutch size, females may lay anywhere from one to five eggs in springtime (late March to early May). The eggs are usually round or oval shaped with a white coloration and are from 26.8 x 23.2 to 29.9 x 25.0 mm in size. The eggs are incubated for about 24 days before the chicks hatch.[7] The young owlets fledge at about 10 weeks. Usually, chicks are born in mid-June or early July. By the end of July, they are almost always fledged and ready to set out on their own.
After the young hatch, the female elf owl watches over them in the nesting cavity while the male often hunts for the young and the female herself. The male elf owl does most of the caretaking himself, feeding his brood independent of the female, who resides in the cavity. Generally this period of communal rearing lasts until the brood is 17 to 21 days of age.[7]
Appearance and behavior
It is the world's lightest owl, although the long-whiskered owlet and the Tamaulipas pygmy owl are of a similarly diminutive length.[8] It is also the world's smallest owl.[9] The mean body weight of this species is 40 g (1.4 oz). These tiny owls are 12.5 to 14.5 cm (4.9 to 5.7 in) long and have a wingspan of about 27 cm (10.5 in).[10] Their primary projection (flight feather) extends nearly past their tail. They have fairly long legs and often appear bow-legged.
They are often found in chaparral, and are easily found during their breeding season. During dusk and just before dawn are the times this owl is most active, they can often be heard calling to one another just after dusk or at sunset in a high-pitched whinny or chuckle. These songs often consist of 5-7 notes that repeat in short duration, similar to the sound of a young puppy. [11] The distinctive vocalizations of elf owls vary according to sex, with males exhibiting a vaster repertoire of complex notes as opposed to females of the same species. Males have two primary classifications of songs, each of which share similar characteristics of structure and function. Most avian observers refer to "Class A" songs to describe those that vary in length (generally 5-15 notes), and are used as both territorial proclamation and to herald the arrival of males to females in the area. While Class A tones reflect changes in environmental factors--wind, precipitation, moonlight, and temperature--Class B songs have significantly less variation among individuals. Class B functions as the primary mating call, stimulating females and encouraging them to accept male sexual advances. As the season goes on and mating begins, Class A songs are observed with lower frequency than Class B. There are also a handful of locational, so-called "scolding", and territorial songs belonging to both male and female birds of the elf owl species. [12]
Hunting is performed mostly during nocturnal hours. Straight line flight is often deployed for this purpose but they will use an arced flight when in the vicinity of the nest and for flying to and from perches. They live in cacti much like some birds, using the shade and climate the cacti provide.
Elf owls feign death when handled, an adaption that encourages a predator to relax its grip so that the owl can escape. Elf owls are also notoriously territorial. Territories are established by the male and are defended by both the male and the female, and males also tend to view their chosen female mate as a territory to be defended, as well.[12] This defense is often accomplished through the use of song. During the breeding season, elf owls are monogamous and stay in breeding pairs, but can be found in small groups during migration and when mobbing predators. Adults as well as young can be subject to predation by other predatory birds such as jays, hawks, and owls.
Migrating
The elf owl is known to migrate in large groups, with patters of migration varying depending on flock and habitat location. Some broods of elf owl migrate to the southwest United States; California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas, in the spring and summer for breeding. In the winter, it is found in central and southern Mexico. Migrant elf owls return north in mid-April to early May. Resident populations occur in a couple of places in south central Mexico and along the Baja peninsula.[13]
Diet
Elf owls feed mainly on arthropods such as moths, crickets, scorpions, centipedes, and beetles. Agaves and ocotillos are ideal places for foraging, as moths and other insects may be found in their flowers. In urban areas they can be seen utilizing outdoor lights that attract bugs as areas for insect hunting. They are often seen chasing after flying insects, with a flight similar to a tyrant flycatcher's. They also feed on scorpions. Once the owl has killed the scorpion, they can be observed removing the stinger before consumption. The elf owls seem to not be bothered by scorpion stings. They will also feed on small mammals, reptiles and birds, on occasion.[14]
Lifespan
Elf owls live 3 to 6 years; in captivity they may live up to 10 years.[15] The most common types of mortality for these owls are predation, exposure, and inter-species as well as intra-species competition.[16]
Subspecies
These subspecies are currently recognized:[17]
- M. w. graysoni Ridgway, 1886 (extinct)
- M. w. idonea (Ridgway, 1914)
- M. w. sanfordi (Ridgway, 1914)
- M. w. whitneyi (J. G. Cooper, 1861)
M. w. idonea, the subspecies in southernmost Texas to central Mexico, is resident, as are the isolated M. w. sanfordi of southernmost Baja California and M. w. graysoni (Socorro elf owl) of Socorro Island, southwest from the tip of Baja California. The Socorro elf owl apparently became extinct in the late 20th century, probably around 1970.
Conservation status
Populations of elf owls have continued to decline in recent years due to a continued loss of native habitats, particularly those in the desert areas of California.[18] Human activities, like increasing water diversion and home construction, have decimated these desert and riparian areas, as well as increasingly abundant invasive species (such as the salt cedar). The destruction of habitat leaves many elf owls unable to nest, hunt, and reproduce in areas like California, Arizona, and elsewhere.[18]
To date, elf owls are not considered a globally threatened species, yet they are listed as "endangered" in California due to a population of fewer than 150,000 individual owls. California has implemented a captive breeding program in an attempt to increase this number, while numerous environmental and government agencies work to preserve their riparian and desert homes.[19]
In fiction
An elf owl named Gylfie is a major character in the Guardians of Ga'Hoole book series by Kathryn Lasky, and the 2010 film adaptation. An elf owl plays a major role in the technothriller The Elf Owl and Imagined Amenities, by Sam Biondo
References
- BirdLife International (2012). "Micrathene whitneyi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- Peterson, Roger Tory, 1908-1996. (1990). A Field Guide to Western Birds. Peterson, Virginia Marie, 1925-, National Audubon Society., National Wildlife Federation., Roger Tory Peterson Institute. (Third edition, completely revised and enlarged ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company. p. 204. ISBN 0-395-51424-X. OCLC 19511450.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "Elf Owl - Distribution Neotropical Birds Online". neotropical.birds.cornell.edu. Retrieved 2020-02-07.
- "Elf Owl Fact Sheet". www.desertmuseum.org. Retrieved 2020-02-07.
- "Elf Owl - Introduction Neotropical Birds Online". neotropical.birds.cornell.edu. Retrieved 2020-02-07.
- "Elf Owl". American Bird Conservancy. Retrieved 2020-11-02.
- Ligon, J. David (February 27, 1968). "The Biology of the Elf Owl, Micrathene whitneyi". Miscellaneous Publications Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan Press. 136: 76 – via JSTO.
- "Elf Owl – Micrathene whitneyi". Owling.com. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
- Sciences, written by Edward Stanley Brinkley ; foreword by Craig Tufts ; photographs supplied by VIREO, the Academy of Natural (2008). Field guide to birds of North America. New York [u.a.]: Sterling. ISBN 978-1-4027-3874-6.
- Owls: A Guide to the Owls of the World by Claus Konig, Friedhelm Welck & Jan-Hendrik Becking. Yale University Press (1999), ISBN 978-0-300-07920-3.
- "Elf Owl". American Bird Conservancy. Retrieved 2020-11-02.
- Ligon, J. David (February 27, 1968). "The Biology of the Elf Owl, Micrathene whitneyi". Miscellaneous Publications Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan Press. 136: 76 – via JSTO.
- Backhouse, Frances (2013). Owls of North America. Buffalo, N.Y.: Firefly Books. ISBN 978-1770852327.
- Ligon, J. David (February 27, 1968). "The Biology of the Elf Owl, Micrathene whitneyi". Miscellaneous Publications Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan Press. 136: 76 – via JSTO.
- "Elf Owl Fact Sheet". Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
- "Micrathene whitneyi (elf owl)". Animal Diversity Web.
- "Micrathene whitneyi". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 2011-11-01.
- "Elf Owl I Owl Research Institute". owlresearchinstitute. Retrieved 2020-11-02.
- "Elf Owl". American Bird Conservancy. Retrieved 2020-11-02.
General references
- The Elf Owl and Imagined Amenities," by Sam Biondo (Kindle edition), December 2013,ASIN: B00FY5491W
- "National Audubon Society" The Sibley Guide to Birds, by David Allen Sibley, ISBN 0-679-45122-6
- "National Geographic" Field Guide to the Birds of North America ISBN 0-7922-6877-6
- Handbook of the Birds of the World Vol 5, Josep del Hoyo editor, ISBN 84-87334-25-3
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Micrathene whitneyi. |
- Elf Owl photo gallery
- Cornell Lab of Ornithology entry for the Elf owl. Includes photograph and audio recording.
- Elf owl fact sheet from the Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum.
