Eosin Y
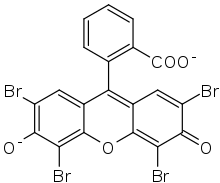
Eosin Y also called C.I. 45380[1][2] or C.I. Acid Red 87,[2][1] is the form of eosin most commonly used in histology, most notably in the H&E (Haematoxylin and Eosin) stain.[1] Eosin Y is also widely used in the Papanicolaou stain (or Pap stain used in the Pap test) and the Romanowsky type cytologic stains.[1][2] It is also used as a photosensitizer in organic synthesis.[3]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(2,4,5,7-tetrabromo-6-oxido-3-oxo-3H-xanthen-9-yl)benzoate [in its deprotonated form] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.629 |
| MeSH | Eosine+Yellowish-(YS) |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H6Br4Na2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 647.89052 |
| Appearance | Red powder |
| Density | 1.018 g·cm−3 |
| Melting point | 295.5 °C (563.9 °F; 568.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Bancroft, John; Stevens, Alan, eds. (1982). The Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques (2nd ed.). Longman Group Limited.
- Lillie, Ralph Dougall (1977). H. J. Conn's Biological stains (9th ed.). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins. pp. 692p.
- Diercxsens, Nicolas (2017-04-10), "Eosin Y", Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp. 1–3, doi:10.1002/047084289x.rn02033, ISBN 978-0-470-84289-8
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.