Fish trap
A fish trap is a trap used for fishing. Fish traps can have the form of a fishing weir or a lobster trap. Some fishing nets are also called fish traps, for example fyke nets.
A typical contemporary trap consists of a frame of thick steel wire in the shape of a heart, with chicken wire stretched around it. The mesh wraps around the frame and then tapers into the inside of the trap. When a fish swims inside through this opening, it cannot get out, as the chicken wire opening bends back into its original narrowness. Contemporary eel traps come in many shapes and sizes and are constructed of many materials. In earlier times, traps were constructed of wood and fibre.
History


Traps are culturally almost universal and seem to have been independently invented many times. There are essentially two types of trap, a permanent or semi-permanent structure placed in a river or tidal area and bottle or pot trap that are usually, but not always baited to attract prey, and are periodically lifted out of the water.
Europe
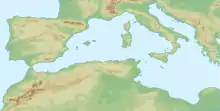
The Mediterranean Sea, with an area of about of 2.5 million km2 (970,000 sq mi), is shaped according to the principle of a bottle trap. It is easy for fish from the Atlantic Ocean to swim into the Mediterranean through the narrow neck at Gibraltar, and difficult for them to find their way out. It has been described as "the largest fish trap in the world".[1]
In southern Italy, during the 17th century, a new fishing technique began to be used. The trabucco is an old fishing machine typical of the coast of Gargano protected as historical monuments by the homonym National Park. This giant trap, built in structural wood, is spread along the coast of southern Adriatic especially in the province of Foggia, in some areas of the Abruzzese coastlines and also in some parts of the coast of southern Tyrrhenian Sea.
South America
The prehistoric Yaghan people who inhabited the Tierra Del Fuego area constructed stonework in shallow inlets that would effectively confine fish at low tide levels. Some of this extant stonework survives at Bahia Wulaia at the Bahia Wulaia Dome Middens archaeological site.[2]
In Chile, mainly in Chiloé, fish weirs and basket fish traps were used.
Australia
Indigenous Australians were, prior to European colonisation, most populous in Australia's better-watered areas such as the Murray-Darling river system of the south-east. Here, where water levels fluctuate seasonally, Aboriginal people constructed ingenious stone fish traps.[3] Most have been completely or partially destroyed. The largest and best-known are those on the Barwon River at Brewarrina, New South Wales, which are at least partly preserved. The Brewarrina fish traps, which are now heritage-listed, caught huge numbers of migratory native fish as the Barwon River rose in flood and then fell.[4][5]
In what is now southern Victoria, near Mount Eccles (Budj Bim) indigenous people created an elaborate system of canals, some more than 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) long. The purpose of these canals was to attract and catch eels, a fish of short coastal rivers (as opposed to rivers of the Murray-Darling system). The eels were caught by a variety of traps including stone walls constructed across canals with a net placed across an opening in the wall. Traps at different levels in the marsh came into operation as the water level rose and fell.[6] These are now a UNESCO World Heritage Site as the Budj Bim Cultural Landscape.[7][8]
North America
Somewhat similar stone-wall traps to the Australian ones were constructed by Native American Pit River people in north-eastern California.[6]
Types and methods
The manner in which fish traps are used depends on local conditions and the behaviour of the local fish. For example, a fish trap might be placed in shallow water near rocks where pikes like to lie. If placed correctly, traps can be very effective. It is usually not necessary to check the trap daily, since the fish remain alive inside the trap, relatively unhurt. Because of this, the trap also allows for the release of undersized fish as per fishing regulations.
| Type | Name | Image | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portable traps usually in the shape of a pot or bottle |
Atlantic cod pot |  |
In 2017 research was reported on the suitability of using baited fishing pots for catching Atlantic cod. Stocks of this once popular commercial fish appear to be recovering after a major fishery collapse. The use of appropriately designed pots can have less environmental impact than other fishing strategies, but to be practical they need to catch their targets both efficiently and selectively.[10] |
| Basic bottle trap |  |
Bottle traps are also known as pot traps. This type of trap is portable, and is used to catch small fish and other small aquatic animals. It consists of a container shaped somewhat like a bottle, usually with an inverted funnel at the entrance. It can be constructed from a plastic bottle, or a glass jar or earthenware pot, or woven with wire or flax. The trap is lowered into the water on a line, where it is left either at the bottom, or suspended at some depth beneath the surface. Bait is usually, but not always used to lure the prey inside. Variants of this basic trap have been used from early times in countries around the world. | |
| Crab trap |  |
Different types of crab traps are used depending on regional preferences, the type of crab targeted and the underwater topography. Typically, they are constructed as wire cages, as shown in the image. | |
| Eel trap |  |
Traditionally, eel traps were widespread, and have been invented independently around the world. The New Zealand Māori wove intricate eel pots they called hīnaki from the stems of climbing plants. At their best, these were works of art.[11] | |
| Fyke net |  |
A fyke net is made from a bag-shaped net held open by hoops. These can be linked together in long chains, and are used to catch eels in rivers. Fyke nets equipped with wings and leaders are used in sheltered places in lakes where there is plenty of plant life. Hundreds of these nets can be connected into systems where it is not practical to build large fixed structures. | |
| Katiska trap |  |
A katiska is a portable fish trap used in Finland. It is a lightweight and made from chicken wire. The trap can either be collapsible or rigid, and is easily placed at any depth since it needs no anchoring. Katiska are commonly used in hobby fishing, since they catch only a small number of fish. The photo shows a fisherman checking a katiska. | |
| Lobster pot |  |
A lobster pot is a portable trap used to trap lobsters or crayfish. An opening permits the lobster to enter a tunnel of netting. Lobster pots are usually constructed in two parts from wire and wood. The lobster enters the first part, called the "chamber" or "kitchen", where there is bait. It then moves into the "parlour", where it is trapped. Lobster pots can hold several lobsters. They are usually dropped to the sea floor about a dozen at a time, and are marked by a buoy so they can be picked up later. | |
| Octopus trap |  |
In Japan, the Mediterranean, and other regions, an ancient variant is used to catch octopuses. They are usually heavy earthenware pots, and do not have an inverted funnel. These traps are left on the sea floor for days at a time. Octopuses enter and remain inside, using the pot as shelter and protection. No bait is used. When the pot is raised, the octopus will not normally try to escape. See also ja:蛸壺. | |
| Soda bottle or glass jar trap |
 |
In Haikou, China, local people make bottle traps with small, glass jars. Local craftspeople produce a variant made from a two-litre soda bottle. This type has an inverted funnel made by cutting off the top of the bottle a few centimetres down the neck, and making vertical cuts downward. This produces tabs which are then be pushed inward, producing the inverted funnel shape. A stone is attached to the side of the bottle, and several meters of line are provided. Numerous holes are drilled through the bottle to allow water to enter and escape. These are sold by the seaside for 6 yuan, along with a small bag of flour for bait. | |
| Stickleback trap | The stickleback trap is a variant of the soda bottle trap. | ||
| Fixed and semi-fixed structures |
Almadraba |  |
Almadraba is an ancient Andalusian way of catching tuna. It is an elaborate way of setting nets in a maze that leads to a central killing pool. In Sicily the mazes of nets, and also the places where the nets are set are called Tonnara, and the overall method of capturing the fishes is called Mattanza. This takes place during spring and the beginning of summer when tuna tend to go into the Mediterranean. |
| Double-heart of stacked stones |
 |
The Double-heart of stacked stones is a stone weir located on the north side of Cimei, an island in the Penghu archipelago to the west of Taiwan. It is a well-preserved ancient fish trap made by stacking stones to form a trap that resembles a flying heart.[12] | |
| Fishing weir |  |
A fishing weir is an obstruction placed in tidal waters or wholly or partially across a river, which is designed to hinder the passage of fish. Traditionally they were built from wood or stones. Fish such as salmon can be trapped when they attempt to swim upstream, other fish such as eels can be trapped when they attempt to migrate downstream. As fish traps, fishing weirs date back to the Bronze Age in Sweden and to Roman times in the UK. They were used by native North Americans and early settlers to catch fish for trade and to feed their communities. | |
| Fish wheel |  |
A fish wheel is a device for catching fish which operates much as a water-powered mill wheel. A wheel complete with baskets and paddles is attached to a floating dock. The wheel rotates due to the current of the stream it is placed into. The baskets on the wheel capture fish traveling upstream. The fish caught in the baskets fall into a holding tank. When the holding tank is full, the fish are removed. | |
| Putcher |  |
Putcher traps are ancient traps used for catching salmon. They are peculiar to the River Severn in Great Britain. A putcher is a conical-shaped basket about five feet long. A number of putchers are tied together in rows standing four or five feet high to form a "rank". The rank is set against the incoming or outgoing tide. Traditionally putchers were made of hazel rods with willow plait. More modern baskets can use steel or aluminium wire.[13] | |
| Trabucco |  |
A trabucco is a shore-operated lift net, a platform anchored to rocks by large logs of Aleppo pine. Two or more long wooden arms jut out into the sea, where they suspend a narrow-meshed net some feet above the water. They are found along the coast of Gargano, where they are protected as historical monuments. Another variant is found along the coasts of Abruzzo and Molise, where they are installed in shallower waters, and use a platform which runs parallel to the coast instead of jutting out into the water. | |
| Wagenya trap |  |
The Wagenya people, in the Congo, build a huge system of wooden tripods across the river. These tripods are anchored on the holes naturally carved in the rock by the water current. To these tripods are anchored large baskets, which are lowered in the rapids to "sieve" the waters for fish. The baskets are designed and sized to trap only large fish. The Wagenya lift the baskets twice daily to check for fish, which are retrieved by swimmers. |
| More images |
|---|
 Traditional trap in Vietnam  Traditional trap in East Timor  Trap used in Tamil Nadu  Eel traps in Haikou, China |
See also
Notes
- Bhuyan, Vishaal B (2011) The Esoteric Investor: Alternative Investments for Global Macro Investors FT Press. ISBN 9780132485074.
- C. Michael Hogan (2008) Bahia Wulaia Dome Middens, Megalithic Portal, ed. Andy Burnham
- Jared Diamond: Guns, Germs, and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies. page 310. W.W. Norton & Company, March 1997. ISBN 0-393-03891-2.
- Graham, Chris (5 February 2019). "Outback Tour: Australia has one of the Oldest Human-Made Structures on Earth. Meh?". New Matilda. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
- Tan, Monica (10 July 2015). "The fish traps at Brewarrina are extraordinary and ancient structures. Why aren't they better protected?". The Guardian. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
- {{cite web|url=http://www.primitiveways.com/ajumawi_fish_traps.html%7Ctitle= Ajumawi Fish Traps|first=Dino|last= Labiste|website=Primitive Ways|access-date=27 October 2019
- "World heritage Places - Budj Bim Cultural Landscape". Australian Government. Dept of the Environment and Energy. 6 July 2019. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- Neal, Matt. "Ancient Indigenous aquaculture site Budj Bim added to UNESCO World Heritage list". ABC News. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- Dam Fishing Fishing techniques of the Baka.
- Meintzer, Phillip; Walsh, Philip; Favaro, Brett (2017-02-08). "Will you swim into my parlour? In situ observations of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) interactions with baited pots, with implications for gear design". PeerJ. 5: e2953. doi:10.7717/peerj.2953. ISSN 2167-8359. PMC 5301977. PMID 28194312.
- Keane, Basil (2009) Te hopu tuna – eeling - Hīnaki – eel pots Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 1 March 2009, retrieved 22 May 2012.
- "A Passage to Penghu". Taipei Times. 2004-10-07. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- Putcher Use in the Severn Estuary
References
- Slack-Smith RJ (2001) Fishing with Traps and Pots Volume 26 of FAO training series, FAO, Rome. ISBN 9789251043073.
- Alvarez, R., Munita, M., Fredes, J. y Mera, R. Corrales de pesca en Chiloé. Imprenta América.
External links
 Media related to Fish traps at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Fish traps at Wikimedia Commons- Corral de pesca
- Fish traps



