Forest degradation
Forest degradation is a process in which the biological wealth of a forest area is permanently diminished by some factor or by a combination of factors. "This does not involve a reduction of the forest area, but rather a quality decrease in its condition."The forest is still there, but with fewer trees, or less species of trees, plants or animals, or some of them affected by plagues. This degradation makes the forest less valuable and may lead to deforestation. Forest degradation is a type of the more general issue of land degradation. Deforestation and forest degradation continue to take place at alarming rates, which contributes significantly to the ongoing loss of biodiversity.[1]
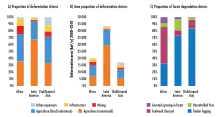

Since 1990, it is estimated that some 420 million hectares of forest have been lost through conversion to other land uses, although the rate of deforestation has decreased over the past three decades. Between 2015 and 2020, the rate of deforestation was estimated at 10 million hectares per year, down from 16 million hectares per year in the 1990s. The area of primary forest worldwide has decreased by over 80 million hectares since 1990. More than 100 million hectares of forests are adversely affected by forest fires, pests, diseases, invasive species drought and adverse weather events.[3]
Interpretations of the term
Deforestation is much worse than forest degradation, but it is clear and visible. On the contrary, forest degradation may start and go on without showing clear effects. It is difficult to measure and even the very term is controversial. In a paper[4] submitted to the XII World Forestry Congress, 2003, Jean-Paul Lanly states: "The situation is even less satisfactory regarding forest degradation due in particular to the imprecision and multiple, and often subjective, interpretations of the term". In 2009 Lund[5] identified more than 50 definitions of forest degradation.
Previously to this August 2017 editing, the Wikipedia page Forest degradation was redirected to Secondary forest, a forest which has re-grown after a timber harvest. This is a confusion: a secondary forest may be perfectly healthy, and a primary forest may be suffering degradation.
The term "permanently" also poses some difficulties: a forest affected by a mild seasonal drought may experience a loss of its biological wealth, but if it is seasonally reversed, then it is not considered degradation. On the contrary, a severe prolonged drought may seriously degrade a forest and make human intervention advisable to limit damages.
Difficulties which hamper the assessment of degradation
According to Lanly,[4] there are 3 difficulties:
- the different choices of the initial state of reference or baseline;
- the chosen criteria: health, biodiversity, production capacity; and
- the opinion on the evolution prospects: will the final result of the process be desirable or undesirable?
For mapping forest degradation in Bolivia, Müller et al.[5] consider areas where only between 30% and 70% of the original forest cover remains. If less than 30% remains, the area is considered as deforested, and if more than 70% remains, the forest is considered intact.
Davidar et al.[6] also think that "Loss of dense and moderately dense forest cover is suggestive of forest degradation." but for the moment no parameter exists "that indicates at what speed forests become degraded and how long it will take for the ecosystem to degrade beyond the point of recovery."
Causes
The Dominican Center for Agricultural and Forest Development[7] lists the following causes of forest degradation:
- Excessive extraction of forest products like timber, charcoal or resin.
- Road building: after it has been built, the road favours soil erosion.
- Open mining: the area where extraction takes place is, of course, completely deforested, but also the surrounding zone suffers a degradation of its fauna and flora.
- Expansion of urban areas.
Davidar et al.[6] add another:
- Livestock grazing: goats or sheep eat tree seedlings, thus slowing natural forest regeneration.
Earth Eclipse,[8] a platform of environment research articles, adds the following causes:
- Acid rain
- Pests and diseases
- Air pollution. Degradation for this cause is specifically called Waldsterben (German word) or forest death.
- Forest fragmentation: a large forest is broken up in smaller woods, which destroys the habitat of large animals.
- Land pollution
- Soil erosion (see image above) and sedimentation
Finally as an additional cause:
- Excessive or unrespectful tourism
Remedies to forest degradation
Generally, any measure to prevent deforestation will also reduce forest degradation. Specifically for degradation, Greenpeace[9] proposes:
- Attaining a responsible forest products industry
- Sustainable forest management
Curbing emissions of sulfur dioxide (to combat acid rain) would also reduce forest degradation for this cause. If a coal-fired power plant uses low-quality coal (with a high sulfur contents), this may be alleviated by flue-gas desulfurization.
Initiatives against forest degradation
- Reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation (REDD+) is an international voluntary climate change mitigation approach to curb deforestation and forest degradation. This mechanism makes part of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) since 2005.
- The United Nations Programme on Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (or UN-REDD Programme) is a collaborative programme created in 2008 by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). It should not be confused with "REDD+. The UN-REDD Programme supports[10] its partner countries (more than 60) through direct funding and technical support to national REDD+ programmes and technical capacity enhancing.
Sources
![]() This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 License statement/permission on Wikimedia Commons. Text taken from The State of the World’s Forests 2020. In brief – Forests, biodiversity and people, FAO & UNEP, FAO & UNEP.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 License statement/permission on Wikimedia Commons. Text taken from The State of the World’s Forests 2020. In brief – Forests, biodiversity and people, FAO & UNEP, FAO & UNEP.
References
- The State of the World’s Forests 2020. In brief – Forests, biodiversity and people. Rome: FAO & UNEP. 2020. p. 9. ISBN 978-92-5-132707-4.
- The State of the World’s Forests 2020. Forests, biodiversity and people – In brief. Rome: FAO & UNEP. 2020. ISBN 978-92-5-132707-4.
- The State of the World’s Forests 2020. In brief – Forests, biodiversity and people. Rome: FAO & UNEP. pp. 9–10. ISBN 978-92-5-132707-4.
- Lanly, Jean-Paul (2003). "DEFORESTATION AND FOREST DEGRADATION FACTORS". Proceedings of the XII World Forestry Congress. Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- Müller, Robert; Pacheco, Pablo; Montero, Juan Carlos (2014). El contexto de la deforestación y degradación de los bosques en Bolivia (PDF). Bolivia: CIFOR. ISBN 978-602-1504-29-1. Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- Davidar, Priya; Sashoo, Sasmita; Mammen, Pratheesh C.; Acharya, Prashanth; Puyravaud, Jean-Philippe; Arjunan, M.; Garrigues, Jean Pierre; Roessingh, Krista (15 May 2010). "Assessing the extent and causes of forest degradation in India: Where do we stand?". Biological Conservation. 143 (12): 2937–2944. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2010.04.032. Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- Ovalles, P. "Causas de la deforestación y degradación de bosques en la República Dominicana" (PDF). CEDAF. CEDAF. Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- Eclipse, Earth. "What is Forest Degradation?". Earth Eclipse. Earth Eclipse. Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- Greenpeace, -. "Solutions to Deforestation". Greenpeace. Greenpeace. Retrieved 23 August 2017.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- PROGRAMME, UN-REDD. "About the UN-REDD Programme". UN-REDD. United Nations. Retrieved 23 August 2017.


