Gaëtan Dugas
Gaëtan Dugas (French: [ɡaetɑ̃ dyɡa]; February 19, 1952 – March 30, 1984) was a Québécois Canadian flight attendant and a relatively early HIV patient who once was widely regarded as "Patient Zero," or the primary case for AIDS in the United States. This claim was later found to be incorrect.[2]
Gaëtan Dugas | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | February 19, 1952 Quebec City, Quebec, Canada |
| Died | March 30, 1984 (aged 32) Quebec City, Quebec, Canada |
| Cause of death | Kidney failure due to AIDS-related infections |
| Nationality | Canadian |
| Occupation | Flight attendant |
| Known for | Long misdescribed as "Patient Zero" of the North American AIDS epidemic[1] |
In March 1984, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) study tracked the sexual liaisons and practices of gay and bisexual men, especially in California and New York. Dugas was code-named as "Patient 0" to indicate his role as the index patient in a cluster of 40 AIDS cases in the United States.[3] Popular media later extrapolated this information to mean that he was the original carrier of AIDS in the country,[4] although the report itself made no such claim. His case was later found to have been only one of many that began in the 1970s, according to a September 2016 study published in Nature.[5][2][6]
Dugas worked as a flight attendant for Air Canada[1][7] and died in Quebec City in March 1984 as a result of kidney failure caused by AIDS-related infections.[8]
1984 Cluster Study
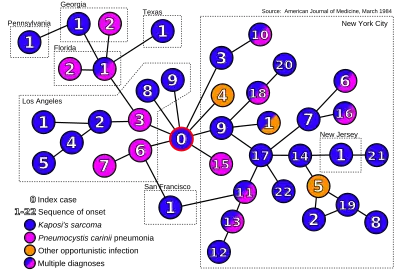
A study published in The American Journal of Medicine in 1984 titled Cluster of Cases of the Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome examined the sexual contacts of gay men infected with AIDS to determine if their histories were consistent with the hypothesis that AIDS was caused by an infectious agent. A graph included with the paper traced the sequence of infection among 40 men and labelled one of the nodes as "Patient 0" (with other nodes including the place of residence and a number indicating the sequence in which they developed AIDS symptoms, such as "NY 14").[3] The paper later stated:
If the infectious-agent hypothesis is true, Patient 0 may be an example of a "carrier" of such an agent. He had had sexual contact with eight other AIDS patients and was the possible source of AIDS for at least three of them. Two of these three men had been his partners before he had overt signs of Kaposi's sarcoma.
The researchers later stated they had originally intended to designate Dugas as "Patient O", with "O" standing for "Out-of-California" but at some point it was changed to a "0".[1]
"Patient Zero" designation
Dugas is featured prominently in Randy Shilts's 1987 book And the Band Played On: Politics, People, and the AIDS Epidemic (1987), which documents the outbreak of the AIDS epidemic in the United States. Shilts refers to Dugas as "Patient Zero" and portrays him as having almost sociopathic behaviour by allegedly intentionally infecting, or at least recklessly endangering, others with the virus. Dugas is described as being a charming, handsome sexual athlete who, according to his own estimation, averaged hundreds of sex partners per year.[1] He claimed to have had over 2,500 sexual partners across North America since becoming sexually active in 1972.[9] In David France's 2016 book How to Survive a Plague, Shilts's editor expressed his regret for having "made a conscious decision to vilify Dugas in the book and publicity campaign in order to spur sales."[10]
Genetic analysis historically provided some support for the Patient Zero theory, in which Dugas was believed to be part of a cluster of homosexual men who travelled frequently, were extremely sexually active, and died of AIDS at a very early stage in the epidemic.[11]
Re-examination of "Patient Zero" designation
A number of authorities have since voiced reservations about the implications of the CDC's Patient Zero study and characterizations of Dugas as being responsible for bringing HIV to cities such as Los Angeles and San Francisco.[1] In the Patient Zero study, the average length of time between sexual contact and the onset of symptoms was 10½ months.[3] While Shilts's book does not make such an allegation, the rumour that Dugas was the principal disseminator of the virus became widespread.[12] In 1988, Andrew R. Moss published an opposing view in The New York Review of Books.[13]
In 2016, a group of researchers led by evolutionary biologist Dr. Michael Worobey conducted a genetic study that looked at blood samples taken from gay and bisexual men in 1978 and 1979 as part of a hepatitis B study, and based on the results of the data, concluded that Dugas was not the source of the virus in the U.S. "On the family tree of the virus, Dugas fell in the middle, not at the beginning."[14] "Beliefs about Patient Zero," Worobey concludes, "are unsupported by scientific data."[14] Worobey's paper, published in Nature in October 2016, finds "neither biological nor historical evidence that he was the primary case in the US or for subtype B as a whole."[5][2][6]
A study by historian Richard McKay of Cambridge and others identified several causes for the Patient Zero myth. During early CDC analysis of cases in California, patient 057 (Dugas) was nicknamed patient "O" for "Out-of-California", but this was interpreted by others as Patient Zero.[1] Dugas was particularly helpful in tracing his network of partners, providing names and addresses for many of them, which was further expanded because others remembered his distinctive name.[12] Although many of the patients analysed reported in excess of 1000 sexual partners, most remembered "only a handful" of names, making their contacts to other cases more difficult to trace.[15][6]
Dr. Robert M. Grant, an AIDS researcher at the University of California, has stated: "No one wants to be the Patient Zero of their village. But this may be helpful because it says, 'Just because you are the first to be diagnosed doesn't mean you started the epidemic.'"[2]
Two films, John Greyson's musical comedy film Zero Patience (1993)[16] and Laurie Lynd's documentary Killing Patient Zero (2019),[17] have also discussed the Patient Zero myth around Dugas.
References
- Johnson, Brian D. (April 17, 2019). "How a typo created a scapegoat for the AIDS epidemic". Maclean's. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- McNeil, Donald G (October 26, 2016). "H.I.V. Arrived in the U.S. Long Before 'Patient Zero'". The New York Times. Retrieved October 26, 2016.
- Auerbach, David M.; Darrow, William W.; Jaffe, Harold W.; Curran, James W. (1984). "Cluster of cases of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Patients linked by sexual contact" (PDF). The American Journal of Medicine. 76 (3): 487–92. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(84)90668-5. PMID 6608269.
- "Researchers Clear 'Patient Zero' From AIDS Origin Story".
- Gallagher, James (October 26, 2016). "HIV Patient Zero cleared by science". BBC News Online. Retrieved October 26, 2016.
- Worobey, Michael; Thomas D. Watts; et al. (October 26, 2016). "1970s and 'Patient 0' HIV-1 genomes illuminate early HIV/AIDS history in North America". Nature. 539 (7627): 98–101. Bibcode:2016Natur.539...98W. doi:10.1038/nature19827. PMC 5257289. PMID 27783600.
- "La découverte de la maladie — Sida, les premières années" [Discovering the illness — AIDS, the first years]. Radio-Canada (in French). January 17, 1992. Archived from the original on August 18, 2004.
- Shilts, Randy (1988). And The Band Played On. Penguin. pp. 439. ISBN 978-0-14-011130-9.
- Gladwell, Malcolm (2000). The Tipping Point. Little, Brown and Company. pp. 21. ISBN 978-0-316-34662-7.
- France, David (December 1, 2016). How to Survive a Plague: The Story of How Activists and Scientists Tamed AIDS. Pan Macmillan. p. PT79. ISBN 978-1-5098-3941-4. Retrieved December 28, 2016.
- Kuiken, C; Thakallapalli, R; Esklid, A; de Ronde, A (November 1, 2000). "Genetic analysis reveals epidemiologic patterns in the spread of human immunodeficiency virus". American Journal of Epidemiology. 152 (9): 814–22. doi:10.1093/aje/152.9.814. PMID 11085392.
- Crewe, Tom (September 27, 2018). "Here was a plague". London Review of Books. Retrieved September 29, 2018.
- Moss, Andrew R. (December 8, 1988). "AIDS Without End". The New York Review of Books. Retrieved December 2, 2006.
- Straube, Trenton (May 16, 2016). "Mapping Out Early AIDS in the U.S." POZ.
- "New research reveals accidental making of 'Patient Zero' myth during 1980s AIDS crisis". University of Cambridge. October 26, 2016.
- Baumgarten, Marjorie (April 1, 1994). "Zero Patience". Austin Chronicle.
- "Documentary Killing Patient Zero seeks to restore reputation of Quebec man unfairly targeted in AIDS epidemic". Toronto Star, April 25, 2019.
External links
- Halifax Rainbow Encyclopedia page for Dugas—he lived in Halifax for several years.
- Gaëtan Dugas at Find a Grave
- AidsVancouver - archive footage of Gaetan Dugas speaking at an Aids Vancouver forum (beginning at ~5:45)
- ‘Patient Zero’ no more - study reported in Science Magazine (Vol. 351, Issue 6277, pp. 1013), American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) (Article)
