Geiselbach
Geiselbach is a community in the Aschaffenburg district in the Regierungsbezirk of Lower Franconia (Unterfranken) in Bavaria, Germany.
Geiselbach | |
|---|---|
 A view of Geiselbach from the north, with the church St. Maria Magdalena | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Geiselbach within Aschaffenburg district 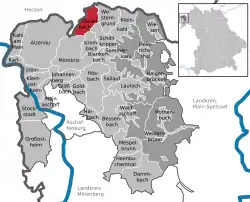 | |
 Geiselbach  Geiselbach | |
| Coordinates: 50°07′N 9°12′E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Bavaria |
| Admin. region | Unterfranken |
| District | Aschaffenburg |
| Subdivisions | 2 Ortsteile |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Marianne Krohnen (CSU) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 9.50 km2 (3.67 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 270 m (890 ft) |
| Population (2019-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 2,003 |
| • Density | 210/km2 (550/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 63826 |
| Dialling codes | 06024 |
| Vehicle registration | AB |
| Website | geiselbach.de |
Geography
Location
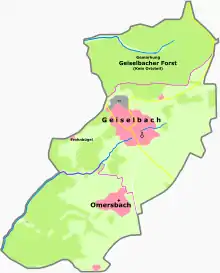
Geiselbach lies on the Hesse-Bavaria boundary, 20 km north of Aschaffenburg and 50 km east of Frankfurt am Main.
Elevations in the community reach from 272 m above sea level at the church up to 381 m at the Ziegelberg.
The municipal area comprises 535 ha in the constituent community of Geiselbach and 415 ha in the constituent community of Omersbach.
History
In 1269, Geiselbach had its first documentary mention in a purchase agreement between the Seligenstadt Monastery and the Archbishopric of Mainz, between Abbot Conrad and Archbishop Werner.
There also exists an earlier document from 1250 in which was about a dispute between the brothers Friedrich and Heinrich von Rannenberg and Reinhard von Hanau about holdings and rights in Geiselbach.
After 1269, the Seligenstadt Monastery relinquished its rights in Geiselbach to the noble families of Büdingen, Hanau and Rannenberg and to the knight Erpho von Orb.
In 1278, the patrician from Gelnhausen Irmgard Ungefüge took over the Geiselbach Vogtei with the villages of Geiselbach, Omersbach and Hofstädten. In three documents from 25 May 1278 it was agreed between the Seligenstadt Abbey and Madam Irmgard that the Abbey could reacquire all rights from her in better times. Even before the turn of the century, in 1290, Sir Erpho von Orb was once again named the Vogt in Geiselbach.
The Seligenstadt Monastery held the lordship over Geiselbach until Secularization in 1802. Most of the villages of the upper Kahlgrund then passed to the Principality of Aschaffenburg. Geiselbach, on the other hand, as a Seligenstadt Monastery holding, passed into ownership of the Landgrave of Hesse, who moved the Vogtei administration from Geiselbach to Seligenstadt.
In 1811, the three villages were united with the Grand Ducal Hessian Amt in Alzenau, which itself became Bavarian in 1816.
In 1972 the formerly self-administering community of Omersbach was amalgamated with Geiselbach, while the community of Hofstädten, which had likewise belonged to the Vogtei of Geiselbach, passed to Schöllkrippen in 1978.
Coat of arms
The community’s arms might be described thus: Gules an uppercase A with crossbar on top in fess and cross stroke in chevron inverted Or among three mullets of six argent.
The community of Geiselbach was acquired in 1296 by the Seligenstadt Monastery from the Archbishopric of Mainz for an undisclosed price. It thereby belonged along with the two neighbouring villages of Hofstädten and Omersbach to the Vogtei of the Dreidörfer (“Three Villages”) over which the monastery managed to get the landlordship and the low jurisdiction through the acquisition. The big A (Abbatio) in the arms is the charge borne by the Seligenstadt Monastery and refers to the monastery’s lordship until Secularization in 1802. The three mullets (stars) symbolize the three-village parish. The tinctures silver and red are Electoral Mainz’s colours and recall Mainz’s lordship until 1803.
The arms have been borne since August 1967.
Notable people
- Peter Stenger (1792–1874), founder of the Stenger Brewery in Naperville, Illinois, USA
- Jakob Heilmann (1846–1927), construction entrepreneur in Munich
- Carl Kaiser (1859–1945), textile salesman, owner of Steigerwald & Kaiser in Leipzig
- Karl Ritter von Weber (1892–1941), General Major
References
- "Tabellenblatt "Daten 2", Statistischer Bericht A1200C 202041 Einwohnerzahlen der Gemeinden, Kreise und Regierungsbezirke". Bayerisches Landesamt für Statistik und Datenverarbeitung (in German). July 2020.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Geiselbach. |
