Hôtel d'Assézat
The Hôtel d'Assézat in Toulouse, France, is a French Renaissance hôtel particulier (urban palace) of the 16th century which houses the Bemberg Foundation, a major art gallery of the city.

The Hôtel d'Assézat differs from the other Renaissance townhouses in Toulouse not only in size and its exceptional ornementation, but also in its pristine condition, a fact which earns it a mention in every overview of French Renaissance. Today, it is home to the Union des sociétés savantes and the Bemberg Foundation.[1] It is one of the first manifestations of French classicism.
History
The Hôtel d'Assézat was likely built by Toulouse architect Nicolas Bachelier for Pierre d'Assézat, an internationally renowned Toulouse woad merchant. The construction of the Hôtel began in 1555 and was not yet completed when Pierre d'Assézat died in 1581. It is an outstanding example of Renaissance palaces architecture of southern France, with an elaborate decoration of the cour d'honneur (courtyard) influenced by Italian Mannerism and by classicism. The use of brick is typical of Toulouse. The Hôtel now belongs to the City of Toulouse and was restored in the 1980s.
Presentation
Pierre Assézat was at the height of his social and professional success when he launched the construction of his mansion close to the Merchant Exchange, of which he had been one of the founders. Nevertheless, he did get caught up in the religious troubles of the time. A Calvinist convert, he was obliged to leave Toulouse after attempting to seize the town along with his fellows capitouls in 1562. He recanted ten years later and returned to his townhouse in Toulouse where he died in 1581.[1]
Assézat launched the first phase of construction in 1555–1557. The main L-shaped structure was built along with the staircase pavilion in the corner. The stonemason Jean Castagnié was entrusted with carrying out the masonry works defined by the architect Nicolas Bachelier. The designs of the façades, featuring twin columns which develop regularly over three floors (Doric, Ionic, Corinthian), takes their inspiration from the great classical models such as the Coliseum. The capitals also precisely adhere to classical models, known from engravings. The erudite architecture—its source can also be traced to the treatises of the royal architect Sebastiano Serlio—expresses order and regularity. On the deaths of Castagnié and Bachelier the construction work stopped; it was restarted in 1560 under the direction of Dominique Bachelier, son of Nicolas. He undertook the creation of the loggia and the passageway, which divided up the courtyard, and the street gate. Much polychrome interplay (brick/stone) and various ornaments (cabochons, diamonds, masks) evoke luxury, surprise and abundance, themes peculiar to mannerist architecture.[1]
Main gate
The monumental gate designed by Dominique Bachelier combines power with delicacy. The gateway arch takes a certain rhythm from several projecting stones decorated with small dots. Serlio's Extraordinary Book of Doors contain this type of composition and it was used on several occasions by Toulousain architects (Hôtel de Molinier and Hôtel de Massas). The Doric pilasters that frame the gate display an alternating succession of diamond-shaped stone, which gives the ensemble a precious aspect. In the upper section the Ionic pilasters around the mullioned window are fluted and delicately ornamented. And with the table that surmounts it, the composition imparts a refined sophistication. Thus, Dominique Bachelier was able to offer the owner a complete composition which evoked both power and a delicate erudition.[1]
The passageway and the consoles
In the courtyard, the passageway features arches decorated with diamond-shaped stone. They rest on large scrolled consoles, whose fronts are decorated with grotesque masks of different design. On the side, the rolls of the scrolls engender plant pods and cloves. Each console is borne upon a lion foot standing on a section of pilaster capped underneath with a magnificent rose. These consoles illustrate, by themselves, the manneristic aesthetic on the unusual and the association of opposites, combining mineral, vegetable and animal kingdoms. These refined motifs, heightened through the polychrome interplay and relief of the passageway, were much appreciated by contemporaries and inspired details on other buildings, such as Hôtel de Massas and Laréole Castle.[1]
Staircase term
In the stairwell, on the landing of the first floor, stands the impressive figure of a male term. Half man, half pilaster, his face grimacing and his hands holding a cushion placed on his head to reduce the pain, this term was condemned to support the weight of the console. Although a symbol of knowledge in the sense that it alludes to mythology (Atlas and Hercules), this motif also amuses thanks to an association of opposites, such as the straining muscles and the soft cushion. Cariatid termes and other telamons were much appreciated in Renaissance Toulouse, notable examples can be found on the windows of Hôtel du Vieux-Raisin and on the main gate of Hôtel de Bagis.[1]
Bemberg Foundation

Since 1994, the Hôtel d'Assézat has housed the Bemberg Foundation (Fondation Bemberg), an art gallery which presents to the public one of the major private collections of art in Europe: the personal collection of the wealthy Argentine Georges Bemberg (1915–2011). His foundation was created in collaboration with the City of Toulouse. The large Bemberg collection features paintings, drawings, sculptures, ancient books and furniture. Paintings and drawings are the highlights of the collection, especially 19th and early 20th century French paintings (with impressionism, Nabis, post-impressionism and fauvism) and Venetian paintings of the 16th and 18th centuries.
The painting and drawing collection includes an impressive set of 30 paintings by Pierre Bonnard and 18th century Venetian paintings by Canaletto, Francesco Guardi, Pietro Longhi, Rosalba Carriera, Giovanni Paolo Pannini, Tiepolo. 18th century French painting is represented by François Boucher, Nicolas Lancret, Elisabeth Vigée-Lebrun and Hubert Robert.
From the Flemish and Netherlandish schools of painting are artworks by the studio of Rogier van der Weyden, Lucas Cranach, Gerard David, Adriaen Isenbrandt, Joachim Patinir, Pieter Brueghel the Younger, Frans Pourbus the Elder. For the 17th century paintings are displayed by Antoon Van Dyck, Pieter de Hooch, Nicolaes Maes, Jan Van Goyen, Philips Wouwerman, Isaac van Ostade.
Italian Renaissance painting is centered on Venice with paintings by Paris Bordone, Jacopo Bassano, Titian, Paul Veronese and Tintoretto while for the 17th century there are works by Pietro Paolini, Giovanni Battista Carlone, Evaristo Baschenis, Mattia Preti.
French Renaissance and 17th century painting are represented with Jean Clouet, François Clouet, Nicolas Tournier while the Foundation bought in 2018 a canvas by Spanish painter Francisco de Zurbarán.
French painting from the second half of the 19th century is well represented with paintings by Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Eugène Boudin, Claude Monet, Henri Fantin-Latour, Edgar Degas, Édouard Vuillard, Odilon Redon, Paul Sérusier, Paul Gauguin, Louis Valtat, Alfred Sisley, Camille Pissarro, Gustave Caillebotte, Berthe Morisot, Paul Signac and Paul Cézanne.
20th century French art is represented by Georges Rouault, André Derain, Henri Matisse, Raoul Dufy, Albert Marquet, Maurice de Vlaminck, Kees van Dongen, Pablo Picasso, Georges Braque, Othon Friesz, Amedeo Modigliani and Maurice Utrillo.
Pictures
- Hôtel d'Assézat
 Entrance on Place d'Assézat.
Entrance on Place d'Assézat. Entrance pavilion
Entrance pavilion.jpg.webp) Main gate
Main gate Influence of an engraving by Serlio
Influence of an engraving by Serlio Frieze of metopes
Frieze of metopes Detail of the main gate with Native American figure
Detail of the main gate with Native American figure Details of the metopes of the main gate frieze
Details of the metopes of the main gate frieze The inner courtyard
The inner courtyard The Tower
The Tower The top of the tower
The top of the tower.jpg.webp) Classic facade
Classic facade Another influence of an engraving by Serlio
Another influence of an engraving by Serlio Fluted and rudented columns
Fluted and rudented columns Doric capitals
Doric capitals Ionic capitals
Ionic capitals Corinthian capitals
Corinthian capitals Door of the main staircase
Door of the main staircase The staircase
The staircase.jpg.webp) Staircase term
Staircase term Entrance of the Union of Academies and Learned societies.
Entrance of the Union of Academies and Learned societies..jpg.webp) Detail of the entrance to the Academies
Detail of the entrance to the Academies Passageway of the east wall
Passageway of the east wall Support arch of the passageway
Support arch of the passageway.jpg.webp) Mannerist decor
Mannerist decor.jpg.webp) Mannerist decor
Mannerist decor Mannerist decorations
Mannerist decorations.jpg.webp) Ionic consoles and pods
Ionic consoles and pods.jpg.webp) Loggia
Loggia Knocker
Knocker.jpg.webp) Window
Window Window
Window Serlian window
Serlian window Merchant's office window on the street
Merchant's office window on the street.jpg.webp) Merchant's office window on the courtyard
Merchant's office window on the courtyard.jpg.webp) Lion muzzle serving as a gargoyle
Lion muzzle serving as a gargoyle
- Bemberg foundation
 Anthony Van Dyck, Portrait of Dorothy, Lady Dacre
Anthony Van Dyck, Portrait of Dorothy, Lady Dacre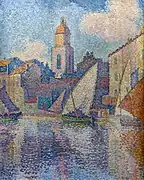 Le clocher de Saint-Tropez by Paul Signac (1896)
Le clocher de Saint-Tropez by Paul Signac (1896)

_-_1531_Inv.1015.jpg.webp)

See also
References
- Explanatory comments of Toulouse Renaissance exhibition (2018), Colin Debuiche.
Bibliography
- Bruno Tollon, Hôtels de Toulouse, p. 313–318, in Congrès archéologique de France. 154e session. Monuments en Toulousain et Comminges. 1996, Société française d'archéologie, Paris, 2002
- Marcel Sendrail, Pierre de Gorsse, Robert Mesuret, L'Hôtel d'Assézat, Édouard Privat éditeur, Toulouse, 1961
- Guy Ahlsell de Toulza, Louis Peyrusse, Bruno Tollon, Hôtels et Demeures de Toulouse et du Midi Toulousain, Daniel Briand éditeur, Drémil Lafage, 1997
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hôtel d'Assézat. |
