Helibor
Helibor (Helsinki Interbank Offered Rate) was a reference rate that was used in 1987–1998 on the Finnish interbank market. It was calculated each day as an average of the interest rates at which the banks offered to lend unsecured, Finnish markka nominated funds to each other.
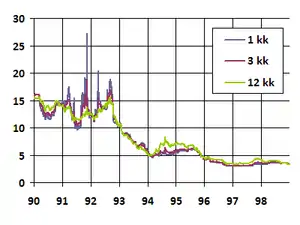
Helibor was quoted for 1, 2, 3, 6, 9 and 12 month maturities. It was widely used as a reference rate for company loans[1] and housing loans.[2] Before deregulation and floating the currency, it was rather high compared to the rest of the Western world, meaning that for instance mortgage interest rates were regularly ca. 15%. This so-called Suomi-lisä was removed by deregulation.
The Bank of Finland began publishing Helibor rates officially in May 1987.[1] Helibor was quoted for the last time on December 31, 1998, after which it was replaced with the Euribor.
Fluctuations in the Helibor played a prominent role in the Finnish banking crisis in the late 1980s and early 1990s.
External links
References
- Mika Vaihekoski. The Finnish Stock Market: Recent Trends and Important Events. Liiketaloudellinen Aikakauskirja — The Finnish Journal of Business Economics, 4/1997.
- G. Geoffrey Booth et al. The financing of residential real estate in Finland: an overview. Archived 2011-07-18 at the Wayback Machine Journal of Housing Research 5(2). 1994.
