Hopeaphenol
Hopeaphenol is a stilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer. It has been first isolated from Dipterocarpaceae[1] like Shorea ovalis.[2] It has also been isolated from wines from North Africa.[3]
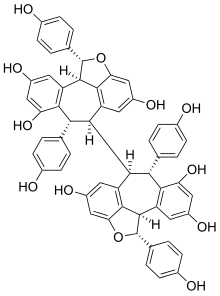 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
(-)-hopeaphenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C56H42O12 | |
| Molar mass | 906.940 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It shows an opposite effect to vitisin A on apoptosis of myocytes isolated from adult rat heart.[4]
See also
References
- The structure of hopeaphenol. P. Coggon, T. J. King and S. C. Wallwork, Chem. Commun. (London), 1966, pages 439-440, doi:10.1039/C19660000439
- The Isolation of Hopeaphenol, a Tetramer Stilbene, from Shorea ovalis Blume. Advances in Natural & Applied Sciences, January–April 2009, Volume 3, Issue 1, page 107 (abstract)
- Habiba Amira Guebailia; Kleopatra Chira; Tristan Richard; Teguiche Mabrouk; Aurélie Furiga; Xavier Vitrac; Jean-Pierre Monti; Jean-Claude Delaunay; Jean-Michel Mérillon (2006). "Hopeaphenol: The First Resveratrol Tetramer in Wines from North Africa". J. Agric. Food Chem. 54 (25): 9559–9564. doi:10.1021/jf062024g. PMID 17147446.
- Seya, Kazuhiko; Kanemaru, Kouta; Sugimoto, Chiharu; Suzuki, Megumi; Takeo, Teruko; et al. (2008-10-16). "Opposite Effects of Two Resveratrol (trans-3,5,4′-Trihydroxystilbene) Tetramers, Vitisin A and Hopeaphenol, on Apoptosis of Myocytes Isolated from Adult Rat Heart". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. American Society for Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics (ASPET). 328 (1): 90–98. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.143172. ISSN 0022-3565.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
