LMMS
LMMS (formerly Linux MultiMedia Studio) is a digital audio workstation application program. When LMMS is executed on a computer with appropriate hardware, it allows music to be produced by arranging samples, synthesizing sounds, playing on a MIDI keyboard, and combining the features of trackers and sequencers. It supports the Linux Audio Developer's Simple Plugin API (LADSPA), LV2 (only master branch, since 24.05.2020) and Virtual Studio Technology (VST) plug-ins (on Win32, Win64,or Wine32).[5] It is free software, written in Qt and released under the GNU General Public License, version 2 (GPLv2).
 | |
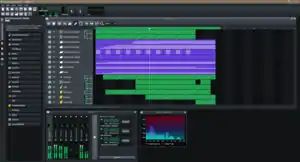 Screenshot of a project in LMMS 1.2.1 | |
| Original author(s) | Paul Giblock Tobias Junghans[1] |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | LMMS developers |
| Initial release | 2004; as Linux MultiMedia Studio |
| Stable release | 1.2.2[2]
/ 4 July 2020; 9 November 2020 |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C++ with Qt[3] |
| Operating system | Cross-platform: Windows, macOS, Linux |
| Platform | x86 and x86-64 (Linux, macOS, Windows), only Linux: arm64, armel, armhf, mips, mips64el, mipsel, ppc64el, s390x[3] |
| Available in | 20 languages[4] |
| Type | Digital audio workstation |
| License | GPLv2[5] |
| Website | lmms |
Overview
System requirements
LMMS is available for multiple operating systems, including Linux, OpenBSD, macOS and Windows. It requires a 1 GHz CPU, 512 MB of RAM and a two-channel sound card.[6]
Program features
LMMS accepts soundfonts and GUS patches. It can import Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) and Hydrogen files. It can read and write customized presets and themes.[7] Audio can be exported in the Ogg, FLAC, MP3, and WAV file formats,[8] and the projects can be saved in the compressed MMPZ file format or the uncompressed MMP file format.[9] It can use VST plug-ins on Win32, Win64, or Wine32, though currently the macOS port doesn't support them.[10]
Editors
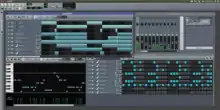
- Song Editor – for arranging your instruments, samples, groups of notes, automation, and more
- Beat+Bassline Editor – for quickly sequencing rhythms
- FX mixer – for sending multiple audio inputs through groups of effects and sending them to other mixer channels, infinite channels are supported
- Piano Roll – edit patterns and melodies
- Automation Editor – move almost any knob or widget over the course of the song
Synthesizers
- BitInvader – wavetable-lookup synthesis
- FreeBoy – emulator of Game Boy audio processing unit (APU)
- Kicker – bass drum synthesizer
- LB302 – imitation of the Roland TB-303
- Mallets – tuneful percussion synthesizer
- Monstro – 3-oscillator synthesizer with modulation matrix
- Nescaline – NES-like synthesizer
- OpulenZ – 2-operator FM synthesizer
- Organic – organ-like synthesizer
- Sf2 Player – a Fluidsynth-based Soundfont player
- SID – emulator of the Commodore 64 chips
- TripleOscillator – 3-oscillator synthesizer with 5 modulation modes: MIX, SYNC, PM, FM, and AM
- Vibed – vibrating string modeler
- Watsyn – 4-oscillator wavetable synthesizer
- ZynAddSubFX
Samplers
- AudioFileProcessor (AFP) – sampler with trimming and looping abilities
Standards
- Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI)
- SoundFont (SF2)
- Virtual Studio Technology (VST)
- Linux Audio Developer's Simple Plugin API (LADSPA)
- LV2 (only master branch, since 24.05.2020)
- Gravis Ultrasound (GUS) patches (PatMan)
- JACK Audio Connection Kit (JACK)
- ZynAddSubFX
See also
- List of music software
- List of Linux audio software
- Comparison of free software for audio
- Multitrack recording
- Comparison of multitrack recording software
References
- "LMMS Alternatives and Similar Software - AlternativeTo.net". AlternativeTo.
- https://github.com/LMMS/lmms/releases/tag/v1.2.2.
- "Debian -- Details of package lmms in buster". Debian. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- "LMMS – Currently supported languages". Retrieved 21 June 2017.
- "LMMS – Linux MultiMedia Studio". SourceForge. Retrieved 17 May 2011.
- "LMMS • Documentation". lmms.io. Archived from the original on 9 September 2017. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- Dave Phillips (17 August 2009). "LMMS: The Linux MultiMedia Studio". Linux Journal. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- "LMMS Sound Editing Software". Software Insider. Retrieved 31 March 2011.
- "lmms.io/utils.php function read_project". Github. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- "VeSTige - LMMS Wiki". lmms.io.
- Tobias Doerffel (December 2005). "Making Music with Linux Multimedia Studio". Linux Magazine (61): 58–60. Retrieved 30 March 2009.
- Dave Phillips (1 October 2008). "State of the Art: Linux Audio 2008, Part II". Linux Journal. Archived from the original on 7 February 2009. Retrieved 30 March 2009.