Lanarkshire and Ayrshire Railway
The Lanarkshire and Ayrshire Railway (L&AR) was an independent railway company built to provide the Caledonian Railway with a shorter route for mineral traffic from the coalfields of Lanarkshire to Ardrossan Harbour, in Scotland.
It opened in stages from 1888, being extended to Neilston and Newton, giving the Caledonian Railway a fully independent route by 1904. At the Ayrshire end the line duplicated the existing Glasgow and South Western Railway route at a time when bulk coal exports could be handled more economically in Clydebank, so that the primary purpose of the line was short-lived. The Caledonian Railway hoped to develop suburban traffic in south Glasgow where the new line passed through those districts, but street tramcars limited the success of this.
The duplicate routes to Ardrossan were wasteful and, as traffic declined, closures took place from 1930. The eastern section from Neilston and Newton to the Cathcart circle lines developed as outer suburban railways, and were electrified in the 1960s. Those branches, as they became, continue in intensive passenger use at the present day, but are the only remaining sections of the Lanarkshire and Ayrshire line remaining in operation.
History
Background

Ardrossan Harbour had come to increasing prominence as a coal port by 1880; export coal came largely from Lanarkshire: 84 collieries in the Hamilton area were sending coal to Ardrossan,[1] and the Caledonian Railway was dominant in the coalfield region. However the coal was transported by rail from the pits to Gushetfaulds (in south Glasgow) and handed to the rival Glasgow and South Western Railway (G&SWR) there for onward haulage. If the Caledonian could make a railway to Ardrossan, all of this lucrative traffic would fall to them.
Moreover, the towns in the area, including Saltcoats and Stevenston, as well as Irvine, were of growing importance for industrial activity and serving them would bring further passenger and goods revenue.

The Caledonian Railway had earlier entertained hopes of building from the Glasgow Barrhead and Neilston Railway (which later formed the trunk of the Glasgow, Barrhead and Kilmarnock Joint Railway: the GB&KJR) to the Ardrossan Railway but those plans were based on dubious share acquisition which the Caledonian could not afford at the time, and that opportunity had long since been lost.[2][3] Nonetheless the GB&KJR was only six miles (9 km) from the G&SWR line at one point. Closing that gap would be hugely advantageous to the Caledonian.[1][3]
Authorisation
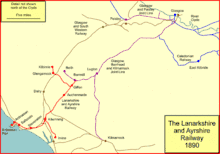
Encouraged and supported by the Caledonian Railway, a group of promoters submitted an independent Bill for the 1883 session, and it gained the Royal Assent on 20 August 1883: the Barrmill and Kilwinning Railway was authorised. It was empowered to build from the Barrmill branch of the GB&KJR line to a new junction with the G&SWR at Kilwinning.
The Earl of Eglinton was the owner of Ardrossan Harbour and wished to encourage any initiative that would enhance the value of his property, and he lent his support to the scheme. Encouraged by this, the company presented a Bill in the 1884 session for a much more ambitious scheme, dropping the junction with the G&SWR and making lines to Ardrossan itself, and to Irvine and Kilbirnie. The 1884 Act also changed the company's name to The Lanarkshire and Ayrshire Railway. Its capital was £375,000. A further Act was obtained in 1885 authorising substantial subscription in the scheme by the Caledonian Railway, which was in any case going to work the line. The Caledonian also committed itself to long term carriage contracts with mineral forwarders, relying on the new line.[note 1] Eglinton was made chairman of the company.[1][2][3]
The G&SWR was alarmed by this intended incursion into its territory and quoted cheap rates for coal from Hamilton and Bothwell; it had running powers over the North British Railway lines there; however its longer mileage and the toll charges to the NBR made it impossible to sustain the cheap rates and the scheme was dropped after six months.[1][3]
Construction and opening

Robert McAlpine and Company was chosen as contractor for the construction of the line.[4]
The line from Barrmill crossed difficult terrain and had steep gradients, but from Kilwinning to Ardrossan the G&SWR was already occupying the best route, and the new line had to be content with an alignment behind all the towns, discouraging passenger use.
The first section of the line opened from Barrmill to Ardrossan station on 3 September (ceremonial) and 4 September 1888 (full public),[1][2][3] although the extension works to the harbour at Ardrossan were incomplete, and a temporary spur was laid in to connect with the G&SWR there at first.[3][4][5]
The Kilbirnie branch from Kilbirnie Junction, known as Giffen from 2 October 1889, was opened for goods traffic on 1 November 1889, and to passengers on 2 December 1889.[2] Although Kilbirnie was a significant town, with a population of 3,405, the dominant feature of the branch was the ironworks at Glengarnock (and also a chemical works there), situated on the west side of the G&SWR main line. The new branch crossed over the G&SWR line and there was a large siding complex at the ironworks, already served by the G&SWR.

The passenger service operated from Kilbirnie to Giffen only, with no through trains beyond that point.
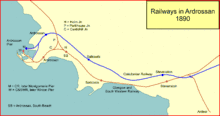
At Ardrossan, the Montgomerie Pier station and steamer terminal was opened on 30 May 1890. This immediately ignited bitter competition for the passenger traffic between Glasgow and the Clyde islands and to Belfast, with some very fast through journeys being timetabled.
Within one week in 1899, 677 traders, merchants and industrialists of Ayr, dissatisfied with the poor service of the G&SWR monopoly, petitioned the Caledonian to extend the Lanarkshire and Ayrshire line to Ayr. The Caledonian did not immediately respond, and the Provost, Town Clerk and a deputation of magistrates went to the Caledonian headquarters and presented a written guarantee of half the traffic of 560 traders for ten years if the Caledonian would construct the line. The Caledonian seriously examined the scheme; a branch off the proposed line to Troon was considered. The (as yet unfinished) Irvine branch would be doubled and the length of the route from Glasgow would be almost identical to the G&SWR's route. Such a line would have been a coup in the battle against the rival G&SWR, but a more balanced view prevailed: the line would have cost £440,000 and would have been subject to an immediate price war, frustrating any likelihood of great profits and the construction would have exhausted the Caledonian's fund of capital for major works, for which the priority lay elsewhere.[1]
The extension to Irvine was opened on 2 June 1890, with through carriages from Glasgow.[1][2]
Extending eastwards

The petition from Ayr urged an extension south and west but the Caledonian and the L&AR were more interested in extending east and north. The L&AR had been successful in capturing the majority of the mineral traffic from Lanarkshire to Ardrossan, but it still required the heavy and slow trains to travel via the junctions on the south side of Glasgow, along congested routes. Part of the haul was along the Glasgow Barrhead and Kilmarnock joint line, shared with the GS&WR, which had difficult gradients, incurring significant extra engine power costs. In 1897 the Caledonian decided to subscribe £152,000 towards the £502,000 cost of extending the L&AR line back from Giffen to Newton. This would considerably shorten the route from the mineral areas and escape involvement with the G&SWR altogether.
The authorising Act of Parliament was obtained on 1 July 1897. The L&AR got authority to build from a junction at Giffen on its line south of the convergence with the GB&KJR near Barrmill, running eastwards south of the earlier line and crossing over the GB&KJR main line south of Lugton, then running north east parallel to that line. It ran to a new Neilston station above the GB&KJR line, then through Whitecraigs to Cathcart, where it connected with the Cathcart District Railway, giving direct access over Caledonian controlled lines to Glasgow Central. The line continued from Cathcart via Burnside to Newton, on the main line to Hamilton and Motherwell.
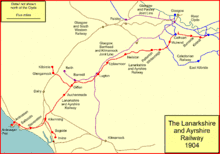
This line was opened from Giffen to Cathcart for goods on 1 April 1903, and for passengers on 1 May 1903. The Cathcart to Newton section was opened on 6 January 1904: now the Caledonian had a fully independent route from Lanarkshire to Ardrossan.[1][3]
While the imperative for the line was mineral traffic, the Caledonian saw that suburban passenger traffic was a growth area since the opening of Glasgow Central station in 1879, and the Cathcart lines from 1886. Urban tramway competition (with horse traction at first) was developing as a competitive threat in the city, with which the Caledonian wished to compete. Stations were opened between Neilston and Kirkhill in relatively rural areas as a speculative development.[1]
Loss of traffic
A major threat was already on the horizon, however, as the Rothesay Dock in Clydebank was under construction. It opened in 1907, equipped with modern mechanical handling equipment for bulk minerals; it was only 20 miles (32 km) from most of the coalfields, and sea-going ships could be loaded there. Much traffic was immediately diverted from Ardrossan, and use of the expensive new L&AR route declined steeply.
After World War I passenger traffic as well as goods and mineral business declined further. Worse was to come, for the Railways Act 1921 put both the G&SWR and the Caledonian/L&AR routes under common ownership of the new London Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS). The former G&SWR routes had better connectivity for the now sparse traffic, and on 28 July 1930 the first closure, to passenger traffic on the Irvine branch, took place. Total closure of the branch followed on 30 December 1930. The Kilbirnie branch too closed in 1930.
This was followed on 4 July 1932 by cessation of local passenger services between Uplawmoor and Ardrossan. Through boat trains and excursions continued to use the line until 1939.
On 16 June 1947 a short spur was installed near Ardeer between the G&SWR and the L&AR lines, enabling G&SWR line boat trains to use Montgomerie Pier. Nonetheless the last boat train ran on the route on 10 September 1965, and the L&AR route between Stevenston and Ardrossan closed completely on 18 April 1966.[1][5]
Electrification
In the 1960s the modernisation of the railways was on the agenda, and consideration was given to the Glasgow suburban network. In fact the North Clyde lines were electrified from 1960. From Neilston to Newton the former L&AR line was in the area of suburban travel, but Uplawmoor was rural, and it was decided to electrify the Neilston and Newton lines on the 25 kV ac system which was then becoming the standard. Cathcart Junction and station were altered (on 6 March 1961) so as to give access towards Kirkhill and Newton from Maxwell Park, and an electrical control room was built at Cathcart. Neilston and Newton were to be treated as two branches served from Glasgow Central. Public service on these routes started on 27 May 1962. The steam service to Uplawmoor had been withdrawn on 2 April 1962.[6]
The present day

Today the only operational section of the former Lanarkshire and Ayrshire Railway is the line between Newton and Neilston. This section has become two suburban branch lines, from Newton to Glasgow Central via Kirkhill (alternating between the Maxwell Park and Mount Florida sides of the Cathcart Circle), and from Neilston to Glasgow Central via the Mount Florida side of the Cathcart Circle. The branches were electrified in the early 1960s. Frequent suburban passenger trains operate on the line, operated by Abellio ScotRail. The arrangement of the passenger platforms at Cathcart is such that the Maxwell Park to Newton trains pass behind them but cannot make a station call.[7]
Some landmarks of the railway still exist throughout the former route: a large viaduct remains to the north of Kilwinning, now used as part of the National Cycle Network.
Two other prominent viaducts, namely the eleven arch span Gree viaduct and the seven arch span Giffenmill viaduct were both located between the former Lugton and Giffen stations were demolished in September 2006,[8] and February 2008 respectively.[9]

Barrmill Munitions Depot near Beith may still be active; it has a rail connection, but it has long been dormant. The route uses the first part of the GB&KJR Beith branch from Lugton to Barrmill, then continuing on the former Lanarkshire and Ayrshire Railway route.
Chronology and topography
Lines opened and closed:
- Irvine branch completely closed 30 December 1939.
- Lugton Junction to Neilston High closed 14 December 1964.
- Stevenston to Ardrossan Montgomerie Pier closed to passengers 18 April 1966, and fully closed 6 May 1968.[1]

Eventual main line:
Opened Ardrossan to Barrmill (on the GB&KJR Beith branch) 4 September 1888; Giffen Junction to Cathcart opened for goods trains 1 April 1903 and to passenger trains 1 May 1903; Cathcart to Newton was opened 6 January 1904. After the Giffen Junction to Cathcart section was opened, the short section of the original main line from Giffen Junction to Barrmill Junction ceased to have a passenger service and was only used for occasional goods transfer purposes.[5] Local passenger trains between Uplawmoor and Ardrossan were withdrawn from 4 July 1932 and stations Lugton to Saltcoats closed. However In 1933 the LMS introduced its "Evening Breathers" excursions in the summer of 1933. These offered a return journey from Glasgow to Stevenston, Saltcoats or Ardrossan for half the single fare; the stations were specially made available for the excursions; they proved extremely popular and were repeated in 1934.
The section between Uplawmoor and Ardrossan limited to goods traffic and Ardrossan boat trains only from 1932; the boat trains were suspended during World War II. In 1947 a spur was constructed at Stevenston from the G&SWR line to the L&AR line and from that time boat trains were routed from Glasgow via Dalry and the G&SWR line as far as this point; goods traffic continued to Auchenmade and Giffen until 1953.
When the plans were being prepared for the South Side electrification of the Glasgow suburban railway network, it was decided to do so as far as Neilston only, and the section between Neilston and Uplawmoor was closed completely in April 1962.[5]
There were several short spurs: a short industrial branch from near Stevenston to Ardeer opened 3 November 1888; a new connection was installed at Stevenston from the G&SWR line towards Ardrossan L&AR opened 16 June 1947 for boat train use; it closed on 25 September 1967; north of Lugton a connection trailed in from Lugton GB&KJR station, at Lugton East Junction; it was in existence from 1903 to 1944.
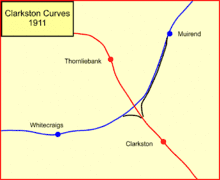
At Clarkston West Junction, the subsequent location of Williamwood station, a facing connection towards Clarkston on the East Kilbride line (the former Busby Railway) diverged; this was installed to give and alternative route for mineral trains from the Bothwell area towards Ardrossan and was opened in 1903. When the extension to Kirkhill and Newton opened the trains took that route instead. The Clarkston spur remained in place but little used, until it was closed on 29 October 1907.[10] At Muirend a trailing junction from Clarkston was installed, but it may never have been actually connected at the Clarkston end, and served as storage sidings from Muirend during its lifetime.[11]
Lugton south connection: Cobb indicates that a connection from the GB&KJR line trailed in where the lines cross south of Lugton; he quotes "LMS 1930?" as the opening date and gives no closing date. No available mapping shows the line and no residual earthworks can be detected in satellite images. Such a line would have simply duplicated the existing connection to Lugton East Junction, and in 1930 use of the L&AR was declining steeply. It may be that this connection never existed and that the reference to it is a mistake.[12]
Stations and locations; stations still open are in bold.
The main line opened from Barrmill to Ardrossan on 4 September 1888; Ardrossan Pier extension opened on 30 May 1890; Giffen to Cathcart opened for goods on 1 April 1903, and for passengers on 1 May 1903: the Cathcart to Newton section was opened on 6 January 1904. The section between Uplawmoor and Stevenston no. 1 junction closed on 16 June 1947; the section from Stevenston no. 1 to Ardrossan closed to passenger trains on 10 September 1965, and completely on 18 April 1966.
- Ardrossan Pier; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 1 February 1919; renamed Ardrossan Montgomerie Pier 1924; not used during World War II; reopened 16 June 1947 using new Stevenston connection; closed 25 September 1967;
- Ardrossan; renamed Ardrossan Town 1 October 1906; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 1 February 1919; renamed Ardrossan North 2 June 1924;
- Saltcoats; opened 4 September 1888; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 1 February 1919; renamed Saltcoats North 2 June 1924;
- Stevenston; opened 4 September 1888; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 1 February 1919; renamed Stevenston Moor Park 2 June 1924;
- Kilwinning; trailing junction from Irvine; opened 4 September 1888; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 1 February 1919; renamed Kilwinning East 1924;
- Lissens Sidings;
- Auchenmade; opened 4 September 1888;
- Kilbirnie Junction; trailing junction from Kilbirnie;
- Kilbirnie Junction station; opened 4 September 1888; renamed Giffen 1889;
- Giffen Junction; facing junction to original main line to Giffen;
- Gree Goods station; opened 1 May 1903; closed circa 1950;
- Lugton; opened 1 May 1903; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 1 February 1919; renamed Lugton High 1924;
- Lugton East Junction; trailing junction from connecting line from Lugton GB&KJR 1903 - 1964;
- Uplawmoor; opened 1 May 1903; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 2 March 1919; closed 2 April 1962; note: the Caldwell station on the GB&KJR line was then renamed Uplawmoor;
- Neilston; opened 1 May 1903; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 2 March 1919; renamed Neilston High 1924; renamed Neilston 1962;
- Netherton Goods station; opened 1 May 1903; closed circa 1960 and track lifted; the site remains in use for materials storage, etc.
- Lyoncross Junction; trailing junction from Paisley and Barrhead District Railway line; a passenger station was planned for the location but the scheme was abandoned when planned passenger operation on the Barrhead line was cancelled; the track configuration at the location is arranged for an island platform;
- Patterton; opened 1 May 1903; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 1 February 1919;
- Whitecraigs; opened 1 May 1903;
- Williamwood; opened 8 July 1929; facing junction to Clarkston 1903 - 1907;
- Muirend; opened 1 May 1903; trailing junction from Clarkston;
- Cathcart North Junction; facing junction to Mount Florida line and trailing junction from Maxwell Park line;
- King's Park; opened early October 1928; the apostrophe is omitted nowadays; trailing connection from Aikenhead Colliery 1904 - 1918;
- Croftfoot; opened April 1931;
- Burnside; opened 1 August 1904;
- Kirkhill;
- Kirkhill Tunnel;
- Kirkhill Junction; facing junction to Carmyle line; opened 1 August 1904; closed 1968;
- Newton; trailing junction with (former Clydesdale Junction Railway) main line.
Irvine Branch
Line opened 2 June 1890; closed to passengers 28 July 1930; closed completely 30 December 1939.
- Kilwinning; see above;
- Bogside; opened June 1900; described as golfers' station until closure 1 January 1917; reopened in daylight hours only 1 February 1919; renamed Bogside Moor 1924; later Bogside Moor Halt;
- Irvine; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 1 February 1919; renamed Irvine Bank Street 2 June 1924.
Kilbirnie branch.
The line opened for goods 1 November 1889, and for passengers 2 December 1889; it closed to passenger trains on 1 December 1930; ordinary goods traffic ceased on the same day but some mineral traffic to Glengarnock ironworks continued; the line closed completely beyond Giffen Royal Naval Armament Depot in 1945; the line remains in place but dormant as far as the RNAD, now named Barrmill Munitions Depot.
- Kilbirnie; renamed Kilbirnie South 2 June 1924;
- Giffen RNAD; later Barrmill Munitions Depot;
- Glengarnock; renamed Glengarnock High 2 June 1924;
- Brackenhills; opened 1 September 1906;
- Barkip Junction; connections to mineral lines;
- Kilbirnie Junction; see above.
The line closed to passenger trains on 1 December 1930, and closed completely in 1945.[11]
Company directors
At the time of the railway opening in 1888, the company directors were:
- G. R. Vernon, M.P. (Chairman)
- J. C. Cuninghame
- The Earl of Eglinton and Winton
- R. W. Knox
- James Neilson
- Archibald Russell
- John Watson
- John Cunninghame
Route diagram and connections to other lines
- Ardrossan Railway at Ardrossan Harbour and Stevenston No. 1
- Busby Railway at Williamwood
- Cathcart District Railway at the Cathcart East and West Junctions
- Clydesdale Junction Railway at Newton West Junction
- Glasgow, Barrhead and Kilmarnock Joint Railway at Barrmill and Lugton
- Glasgow Central Railway at Kirkhill Junction and Newton railway station
- Paisley and Barrhead District Railway at Lyoncross Junction between Patterton and Neilston
References
- John Thomas revised J S Paterson, A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain: Volume 6, Scotland, the Lowlands and the Borders, David and Charles, Newton Abbot, 1984, ISBN 0 946537 12 7
- E F Carter, An Historical Geography of the Railways of the British Isles, Cassell, London, 1959
- David Ross, The Caledonian: Scotland's Imperial Railway: A History, Stenlake Publishing Limited, Catrine, 2014, ISBN 978 1840 335842
- John Thomas, Forgotten Railways: Scotland, David and Charles, Newton Abbot, 1976, ISBN 0 7153 7185 1, pages 91 to 92
- Gordon Stansfield, Ayrshire and Renfrewshire's Lost Railways, Stenlake Publishing Ltd, Catrine, 1999, ISBN 1 84033 077 5
- J C Gillham, The Age of the Electric Train, Ian Allan Limited, London, 1988, ISBN 0 7110 1392 6
- Abellio ScotRail Travel Information
- Beith Online - Giffen Viaduct Archived 28 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- "North Ayrshire Council - Planning Committee Report". 5 April 2004. Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 27 August 2007.
- Jack Kernahan, The Cathcart Circle, Scottish Railway Preservation Society, Falkirk, 1980, ISBN 0 904396 01 0
- M E Quick, Railway Passenger Stations in England Scotland and Wales—A Chronology, The Railway and Canal Historical Society, 2002
- Col M H Cobb, The Railways of Great Britain -- A Historical Atlas, Ian Allan Publishing Limited, Shepperton, 2003, ISBN 07110 3003 0
Notes
- Sources are contradictory about the timing of the main authorisation. Paterson, page 133 says that the £375,000 and the Ardrossan line were in the 1884 Act; Carter (page 457) implies it was the capital of the 1883 scheme; Ross is ambiguous on the timing of the main authorisation (on page 122) but says that the Act of 16 July 1885 authorised it "to invest up to £150,000 of the £375,000 capital". Paterson, referring to the 1884 Act, says that "all but £15,000 of the capital required [was] subscribed without Caledonian help."
Sources
- Awdry, Christopher (1990). Encyclopaedia of British Railway Companies. Sparkford: Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 1-8526-0049-7. OCLC 19514063. CN 8983.
- Butt, R. V. J. (1995). The Directory of Railway Stations: details every public and private passenger station, halt, platform and stopping place, past and present (1st ed.). Sparkford: Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 978-1-85260-508-7. OCLC 60251199.
- Jowett, Alan (March 1989). Jowett's Railway Atlas of Great Britain and Ireland: From Pre-Grouping to the Present Day (1st ed.). Sparkford: Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 978-1-85260-086-0. OCLC 22311137.
- Stansfield, G. (1999). Ayrshire & Renfrewshire's Lost Railways. Ochiltree: Stenlake Publishing. ISBN 1-8403-3077-5.
- Thomas, John (1976). Forgotten Railways: Scotland (1st ed.). Newton Abbot: Devon: David & Charles. ISBN 0-7153-7185-1. OCLC 3103506.
- Thomas, John (1981). Forgotten Railways: Scotland (2nd ed.). Newton Abbot: Devon: David & Charles. ISBN 0-7153-8193-8. OCLC 13641185.
- Wham, Alasdair (1997). The Lost Railway Lines of Ayrshire : Ayrshire Railway Walks. Wigtown: G.C. Book Publishers. ISBN 1-8723-5027-5. OCLC 38356283.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lanarkshire and Ayrshire Railway. |
Tait, W. A. P. (1891). "The Lanarkshire and Ayrshire Railways (abstract)". Minutes of the Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers. 105 (1891): 298 to 301. doi:10.1680/imotp.1891.20492.