Mambiloid languages
The twelve Mambiloid languages are languages spoken by the Mambila and related peoples mostly in eastern Nigeria and in Cameroon. In Nigeria the largest group is Mambila (there is also a small Mambila population in Cameroon). In Cameroon the largest group is Vute.
| Mambiloid | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Nigeria and Cameroon |
| Linguistic classification | Niger–Congo |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | mamb1309 |
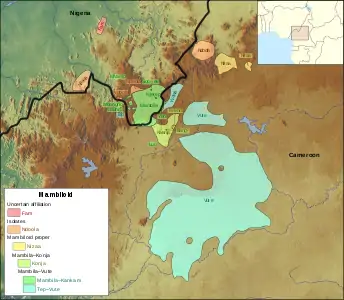 The Mambiloid languages shown within Nigeria and Cameroon | |
Languages
The following classification follows Blench (2011). Languages with (?) are not listed in that source, but close to other languages according to Ethnologue. Ndoro–Fam may be a separate branch of Benue–Congo.
- Ndoola (Ndoro)
- Mambiloid proper
Ethnologue also lists Njerep, which most likely lies somewhere in the Mambila–Kamkam branch. The extinct Yeni, Luo and Kasabe languages were apparently Mambiloid, the first two close to Njerep.
Fam is sometimes classified with Ndoro, but appears to be more divergent.
The unclassified language Bung shows its strongest resemblance to be with the Ndung dialect of Kwanja. It also has words in common with other Mambiloid languages such as Tep, Somyev and Vute, while a number of words' origins remain unclear (possibly Adamawan).[1]
Names and locations (Nigeria)
Below is a list of language names, populations, and locations (in Nigeria only) from Blench (2019).[2]
| Language | Dialects | Alternate spellings | Own name for language | Endonym(s) | Other names (location-based) | Other names for language | Exonym(s) | Speakers | Location(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mbɔŋnɔ | Bungnu | Mbọngnọ | Mbọngnọ | Kamkam | Kakaba, Bunu | 800 (1952 W&B); 3000 est. Blench and Connell (1999) | Taraba State, Sardauna LGA, Kakara town | ||
| Ndoola | At least 2 dialects | Ndoro | Ndoola | Ndoola | Njoyamɛ (in Cameroon) | 1169 (1952 W&B); 10,000 total, 1,300 in Cameroon (1982 SIL); estimated more than 15,000 (1999) | Taraba State, Sardauna and Gashaka LGAs; and in Cameroon (1 village only) | ||
| Vute | At least 6 dialects | Bute, Mbute, Wute, Voute | Mbutere | 1,000 or less in Nigeria; 30,000 in Cameroon (1985 EELC) | Taraba State, Sardauna LGA; northeast Mambila Plateau, but mainly in Cameroon | ||||
| Tep | A single village and associated hamlets. <4000 | Taraba State. Mambila Plateau | |||||||
| Mambila | Almost every village has a separate dialect forming a dialect chain. Dialect centres are: Bang, Dorofi, Gembu, Hainari, Kabri, Mayo Ndaga, Mbamnga, Tamien, Warwar. At least 4 dialects in Cameroon. | Ju Nɔri | Nɔr | Mambila, Mambilla, Mambere | 18,000 (1952); 60,000 (1973 SIL); 10,000 in Cameroon | Taraba State, Sardauna LGA. Mambila Plateau. Cameroon. | |||
| Mvanɨp | Mvanɔ | Magu | 100 (Blench 1999) | Taraba State, Sardauna LGA. A single quarter of Zongo Ajiya town in the northwest of the Mambila Plateau. | |||||
| Ndunda | 400 (Blench 1999) | Taraba State, Sardauna LGA. In northwest Mambila Plateau. | |||||||
| Somyɛv | Kila, Zuzun | 4 speakers (2006) | Taraba State, Sardauna LGA, (Blacksmiths’ dialect). Kila Yang village, 10 km. west of Mayo Ndaga. Also formerly spoken in Cameroon | ||||||
| Fam | Fam | Fam | Kɔŋa, Konga | Fewer than 1,000 (1984); <500 (2016) | Taraba State, Bali LGA, 17km east of Kungana |
References
- Bruce Connell, 1997: Moribund Languages of the Nigeria-Cameroon Borderland Archived 2004-08-14 at the Wayback Machine
- Blench, Roger (2019). An Atlas of Nigerian Languages (4th ed.). Cambridge: Kay Williamson Educational Foundation.
- Blench, Roger, 2011. 'The membership and internal structure of Bantoid and the border with Bantu'. Bantu IV, Humboldt University, Berlin.
![]() This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 3.0 license.
This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 3.0 license.
External links
- Marieke Martin, 2011. 'The Erosion of Noun Classes in Mambiloid'