Mankera
Mankera (Urdu: منكيره), is the principal town of Mankera Tehsil, an administrative subdivision of Bhakkar District, in the Punjab province of Pakistan.[2] It is situated about 320 kilometres west of the city of Lahore.
Mankera
منکیرہ | |
|---|---|
City | |
 A mosque in Mankera | |
 Mankera Location in Pakistan  Mankera Mankera (Pakistan) | |
| Coordinates: 31°23′N 71°26′E | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| Division | Sargodha |
| District | Bhakkar |
| Population | |
| • City | 14,184 |
| Time zone | UTC+5 (PST) |
| • Summer (DST) | +6 |
| Area code(s) | +92453 |
| Website | mankera.wapka.mobi |
Bhakkar is located in the west of Punjab. The mighty Indus River flows on the Western side of the District which plays havoc during monsoon season and the Jehlum and Chenab rivers both flow on the eastern side they also sometimes plays havoc during monsoon season. One third of the land is sandy of which small portion is irrigated by Thal canal and tube wells. Rest of the sandy land is cultivated and is entirely dependent upon rains. People mostly depend on agriculture which is highly dependent on rain falls. As such people are poor, backward and traditional. Education and health facilities are not adequately available.
History
The origins of Mankera according to tradition go back one thousand years BC, it is believed that Mankera was originally Malkherkot, founded by a Rajput called Mal Khera. Mekan family have deep roots in Mankera. Mekan Raja ruled Mankera for 500 year. There is evidence that suggests that a state by this name existed during Alexander's invasion of the sub-continent. There is another version about the name ofMankera also, though not verified and having an evidence as such. Here most of the land is sandy with small, medium and huge sand dunes, weather extremely hot which used to attract heavy sand storms during summer. Due to sand storms sand dunes used to shift from one place to another. In local language sand dunes are called "Manr'r" and process of shifting of sand is called "kera". Both words combined to make "Manr'rKera" and slowly turned to Mankera. The Arabs however called it Manker Kot, and during Muhammad bin Qasim's rule in greater Sindh, the conquest of Mankera by one of his generals, Abul Asswad bin Zahar is recorded. The first Muslim governor of Mankera was Ahmed bin Khuzema who died in Mankera and is buried in Mankera fort.
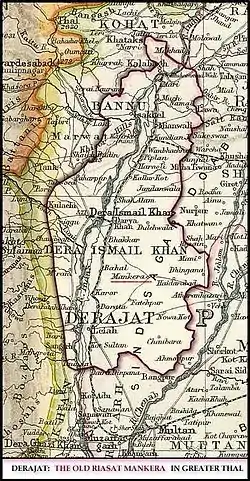
Following the downfall of Arab rule in Sindh, the Hindu king of Kanauj took possession of Mankera followed by the Mekan. The Abdali kings annexed Mankera and the adjoining areas and the Baloch gave way to Saddo Zai Pathans. The Pathan rule of the state ended with the famous siege of Mankera by Ranjit Singh which resulted in the forfeiture of Nawab Surbuland's claim to Mankera and his retreat to Dera Ismail Khan.
Mankera fort, the principal feature of the town lies half a kilometre to the left of the Bhakkar highway. The fort was constructed in two phases. The initial construction of the brick fort was carried out during the time of the Baloch rule, and further fortification in the form of a thick mud wall was undertaken during the Pathan rule.The mud is taken from winter depths of Indus River then form it to fine powder. This powder type mud was mixed with water for several days and properly meshed. In this way wet mud transform into glue type mud thats why it is too strong and mintain life till presence in walls of forts. Today the fort and its fortification is mostly in ruins. (Much to my surprise, Mankera's historical sites have never been considered worthy of any official recognition.) The major part of the mud wall still exists, however decay and neglect is abundantly clear. The main fort is mostly in ruins except for a well, a tomb, and a few signs of masonry. The outer walls of the citadel are however intact. During the dying days of the Mughal empire, Mankera's Saddo Zai rulers with the help of their Abdali benefactors emerged as a force to reckon with in this area. Mankera was the seat of their dominions. Nowadays the Tomb of Mankera is not in the good condition and is broken at all the places and the walls.
The Sikh occupation of Mankera is abundantly evident. Next to the Jamia Masjid of Mankera are the ruins of a temple built during the Sikh rule, and even the tomb of Nawab Surbuland Khan, just outside the main citadel has a Hindu aura about its construction.
The Sikh annexation of this area began in 1821, and was completed with the fall of Mankera in the autumn of that year. Ranjit Singh personally led the troops that besieged Mankera. The siege lasted for twenty-two days and at a great cost to the invaders. Mankera, fortified by the brick wall had a distinct advantage of its position being in the middle of a desert. The besieging army had not only to deal with the gallant musketry of the Mankera troops but had to find out ways to deal with the natural difficulties as well. Water had to be carried for the troops from considerable distances. Ranjit Singh's ingenuity saved the day, as he ordered his army to dig several wells. Twelve such wells were dug.
The siege dragged on for twenty-two days during which time the Nawab held his own; however the desertions of his sardars and the demolition of one of the minarets of Jamia Masjid—taken as a bad omen—forced the Nawab to surrender the fort to the Sikhs. The iron ball shot from the big guns, including the Zam Zama employed by Ranjit Singh during the Mankera expedition is still preserved in the mosque's compound. Following the surrender, the area was put under the direct control of Lahore empire. Sikhs and Hindus were settled inside the main fort ( outer ) except one Muslim family which continued living here. This Muslim family had settled here from Leiah during the dynasty of Saddo Zai. After independence and creation of Pakistan in August 1947, Hindus and Sikhs migrated to India and their vacated houses were given to the people migrated from India under a settlement scheme. The Sikh rule of Mankera ended in 1847 and for the next one hundred and forty years Mankera existed as a non-entity.
Mankera's other claim to fame is the incident, which took place in 1794 when Prince Hummayun Shah, son of Taimur Shah, the Abdali King and a claimant to the throne of Kabul, made a vain attempt to overthrow his brother, Zaman Shah. His brother comprehensively defeated him and Hummayun fled to Thal Sagar. The Saddo Zai Nawab of Mankera, Nawab Mohammad Khan, apprehended him at Leaih. Hummayun's son was killed in the scuffle that followed his arrest, and at the behest of Zaman Shah, Nawab had Hummayun's eyes put out. Hummayun spent the rest of his life imprisoned in Mankera fort. A tomb in the middle of the fort is believed to be that of Prince Hummayun, and is considered a minor saint by the locals. On the other hand, the Nawab received the title of Surbuland Khan and the territory of Dera Ismail Khan from the King. It was the same Surbuland Khan who had to surrender to Ranjit Singh some twenty-and-seven years later, and retreat to Dera Ismail Khan.
Mankera today



Mankera's is Sub-Division (Tehsil) under the supervision of District Government Currently. Mankera's main bazaar (market) has neat rows of shops on either side. The town has seven Government Schools − one High School and one Elementary School for boys and one High and four Primary Schools for girls. The first Primary School has been in existence for over a hundred years. There are also many other private schools in the town. A special school for disabled children and the addition of a Degree College and a Commerce College provide the town with ample resources to educate its youth. A forty-bed hospital caters to the health needs of the populace. The famous Jamia Masjid has been demolished and reconstructed. The streets are paved and wide, and the people congenial and hospitable. Tehsil Municipal Administrations sewerage and sanitation system is very poor. Mankera has a rich Indo-Islamic Culture, which is known as The colorful culture. Mankera is the second biggest tehsil after Shergarh. The major source of income of Mankera's people is chickpeas (chana). Now, Mankera is developing day by day, new shops of all types have been made in bazar.
Malik Qadar Baksh was a famous teacher who raised form Tehsil Mankera. He taught thousands of students in entire Punjab, Shahpur Sargodha, Mitha Tiwana, Jhang and district Headquarter Bhakkar. His students have served and are serving throughout the country with great pride. His family is an icon of excellence and education in District Bhakkar. He left this world in October 20, 1983 and buried in Sher Shah graveyard of Mankera City. All his six sons held top slots in Government and Banking sectors of Pakistan. His eldest son Malik Muhammad Iqbal PSP retired from Police Services of Pakistan as IG/DG FIA. Shahid Iqbal served in Allied Bank of Pakistan and retired as Vice President, Dr. Khalid Iqbal retired as Medical Superintendent from DHQ Rawalpindi. Zafar Iqbal retired as Secretary BISE Faisalabad, Hassan Iqbal PAS is current Federal Secretary CAAD Islamabad, His youngest son Farooq Raza is serving in Bank Al-Falah in credit administration department in a key position.
- Sheikh Qadar Baksh Was a famous person who raised from Mankera city. He was very religious person who built a Madrassa in Mankera. He also provided a big place to Govt of british in 1871. He had 4 sons. Nabi Bakhsh, Allah Bakash, Haji Muhammad Bakhsh and Haji Abdullah.
Muhammad Bakash was companion of Poonja Jinnah and also he had relations with Shiekh Noor Muhammad. He helped Quaid-e-Azam Muhammad Ali Jinnah in his purpose in getting Pakistan. He had 7 sons. He Provided land to Army of Pakistan in early days of Pakistan which is now present as Rest house in Mankera. His eldest son Muhammad Masoom was Hafiz-e-Quran. He was also very religious.
Transport
The nearest airport to Mankera is Dera Ismail Khan – travelers used to be able to catch a flight either Islamabad or Peshawar to this city and then onto Mankera. However this airport is now out of use – the only way to get there is by bus. The bus takes 6 hours from Peshawar to reach Dera Ismail Khan and 7 hours from Islamabad and 6 hours from lahore. From Dera Ismail Khan it takes two hours to reach Mankera and from Bhakkar it takes a drive of 45 minutes.
The direct Bus service is also available from Lahore. Mankera is 360 km away from Lahore and it is located on main Lahore-Dera Ismail Khan road.
One can easily get to Mankera through a fast APV car service from Niazi Adda, but APV car service is from Lahore to Jhang. From Jhang city, there is an AC and Non-AC bus/van service for Bhakkar and Dera Ismail Khan. Mankera is just 25 km apart from Chowk Saraiy Mohajir which occurs on MM road (Mianwali-Multan Road), this is the same road which is from Islamabad to Karachi through Chakwal, Mianali, Muzzafar Garh, Multan, BahawalPur, Rahim Yar Khan and Hyderabad.
Main Town Tehsil Mankera
- Mankera City
- Hyderabad Thall
- Sarai Mahajir
- Mahni
- Patti Balanda
- [Goharwala union council
- Litan
- Basti Islamabad
- [[Bumb/ koroo}
- [[kapahi}
Dera Bathal Wala(Bhatti Brotheri)
Dera Bathal Wala is situated at the bank of Rakh Khew at the distance of half a mile approximately. It is named as Bathal Wala because a tribe of mianwali named Bathal brotheri occupied maximum land in that area and they built a well in that old times when water was very scarce there. shepherds and other people from around and far places and the travelers used to come here to quench the thirst. this way became known as khooh(well) Bathal Wala. it was more like a barren land and there were bushes and forest all around. in 1950's around Ranjhu Bhatti along with his sons Azeem Bhatti, Allah Daad Bhatti, Ibraheem Bhatti and Raza Muhammad Bhatti, bought the land and worked on it and made it harvest-able. chickpeas, watermelon and gowara were main crops. now chickpeas are main crop along with wheat.
