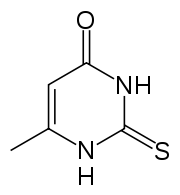
Methylthiouracil
Methylthiouracil is an organosulfur compound that is used antithyroid preparation. It is a thioamide, closely related to propylthiouracil. Methylthiouracil is not used clinically in the United States, it has a similar mechanism of action and side effect to that of propylthiouricil. The drug acts to decrease the formation of stored thyroid hormone, as thyroglobulin in the thyroid gland. The clinical effects of the drug to treat the hyperthyroid state can have a lag period of up to two weeks, depending on the stores of thyroglobulin and other factors.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.230 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C5H6N2OS |
| Molar mass | 142.18 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Synthesis
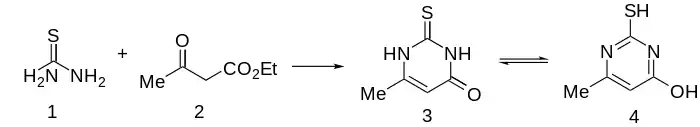
Methylthiouracil is prepared quite simply by condensation of ethyl acetoacetate with thiourea.[2]
Further work in this series shows that better activity was obtained by incorporation of a lipophilic side chain.
References
- List R (1886). "I. Zur Condensation von Thioharnstoff und Acetessigäther". Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 236 (1–2): 1–32. doi:10.1002/jlac.18862360102.
- Vorbrüggen H, Ruh-Pohlenz C (April 2004). "Synthesis of nucleosides". Organic reactions. 55: 1–630. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or055.01.