NGC 4622
NGC 4622 is a face-on unbarred spiral galaxy with a very prominent ring structure located in the constellation Centaurus. The galaxy is a member of the Centaurus Cluster.[2]
| NGC 4622 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Centaurus |
| Right ascension | 12h 42m 37.7s[1] |
| Declination | −40° 44′ 35″[1] |
| Redshift | 4367 ± 39 km/s[1] |
| Distance | 200 million ly[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 12.6[1] |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | SA(r)ab[1] |
| Apparent size (V) | 1′.7 × 1′.6[1] |
| Other designations | |
| PGC 42701[1] | |
Spiral structure
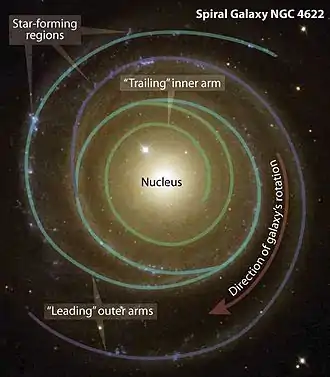
The spiral galaxy, NGC 4622 (also called Backward galaxy), lies approx. 111 million light years away from Earth in the constellation Centaurus. NGC 4622 is an example of a galaxy with leading spiral arms.[2] In spiral galaxies, spiral arms were thought to trail; the tips of the spiral arms winding away from the center of the galaxy in the direction of the disks orbital rotation. In NGC 4622, however, the outer arms are leading spiral arms; the tips of the spiral arms point towards the direction of disk rotation. This may be the result of a gravitational interaction between NGC 4622 and another galaxy or the result of a merger between NGC 4622 and a smaller object.[2]
NGC 4622 also has a single inner trailing spiral arm.[2] Although it was originally suspected that the inner spiral arm was a leading arm, the observations that established that the outer arms were leading also established that the inner arm was trailing.[2]
These results were met with skepticism in part because they contradicted conventional wisdom with one quote being “so you’re the backward astronomers who found the backward galaxy.” The fact that a pair of arms could lead was not easy to accept. Astronomical objections centered on the fact that dust reddening and cloud silhouettes were used to determine that the outer arms lead. The galaxy disk is tilted only 19 degrees from face-on making near to far-side effects of dust hard to discern and because clumpy dust clouds might be concentrated on one side of the disk, creating misleading results.
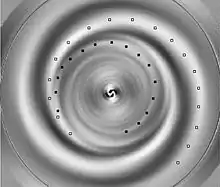
In response, the “backward astronomers” determined[3] NGC 4622's spiral arm sense with a method independent of the previous work. The new Fourier component method is actually assisted by the small tilt, and dust reddening and cloud silhouettes are not used in the latest analysis. The Fourier component method reveals two new weak arms in the inner disk winding opposite the outer strong clockwise pair. Thus the galaxy must have a pair of arms winding in the opposite direction from most galaxies. Analysis of a color-age star formation angle sequence of the Fourier components establishes that the strong outer pair is the leading pair.
While the presence of backward arms in a galaxy may seem like an inconvenient truth to many, two independent methods now indicate that NGC 4622's arms do indeed behave in a very unusual fashion, with the outer arms winding outward in the same direction the disk turns.
A Fourier component image of the arm pairs is shown with one of the pair of arms marked for the newly discovered inner CCW pair (black dots) as well as one of the already known (CW) outer pair (white dots).
Supernova
On May 25, an image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope captured a supernova in NGC 4622. It was discovered by R. Buta and GG Byrd of the University of Alabama as well as T. Freeman of Bevill State Community College.[4] The type of supernova was not determined.[5]
Group and cluster
According to AM Garcia, NGC 4622 is a member of the NGC 4709 group which consists of at least 42 galaxies including NGC 4616, NGC 4622B (also called PGC 42852), NGC 4679 and NGC 4709.[6]
The NGC 4709 group is part of the Centaurus Cluster.[7]
See also
- Messier 64 – a spiral galaxy with its gas disk orbiting opposite the disk of stars
References
- "NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database". Results for NGC 4622. Retrieved 2007-03-30.
- R. J. Buta; G. G. Byrd; T. Freeman (2003). "The Ringed Spiral Galaxy NGC 4622. I. Photometry, Kinematics, and the Case for Two Strong Leading Outer Spiral Arms". Astronomical Journal. 125 (2): 634–666. arXiv:astro-ph/0211002. Bibcode:2003AJ....125..634B. doi:10.1086/345821.
- G. G. Byrd; T. Freeman; S. Howard; R. J. Buta (2008). "The Ringed Spiral Galaxy NGC4622. II. An Independent Determination that the Two Outer Arms Lead". Astronomical Journal. 135 (1): 408–413. Bibcode:2008AJ....135..408B. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/135/1/408.
- "Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams (UAI), IAUC 7833: SNe; 2001jx". Retrieved September 23, 2020.
- "Bright Supernovae - 2001". Retrieved September 23, 2020.
- Garcia, A.M. (1993). "General study of group membership. II - Determination of nearby groups". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series. 100 #1 (July): 47–90. Bibcode:1993A&AS..100...47G.
- Jerjen, H.; Dressler, A. (1997). "Studies of the Centaurus cluster. I. A catalogue of galaxies in the central region of the Centaurus cluster" (pdf). A & A Supplement series. 12 (July): 1–12. doi:10.1051/aas:1997355.
External links
 Media related to NGC 4622 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to NGC 4622 at Wikimedia Commons- Hubble Heritage site: Pictures and description
- SKY-MAP.ORG : NGC 4622