Neptunocene
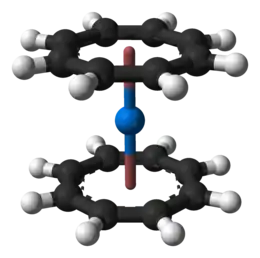
Neptunocene, Np(C8H8)2, is an organoneptunium compound composed of a neptunium atom sandwiched between two cyclooctatetraenide rings. It was one of the first organoneptunium compounds to be synthesized. Neptunocene, a member of the "actinocenes," a group of metallocenes incorporating elements from the actinide series.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Bis(η8-cyclooctatetraenyl)neptunium(IV) | |
| Other names
Neptunium cyclooctatetraenide Np(COT)2 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H16Np | |
| Molar mass | 445 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Ignites in air |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Property and synthesis
It was synthesized in 1970 by reacting neptunium(IV) chloride with dipotassium cyclooctatetraenide (K2(C8H8)). It is isomorphous to uranocene and plutonocene, and they behave chemically identically. All three compounds are insensitive to water or dilute bases, but are sensitive to air, reacting quickly to form oxides, and are only slightly soluble in benzene and toluene.[1]
References
- Yoshida, Zenko; Johnson, Stephen G.; Kimura, Takaumi; Krsul, John R. (2006). "Neptunium". In Morss, Lester R.; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean (eds.). The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (PDF). 3 (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Springer. pp. 699–812. doi:10.1007/1-4020-3598-5_6.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.