Obelisk
An obelisk (/ˈɒbəlɪsk/; from Ancient Greek: ὀβελίσκος obeliskos;[1][2] diminutive of ὀβελός obelos, "spit, nail, pointed pillar"[3]) is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally they were called tekhenu by their builders, the Ancient Egyptians. The Greeks who saw them used the Greek term obeliskos to describe them, and this word passed into Latin and ultimately English.[4] Ancient obelisks are monolithic; that is, they consist of a single stone. Most modern obelisks are made of several stones.

Ancient obelisks
Egyptian


Obelisks were prominent in the architecture of the ancient Egyptians, and played a vital role in their religion placing them in pairs at the entrance of the temples. The word "obelisk" as used in English today is of Greek rather than Egyptian origin because Herodotus, the Greek traveller, was one of the first classical writers to describe the objects. A number of ancient Egyptian obelisks are known to have survived, plus the "Unfinished Obelisk" found partly hewn from its quarry at Aswan. These obelisks are now dispersed around the world, and fewer than half of them remain in Egypt.
The earliest temple obelisk still in its original position is the 68-foot (20.7 m) 120-metric-ton (130-short-ton)[5] red granite Obelisk of Senusret I of the Twelfth Dynasty at Al-Matariyyah in modern Heliopolis.[6]
The obelisk symbolized the sun god Ra, and during the religious reformation of Akhenaten it was said to have been a petrified ray of the Aten, the sundisk.
Benben was the mound that arose from the primordial waters Nu upon which the creator god Atum settled in the creation story of the Heliopolitan creation myth form of Ancient Egyptian religion. The Benben stone (also known as a pyramidion) is the top stone of the Egyptian pyramid. It is also related to the obelisk.
It is hypothesized by New York University Egyptologist Patricia Blackwell Gary and Astronomy senior editor Richard Talcott that the shapes of the ancient Egyptian pyramid and obelisk were derived from natural phenomena associated with the sun (the sun-god Ra being the Egyptians' greatest deity at that time).[7] The pyramid and obelisk's significance have been previously overlooked, especially the astronomical phenomena connected with sunrise and sunset: Zodiacal light and sun pillars respectively.
Nubian
Ancient Nubian kings of the twenty-fifth Dynasty sought to legitimize their rule over Egypt by constructing Egyptianizing monuments in the Middle Nile region. Historical sources mention that king Piye built at least one obelisk. The obelisk was made of local black granite and was found at the site of Kadakol. It had been cut down to make it into a column, presumably for one of the early Christian churches in the area of Old Dongola. Today the obelisk is exhibited in the National Museum in Khartoum.[8] The obelisk is inscribed with the kings official titulary: Strong-bull, Appearing-in-Dominion (Thebes), King-of-Upper-and-Lower-Egypt, Two-ladies, Ruler-of-Egypt, Son-of-Rê, Pi(ankh)y: what he made as his monument for his father Amen-Rê, lord of [...].[9]
An obelisk of King Senkamanisken was found at Gebel Barkal in 1916 by the Harvard University - Museum of Fine Arts Expedition to Sudan. There are remains of another small obelisk inscribed with the cartouche of King Aktisanes at the site of Gebel Barkal.[10]
Ancient Egyptian obelisks in Ancient Rome
Around 30 BCE, after Cleopatra, "the last Pharaoh", committed suicide, Rome seized control of Egypt. The Ancient Romans were awestruck by the obelisks they saw, and looted the various temple complexes, in one case they destroyed walls at the Temple of Karnak to haul them out. There are now more than twice as many obelisks that were seized and shipped out by Rome as remain in Egypt. The majority were dismantled during the Roman period over 1,700 years ago and the obelisks were sent to different locations.
The largest standing and tallest Egyptian obelisk is the Lateran Obelisk in the square at the west side of the Lateran Basilica in Rome at 105.6 feet (32.2 m) tall and a weight of 455 metric tons (502 short tons).[11] More well known is the iconic 25 metres (82 ft), 331-metric-ton (365-short-ton) obelisk at Saint Peter's Square.[11] Brought to Rome by the Emperor Caligula in 37 CE, it has stood at its current site and on the wall of the Circus of Nero, flanking St Peter's Basilica.
The elder Pliny in his Natural History refers to the obelisk's transportation from Egypt to Rome by order of the Emperor Gaius (Caligula) as an outstanding event. The barge that carried it had a huge mast of fir wood which four men's arms could not encircle. One hundred and twenty bushels of lentils were needed for ballast. Having fulfilled its purpose, the gigantic vessel was no longer wanted. Therefore, filled with stones and cement, it was sunk to form the foundations of the foremost quay of the new harbour at Ostia.[12]
Pope Sixtus V was determined to erect the obelisk in front of St Peter's, of which the nave was yet to be built. He had a full-sized wooden mock-up erected within months of his election. Domenico Fontana, the assistant of Giacomo Della Porta in the Basilica's construction, presented the Pope with a little model crane of wood and a heavy little obelisk of lead, which Sixtus himself was able to raise by turning a little winch with his finger. Fontana was given the project. Half-buried in the debris of the ages, it was first excavated as it stood; then it took from 30 April to 17 May 1586 to move it on rollers to the Piazza: it required nearly 1000 men, 140 carthorses, and 47 cranes. The re-erection, scheduled for 14 September, the Feast of the Exaltation of the Cross, was watched by a large crowd. It was a famous feat of engineering, which made the reputation of Fontana, who detailed it in a book illustrated with copperplate etchings, Della Trasportatione dell'Obelisco Vaticano et delle Fabriche di Nostro Signore Papa Sisto V (1590),[13][14] which itself set a new standard in communicating technical information and influenced subsequent architectural publications by its meticulous precision.[15] Before being re-erected the obelisk was exorcised. It is said that Fontana had teams of relay horses to make his getaway if the enterprise failed. When Carlo Maderno came to build the Basilica's nave, he had to put the slightest kink in its axis, to line it precisely with the obelisk.
Three more obelisks were erected in Rome under Sixtus V: at Santa Maria Maggiore, in 1587; at the Lateran Basilica, in 1588; and at the Piazza del Popolo, in 1589.[16] An obelisk stands in front of the church of Trinità dei Monti, at the head of the Spanish Steps. Another obelisk in Rome is sculpted as carried on the back of an elephant. Rome lost one of its obelisks, the Boboli obelisk which had decorated the temple of Isis, where it was uncovered in the 16th century. The Medici claimed it for the Villa Medici, but in 1790 they moved it to the Boboli Gardens attached to the Palazzo Pitti in Florence, and left a replica in its place.
Not all the Egyptian obelisks in the Roman Empire were set up at Rome: Herod the Great imitated his Roman patrons and set up a red granite Egyptian obelisk in the hippodrome of his new city Caesarea in northern Judea. This one is about 40 feet (12 m) tall and weighs about 100 metric tons (110 short tons).[17] It was discovered by archaeologists and has been re-erected at its former site.
In 357 CE, Emperor Constantius II had two Karnak Temple obelisks removed and transported down the Nile to Alexandria to commemorate his ventennalia, the 20th year of his reign. Afterward, one was sent to Rome and erected on the spina of the Circus Maximus, and is today known as the Lateran Obelisk. The other one, known as the Obelisk of Theodosius, remained in Alexandria until 390 CE, when Emperor Theodosius I had it transported to Constantinople (now Istanbul) and put up on the spina of the Hippodrome of Constantinople (now Sultan Ahmet Square).[18] It once stood 95 feet (29 m) tall and weighed 380 metric tons (420 short tons); however, its lower section (which reputedly also once stood in the hippodrome) is now lost, reducing the obelisk's size to 65 feet (20 m).[19]
Ancient Egyptian obelisks in modern cities

The Ancient Romans populated their city with 8 large and 42 small Egyptian obelisks. More have been re-erected elsewhere, and the best-known examples outside Rome are the pair of 21-metre (69 ft) 187-metric-ton (206-short-ton) Cleopatra's Needles in London, England (21 metres or 69 feet) and New York City, USA (21 metres or 70 feet) and the 23-metre (75 ft) over-250-metric-ton (280-short-ton) Luxor Obelisk at the Place de la Concorde in Paris, France.[20]
Obelisks were being shipped out of Egypt as late as the nineteenth century when three of them were sent to London, New York and Paris. Their transportation was covered by various newspapers.[21]

There are ancient Egyptian obelisks in the following locations:
- Egypt – 11
- Pharaoh Seti II, Karnak Temple, Luxor, 7 m (23 ft)
- Pharaoh Thutmosis I, Karnak Temple, Luxor
- Pharaoh Ramses II, Luxor Temple
- Pharaoh Hatshepsut, Karnak Temple, Luxor
- Pharaoh Senusret I, Al-Masalla area of Al-Matariyyah district in Heliopolis, Cairo
- Pharaoh Ramses II, Tahrir Square, Cairo
- Pharaoh Ramses III, Luxor Museum
- Pharaoh Ramses II, Gezira Island, Cairo, 20.4 m (67 ft)[22]
- Pharaoh Ramses II, Cairo International Airport, 16.97 m (55.7 ft)
- Pharaoh Hatshepsut, "The Unfinished obelisk", Stone Quarries, Aswan
- Pharaoh Senusret I, Faiyum
- France – 1
- Pharaoh Ramses II, Luxor Obelisk, in Place de la Concorde, Paris[21]
- Israel – 1
- Italy – 13 (includes the only one located in the Vatican City)
- Rome — 8 ancient Egyptian obelisks (see List of obelisks in Rome)
- Piazza del Duomo, Catania (Sicily)
- Boboli Obelisk (Florence)
- Urbino
- Poland – 1
- Turkey – 1
- Pharaoh Tuthmosis III, the Obelisk of Theodosius in the Hippodrome of Constantinople (now Sultan Ahmet Square), Istanbul
- United Kingdom – 4
- Pharaoh Tuthmosis III, "Cleopatra's Needle", beside the Thames Victoria Embankment, in London
- Pharaoh Amenhotep II, in the Oriental Museum, University of Durham
- Pharaoh Ptolemy IX, Philae obelisk, at Kingston Lacy, near Wimborne Minster, Dorset
- Pharaoh Nectanebo II, British Museum, London (pair of obelisks)
- United States – 1
- Pharaoh Tuthmosis III, "Cleopatra's Needle", in Central Park, New York
Assyrian
Obelisk monuments are also known from the Assyrian civilization, where they were erected as public monuments that commemorated the achievements of the Assyrian king.
The British Museum possesses four Assyrian obelisks:
The White Obelisk of Ashurnasirpal I (named due to its colour), was discovered by Hormuzd Rassam in 1853 at Nineveh. The obelisk was erected by either Ashurnasirpal I (1050–1031 BCE) or Ashurnasirpal II (883–859 BCE). The obelisk bears an inscription that refers to the king's seizure of goods, people and herds, which he carried back to the city of Ashur. The reliefs of the Obelisk depict military campaigns, hunting, victory banquets and scenes of tribute bearing.
The Rassam Obelisk, named after its discoverer Hormuzd Rassam, was found on the citadel of Nimrud (ancient Kalhu). It was erected by Ashurnasirpal II, though only survives in fragments. The surviving parts of the reliefs depict scenes of tribute bearing to the king from Syria and the west.[24]
The Black Obelisk was discovered by Sir Austen Henry Layard in 1846 on the citadel of Kalhu. The obelisk was erected by Shalmaneser III and the reliefs depict scenes of tribute bearing as well as the depiction of two subdued rulers, Jehu the Israelite, and Sua the Gilzanean, making gestures of submission to the king. The reliefs on the obelisk have accompanying epigraphs, but besides these the obelisk also possesses a longer inscription that records one of the latest versions of Shalmaneser III's annals, covering the period from his accessional year to his 33rd regnal year.
The Broken Obelisk, that was also discovered by Rassam at Nineveh. Only the top of this monolith has been reconstructed in the British Museum. The obelisk is the oldest recorded obelisk from Assyria, dating to the 11th century BCE.[25]
Axumite (Ethiopia)
A number of obelisks were carved in the ancient Axumite Kingdom of today northern Ethiopia. Together with (21-metre-high or 69-foot) King Ezana's Stele, the last erected one and the only unbroken, the most famous example of axumite obelisk is the so-called (24-metre-high or 79-footh) Obelisk of Axum. It was carved around the 4th century CE and, in the course of time, it collapsed and broke into three parts. In these conditions it was found by Italian soldiers in 1935, after the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, looted and taken to Rome in 1937, where it stood in the Piazza di Porta Capena. Italy signed a 1947 UN agreement to return the obelisk but did not affirm its agreement until 1997, after years of pressure and various controversial settlements. In 2003 the Italian government made the first steps toward its return, and in 2008 it was finally re-erected.
The largest known obelisk, the Great Stele at Axum, now fallen, at 33 metres (108 ft) high and 3 m (9.8 ft) by 2 m (6 ft 7 in) at the base (520 metric tons or 570 short tons)[26] is one of the largest single pieces of stone ever worked in human history (the largest is either at Baalbek or the Ramesseum) and probably fell during erection or soon after, destroying a large part of the massive burial chamber underneath it. The obelisks, properly termed stelae or the native hawilt or hawilti as they do not end in a pyramid, were used to mark graves and underground burial chambers. The largest of the grave markers were for royal burial chambers and were decorated with multi-storey false windows and false doors, while nobility would have smaller less decorated ones. While there are only a few large ones standing, there are hundreds of smaller ones in "stelae fields".
Ancient Roman
The Romans commissioned obelisks in an ancient Egyptian style. Examples include:
- Arles, France – Arles Obelisk, in Place de la République, a 4th-century obelisk of Roman origin
- Benevento, Italy – Domitian Obelisk[27][28]
- Munich, Germany – Obelisk of Titus Sextius Africanus, at Staatliche Sammlung für Ägyptische Kunst, 1st century CE, 5.8 metres (19 ft)
- Rome – there are five, see List of obelisks in Rome
Byzantine

- Istanbul, Turkey – Walled Obelisk, at Hippodrome of Constantinople (now Sultan Ahmet Square), built by Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (905–959) and originally covered with gilded bronze plaques
Pre-Columbian
The prehistoric Tello Obelisk, found in 1919 at Chavín de Huantar in Peru, is a monolith stele with obelisk-like proportions. It is 2.52 metres tall and was carved in a design of low relief with Chavín symbols, such as bands of teeth and animal heads. Long housed in the Museo Nacional de Arqueología, Antropología e Historia del Perú in Lima, it was relocated to the Museo Nacional de Chavín, which opened in July 2008. The obelisk was named for the archeologist Julio C. Tello, who discovered it and was considered the 'father of Peruvian archeology'. He was America's first indigenous archeologist.[29]
Recent erections
In late summer 1999, Roger Hopkins and Mark Lehner teamed up with a NOVA crew to erect a 25-ton obelisk. This was the third attempt to erect a 25-ton obelisk; the first two, in 1994 and 1999, ended in failure. There were also two successful attempts to raise a 2-ton obelisk and a 9-ton obelisk. Finally in August–September 1999, after learning from their experiences, they were able to erect one successfully.
First Hopkins and Rais Abdel Aleem organized an experiment to tow a block of stone weighing about 25 tons. They prepared a path by embedding wooden rails into the ground and placing a sledge on them bearing a megalith weighing about 25 tons. Initially they used more than 100 people to try to tow it but were unable to budge it. Finally, with well over 130 people pulling at once and an additional dozen using levers to prod the sledge forward, they moved it. Over the course of a day, the workers towed it 10–20 feet. Despite problems with broken ropes, they proved the monument could be moved this way.[30] Additional experiments were done in Egypt and other locations to tow megalithic stone with ancient technologies, some of which are listed here.
One experiment was to transport a small obelisk on a barge in the Nile River. The barge was built based on ancient Egyptian designs. It had to be very wide to handle the obelisk, with a 2 to 1 ratio length to width, and it was at least twice as long as the obelisk. The obelisk was about 3.0 metres (10 ft) long and no more than 5 metric tons (5.5 short tons). A barge big enough to transport the largest Egyptian obelisks with this ratio would have had to be close to 61-metre-long (200 ft) and 30-metre-wide (100 ft). The workers used ropes that were wrapped around a guide that enabled them to pull away from the river while they were towing it onto the barge. The barge was successfully launched into the Nile.
The final and successful erection event was organized by Rick Brown, Hopkins, Lehner and Gregg Mullen in a Massachusetts quarry. The preparation work was done with modern technology, but experiments have proven that with enough time and people, it could have been done with ancient technology. To begin, the obelisk was lying on a gravel and stone ramp. A pit in the middle was filled with dry sand. Previous experiments showed that wet sand would not flow as well. The ramp was secured by stone walls. Men raised the obelisk by slowly removing the sand while three crews of men pulled on ropes to control its descent into the pit. The back wall was designed to guide the obelisk into its proper place. The obelisk had to catch a turning groove which would prevent it from sliding. They used brake ropes to prevent it from going too far. Such turning grooves had been found on the ancient pedestals. Gravity did most of the work until the final 15° had to be completed by pulling the obelisk forward. They used brake ropes again to make sure it did not fall forward. On 12 September they completed the project.[31]
This experiment has been used to explain how the obelisks may have been erected in Luxor and other locations. It seems to have been supported by a 3,000 year-old papyrus scroll in which one scribe taunts another to erect a monument for "thy lord". The scroll reads "Empty the space that has been filled with sand beneath the monument of thy Lord."[32] To erect the obelisks at Luxor with this method would have involved using over a million cubic meters of stone, mud brick and sand for both the ramp and the platform used to lower the obelisk.[33] The largest obelisk successfully erected in ancient times weighed 455 metric tons (502 short tons). A 520-metric-ton (570-short-ton) stele was found in Axum, but researchers believe it was broken while attempting to erect it.
Obelisks have also been used in surveying as boundary markers.
Clock and calendar
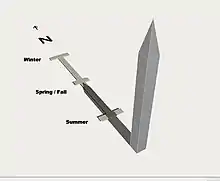
The moment the Sun reaches its zenith (high noon) the shadow of an obelisk points directly north. Midway between the longest shadow of the year and the shortest shadow of the year, is the equinox.[34]
See also
Notes
- ὀβελίσκος. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project.
- Harper, Douglas. "obelisk". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- οβελός in Liddell and Scott.
- Baker, Rosalie F.; Baker, Charles (2001). Ancient Egyptians: People of the pyramids. Oxford University Press. p. 69. ISBN 978-0195122213. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
Tekhenu egyptian
- "A World of Obelisks: Cairo". NOVA Online: Mysteries of the Nile. PBS. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- Griffith, Francis Llewellyn (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. 19 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 945.
- Blackwell Gary, Patricia; Talcott, Richard (June 2006). "Stargazing in Ancient Egypt" (PDF). Astronomy. pp. 62–67. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- Lacovara, Petere (2018). "Pyramids and Obelisks beyond Egypt". Aegyptiaca (2): 130. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- Tormod, Eide. "Fontes historiae Nubiorum: Textual Sources for the History of the Middle Nile region between the eighth century BC and the sixth century AD". 1 (54): 54. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Lacovara, Petere (2018). "Pyramids and obelisks beyond Egypt". Aegyptiaca (2): 131–135. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- "A World of Obelisks: Rome". NOVA Online: Mysteries of the Nile. PBS. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- Lees-Milne, James (1967). Saint Peter's.
- "Della trasportatione dellªobelisco Vaticano et delle fabriche di Nostro Signore Papa Sisto ..." purl.pt.
- "Della trasportatione dell'obelisco vaticano et delle fabriche di nostro signore papa Sisto V fatte dal cavallier Domenico Fontana, architetto di Sva Santita, libro primo". NYPL Digital Collections. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- Fontana, Domenico (1590). "Moving the Obelisk". Martayan Lan Rare Books. Rome, IT: Domenico Basa. Archived from the original on 21 May 2013. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- Fontana, Domenico (1590). Della trasportatione dell'obel. Zürich (NEBIS): ETH-Bibliothek – e-rara. doi:10.3931/e-rara-117.
- "Caesarea Obelisk". Highskyblue.web.fc2.com. 18 June 2001. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- Habachi, Labib (1985). The Obelisks of Egypt: Skyscrapers of the past. American University in Cairo Press. pp. 145–151. ISBN 978-9774240225.
- "A World of Obelisks: Istanbul". NOVA Online: Mysteries of the Nile. PBS. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- "A World of Obelisks: World". NOVA Online | Mysteries of the Nile. PBS. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- Brier, Bob (2018). "The secret life of the Paris obelisk". Aegyptiaca (2): 75–91. Retrieved 18 June 2019.
- "History of the Egyptian Obelisks". Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- "Obelisk of Ramesses II in the Museum's courtyard". Muzeum Archeologiczne w Poznaniu. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- "Rassam Obelisk". British Museum. Collection object details.
- "Broken Obelisk". British Museum. Collection object details.
- Scarre, Chris, ed. (1999). The Seventy Wonders of the Ancient World.
- "museodelsannio.com". Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- "Domitian Obelisk (In Piazza Papiniano, Benevento)". obelisks.org. Retrieved 15 September 2019.
- Burger, Richard L. The Life and Writings of Julio C. Tello. University of Iowa Press. Retrieved 27 September 2010.
- "Dispatches", NOVA
- "Mysteries of the Nile | August 27, 1999: The Third Attempt". Pbs.org. 27 August 1999. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- NOVA (TV series) Secrets of Lost Empire II: "Pharaoh's Obelisks"
- Time Life Lost Civilizations series: Ramses II: Magnificence on the Nile, New York: TIME/Life, 1993, pp. 56–57
- Euclid (300 BCE). Euclid's Elements. Check date values in:
|year=(help)
References
- Curran, Brian A., Anthony Grafton, Pamela O. Long, and Benjamin Weiss. Obelisk: A History. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2009. ISBN 978-0-262-51270-1.
- Chaney, Edward, "Roma Britannica and the Cultural Memory of Egypt: Lord Arundel and the Obelisk of Domitian", in Roma Britannica: Art Patronage and Cultural Exchange in Eighteenth-Century Rome, eds. D. Marshall, K. Wolfe and S. Russell, British School at Rome, 2011, pp. 147–70.
- Iversen, Erik, Obelisks in exile. Copenhagen, Vol. 1 1968, Vol. 2 1972
- Wirsching, Armin, Obelisken transportieren und aufrichten in Aegypten und in Rom. Norderstedt: Books on Demand 2007 (3rd ed. 2013), ISBN 978-3-8334-8513-8
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Obelisks. |
- Obelisks of the World
- Obelisks of Rome (series of articles in Platner's A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome 1929)
- History of the obelisk of Arles (in French)
- Octavo Edition of Domenico Fontana's book depicting how he erected the Vatican obelisk in 1586.
- National Geographic: "Researchers Lift Obelisk With Kite to Test Theory on Ancient Pyramids"
- Obelisk of Psametik II from Heliopolis, removed and reerected by Augustus in the northern Campus Martius, Rome

