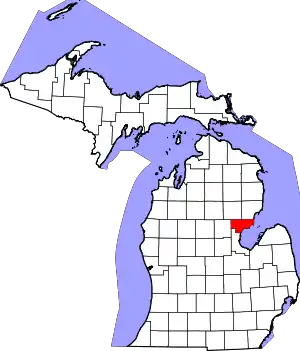
Omer, Michigan
Omer is a city in Arenac County in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 313.
Omer, Michigan | |
|---|---|
 Signage along U.S. Route 23 | |
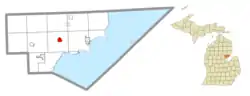 Location within Arenac County | |
 Omer Location within the state of Michigan | |
| Coordinates: 44°02′51″N 83°51′16″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Michigan |
| County | Arenac |
| Incorporated | 1903 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Council–manager |
| • Mayor | Lawrence Lee |
| • City clerk | Susan Hegenauer |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1.16 sq mi (3.00 km2) |
| • Land | 1.13 sq mi (2.93 km2) |
| • Water | 0.03 sq mi (0.07 km2) |
| Elevation | 610 ft (186 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 313 |
| • Estimate (2019)[3] | 289 |
| • Density | 255.30/sq mi (98.54/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP code(s) | 48749 |
| Area code(s) | 989 |
| FIPS code | 26-60660[4] |
| GNIS feature ID | 0634057[5] |
While signage along the passing U.S. Route 23 mentions Omer as "Michigan's Smallest City," it is actually the state's second-smallest city in terms of population at the 2010 census after the city of Lake Angelus in Oakland County, which had a population of 290.[6]
History
Omer was founded by George Gorie and George Carscallen, who set up a sawmill along the Rifle River in 1866. The town was originally named Rifle River Mills, but Carscallen, the first postmaster, wanted to rename the town Homer. However, he found a post office in another town called Homer, Michigan and simply dropped the leading H, producing the final name. The community received a station on the Detroit and Mackinaw Railroad, while in 1872 the area was platted. In 1883, Omer was split off from Bay County into the newly formed Arenac County.[7]
Omer was incorporated as a city in 1903.[6] A fire in 1914 almost eliminated the city, destroying 40 buildings and ending the early thrive that Omer had. Two years later, a flood curtailed rebuilding efforts by washing out the local dam.
Omer is the location of the story of the "cussing canoeist", the man who received a ticket under a century-old law for shouting a long stream of expletives in the presence of a woman and her two young children after he fell out of a canoe on the Rifle River. The American Civil Liberties Union intervened on the canoeist's behalf and got the law struck down in court.[6]
A second news story of note concerned the successful secession of two households from the city because the City of Omer was charging them a water tax while refusing to deliver water service to their property.[8][9]
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 1.16 square miles (3.00 km2) of which 1.13 square miles (2.93 km2) is land and 0.03 square miles (0.08 km2) is water.[10]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1910 | 367 | — | |
| 1920 | 266 | −27.5% | |
| 1930 | 216 | −18.8% | |
| 1940 | 295 | 36.6% | |
| 1950 | 321 | 8.8% | |
| 1960 | 322 | 0.3% | |
| 1970 | 366 | 13.7% | |
| 1980 | 403 | 10.1% | |
| 1990 | 385 | −4.5% | |
| 2000 | 337 | −12.5% | |
| 2010 | 313 | −7.1% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 289 | [3] | −7.7% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[11] | |||

2010 census
As of the census[2] of 2010, there were 313 people, 131 households, and 82 families residing in the city. The population density was 277.0 inhabitants per square mile (107.0/km2). There were 162 housing units at an average density of 143.4 per square mile (55.4/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 94.2% White, 0.3% African American, 4.2% Native American, 0.3% from other races, and 1.0% from two or more races.
There were 131 households, of which 32.1% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 41.2% were married couples living together, 13.0% had a female householder with no husband present, 8.4% had a male householder with no wife present, and 37.4% were non-families. 28.2% of all households were made up of individuals, and 13.7% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.39 and the average family size was 2.84.
The median age in the city was 40.8 years. 22.4% of residents were under the age of 18; 8.6% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 25% were from 25 to 44; 26.2% were from 45 to 64; and 17.9% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the city was 50.2% male and 49.8% female.
2000 census
As of the census[4] of 2000, there were 337 people, 143 households, and 98 families residing in the city. The population density was 272.2 per square mile (104.9/km2). There were 163 housing units at an average density of 131.7 per square mile (50.8/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 95.85% White, 1.19% Native American, 0.59% from other races, and 2.37% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.78% of the population.
There were 143 households, out of which 26.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 54.5% were married couples living together, 10.5% had a female householder with no husband present, and 30.8% were non-families. 24.5% of all households were made up of individuals, and 13.3% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.36 and the average family size was 2.82.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 22.6% under the age of 18, 7.1% from 18 to 24, 26.1% from 25 to 44, 25.2% from 45 to 64, and 19.0% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 40 years. For every 100 females, there were 97.1 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.2 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $28,125, and the median income for a family was $33,250. Males had a median income of $26,607 versus $21,250 for females. The per capita income for the city was $16,755. About 12.4% of families and 15.2% of the population were below the poverty line, including 15.8% of those under age 18 and 16.7% of those age 65 or over.
Transportation
- Indian Trails provides daily intercity bus service between St. Ignace and Bay City, Michigan.[12]
Major Highways
Local attractions
Like many small towns in northern mid-Michigan, the height of activity in Omer centers on an influx of people during the spring and summer. The Rifle River that intersects the city attracts thousands per year during the sucker season. Folks from all over the Midwest and Canada line the shores and engage in the sport of sucker fishing in the spring. Up until the late 1980s, Omer held an annual Sucker Festival and tournament, wherein the town would swell to some 3,000 sucker dippers and revelers. But it was eventually ended when it became too expensive for the small city to buy the insurance necessary to host it. The tournament was revived in 2008, thanks to two local sponsors.[13]
References
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 25, 2020.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2012-11-25.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". United States Census Bureau. May 24, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Omer, Michigan
- "The 18 tiniest cities in Michigan". The Flint Journal. December 4, 2016. p. 20. Retrieved December 5, 2016.
- Romig, Walter (1986). Michigan Place Names: The History of the Founding and the Naming of More Than Five Thousand Past and Present Michigan Communities. Great Lakes Books Series. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. p. 415. ISBN 081431838X.
- Seidel, Jeff (December 22, 2002). "City limits: Tiny Omer, Mich., votes on secession and what community really means". Detroit Free Press. Archived from the original on December 28, 2002.
- Reynolds, Dean. "Taxed for Nothing? Family Wants to Secede From Small Michigan Town Over $41.62". ABC News. Archived from the original on June 14, 2004.
- "US Gazetteer files 2010". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2012-01-25. Retrieved 2012-11-25.
- "Census of Population and Housing". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- "Bay City–Alpena–Cheboygan–St. Ignace" (PDF). Indian Trails. March 19, 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 24, 2013. Retrieved 2013-04-03.
- Payne, Amy L. (March 28, 2008). "Sucker revival: Omer hosting new tournament, festivities during annual sucker run on the Rifle River". MLive.com.