Palladium(II) bis(acetylacetonate)
Palladium(II) bis(acetylacetonate) is a compound with formula Pd(C5H7O2)2. This yellow solid is the most common palladium complex of acetylacetonate. This compound is commercially available and used as a catalyst precursor in organic synthesis. The molecule is relatively planar with idealized D2h symmetry.[2]
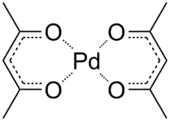 | |
_acetylacetonate_3D_ball.png.webp) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Palladium(II) 2,4-pentanedionate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.404 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14O4Pd | |
| Molar mass | 304.64 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 200 to 251 °C (392 to 484 °F; 473 to 524 K) (decomposes) |
| Structure[2] | |
| monoclinic | |
| P21/n, No. 14 | |
a = 9.9119 Å, b = 5.2232 Å, c = 10.3877 Å α = 90°, β = 95.807°, γ = 90° | |
Lattice volume (V) |
535.04 Å3 |
Formula units (Z) |
2 |
| Hazards | |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Palladium(II) acetylacetonate at Sigma-Aldrich
- Hamid, Mazhar; Zeller, Matthias; Hunter, Allen D.; Mazhar, Muhammad; Tahir, Asif Ali (2005). "Redetermination of bis(2,4-pentanedionato)palladium(II)". Acta Crystallographica Section E. 61 (11): m2181–m2183. doi:10.1107/S1600536805030692.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.