Palladium(II) chloride
Palladium(II) chloride, also known as palladium dichloride and palladous chloride, are the chemical compounds with the formula PdCl2. PdCl2 is a common starting material in palladium chemistry – palladium-based catalysts are of particular value in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with palladium metal at high temperatures.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Palladium dichloride, Palladous chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.724 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| PdCl2 | |
| Molar mass | 177.326 g/mol (anhydrous) 213.357 g/mol (dihydrate) |
| Appearance | dark red solid hygroscopic (anhydrous) dark brown crystals (dihydrate) |
| Density | 4.0 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 679 °C (1,254 °F; 952 K) (decomposes) |
| soluble in trace amounts, better solubility in cold water | |
| Solubility | soluble in organic solvents dissolves rapidly in HCl |
| −38.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| rhombohedral | |
| square planar | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
2704 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Palladium(II) fluoride Palladium(II) bromide Palladium(II) iodide |
Other cations |
Nickel(II) chloride Platinum(II) chloride Platinum(II,IV) chloride Platinum(IV) chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Structure
Two forms of PdCl2 are known, denoted α and β. In both forms, the palladium centres adopt a square-planar coordination geometry that is characteristic of Pd(II). Furthermore, in both forms, the Pd(II) centers are linked by μ2-chloride bridges. The α-form of PdCl2 is a polymer, consisting of "infinite" slabs or chains. The β-form of PdCl2 is molecular, consisting of an octahedral cluster of six Pd atoms. Each of the twelve edges of this octahedron is spanned by Cl−. PtCl2 adopts similar structures, whereas NiCl2 adopts the CdCl2 motif, featuring hexacoordinated Ni(II).[1]

-chloride-xtal-3D-balls.png.webp) | 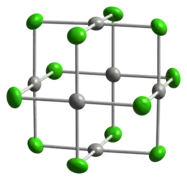 |
crystal structure of α-PdCl2 | found in the crystal structure of β-PdCl2 |
Two further polymorphs, γ-PdCl2 and δ-PdCl2, have been reported and show negative thermal expansion. The high-temperature δ form contains planar ribbons of edge‐connected PdCl4 squares, like α-PdCl2. The low‐temperature γ form has corrugated layers of corner‐connected PdCl4 squares.[2]
Preparation
Palladium(II) chloride is prepared by dissolving palladium metal in aqua regia or hydrochloric acid in the presence of chlorine. Alternatively, it may be prepared by heating palladium sponge metal with chlorine gas at 500 °C.
Reactions
Palladium(II) chloride is a common starting point in the synthesis of other palladium compounds. It is not particularly soluble in water or non-coordinating solvents, so the first step in its utilization is often the preparation of labile but soluble Lewis base adducts, such as bis(benzonitrile)palladium dichloride and bis(acetonitrile)palladium dichloride.[3] These complexes are prepared by treating PdCl2 with hot solutions of the nitriles:
- PdCl2 + 2 RCN → PdCl2(RCN)2
Although occasionally recommended, inert-gas techniques are not necessary if the complex is to be used in situ. As an example, bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride may be prepared from palladium(II) chloride by reacting it with triphenylphosphine in benzonitrile:[4]
- PdCl2 + 2 PPh3 → PdCl2(PPh3)2
Further reduction in the presence of more triphenylphosphine gives tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0); the second reaction may be carried out without purifying the intermediate dichloride:[5]
- PdCl2(PPh3)2 + 2 PPh3 + 2.5 N2H4 → Pd(PPh3)4 + 0.5 N2 + 2 N2H5+Cl−
Alternatively, palladium(II) chloride may be solubilized in the form of the tetrachloropalladate anion, e.g. sodium tetrachloropalladate, by reacting with the appropriate alkali metal chloride in water:[6] Palladium(II) chloride is insoluble in water, whereas the product dissolves:
- PdCl2 + 2 MCl → M2PdCl4
This compound may also further react with phosphines to give phosphine complexes of palladium.[6]
Palladium chloride may also be used to give heterogeneous palladium catalysts: palladium on barium sulfate, palladium on carbon, and palladium chloride on carbon.[7]

Uses
Even when dry, palladium(II) chloride is able to rapidly stain stainless steel. Thus, palladium(II) chloride solutions are sometimes used to test for the corrosion-resistance of stainless steel.[8]
Palladium(II) chloride is sometimes used in carbon monoxide detectors. Carbon monoxide reduces palladium(II) chloride to palladium:
- PdCl2 + CO + H2O → Pd + CO2 + 2HCl
Residual PdCl2 is converted to red PdI2, the concentration of which may be determined colorimetrically:[9]
- PdCl2 + 2 KI → PdI2 + 2 KCl
Palladium(II) chloride is used in the Wacker process for production of aldehydes and ketones from alkenes.
Palladium(II) chloride can also be used for the cosmetic tattooing of leukomas in the cornea.
References
- Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- J. Evers, W. Beck, M. Göbel, S. Jakob, P. Mayer, G. Oehlinger, M. Rotter, T. M. Klapötke (2010). "The Structures of δ‐PdCl2 and γ‐PdCl2: Phases with Negative Thermal Expansion in One Direction". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49 (33): 5677–5682. doi:10.1002/anie.201000680. PMID 20602377.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Gordon K. Anderson, Minren Lin (1990). "Bis(Benzonitrile)Dichloro Complexes of Palladium and Platinum". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorg. Synth. Inorganic Syntheses. 28. pp. 60–63. doi:10.1002/9780470132593.ch13. ISBN 9780470132593.
- Norio Miyaura and Akira Suzuki (1993). "Palladium-catalyzed reaction of 1-alkenylboronates with vinylic halides: (1Z,3E)-1-Phenyl-1,3-octadiene". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 8, p. 532
- D. R. Coulson; Satek, L. C.; Grim, S. O. (1972). 23. Tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0). Inorg. Synth. Inorganic Syntheses. 13. pp. 121–124. doi:10.1002/9780470132449.ch23. ISBN 9780470132449.
- Daniele Choueiry and Ei-ichi Negishi (2002). "II.2.3 Pd(0) and Pd(II) Complexes Containing Phosphorus and Other Group 15 Atom Ligands" (Google Books excerpt). In Ei-ichi Negishi (ed.). Handbook of Organopalladium Chemistry for Organic Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 0-471-31506-0.
- Ralph Mozingo (1955). "Palladium Catalysts". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 3, p. 685
- For example, http://www.marinecare.nl/assets/Uploads/Downloads/Leaflet-Passivation-Test-Kit.pdf%5B%5D
- T. H. Allen, W. S. Root (1955). "Colorimetric Determination of Carbon Monoxide in Air by an improved Palladium Chloride Method". J. Biol. Chem. 216 (1): 309–317. PMID 13252030.