Allylpalladium chloride dimer
Allylpalladium(II) chloride dimer (APC) is a chemical compound with the formula [(η3-C3H5)PdCl]2. This yellow air-stable compound is an important catalyst used in organic synthesis.[2] It is one of the most widely used transition metal allyl complexes.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Allylpalladium(II) chloride dimer | |
| Other names
Allylpalladium chloride dimer bis(allyl)di-μ-chloro-dipalladium(II) APC | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.423 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10Cl2Pd2 | |
| Molar mass | 365.85 g/mol |
| Appearance | Pale yellow, crystalline solid |
| Density | Solid |
| Melting point | decomp at 155-156 °C |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Chloroform benzene acetone methanol |
| Structure[1] | |
| monoclinic | |
| P21/n, No. 14 | |
Formula units (Z) |
2 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | http://www.colonialmetals.com/pdf/5048.pdf |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
(η3-allyl)(η5 – cyclopentadienyl)palladium(II) di-μ-chlorobis(crotyl)dipalladium |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Structure
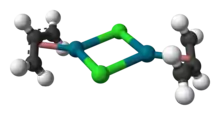
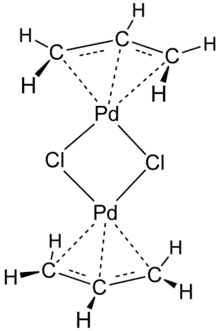
The compound has a dimeric structure that is centrosymmetric. Each allyl group lies in a plane at an angle of about 111.5° to the square formed by the palladium and carbon atoms, and the Pd–C distances are all equal. Its unit cell is monoclinic.[1]
Synthesis
The compound is prepared by purging carbon monoxide through a methanolic aqueous solution of sodium tetrachloropalladate (prepared from palladium(II) chloride and sodium chloride), and allyl chloride.[2]
- 2 Na2PdCl4 + 2 CH2=CHCH2Cl + 2 CO + 2 H2O → [(η3-C3H5)PdCl]2 + 4 NaCl + 2 CO2 + 4 HCl
Another method is the reaction of propene with palladium(II) trifluoroacetate, followed by ion exchange with chloride:[3]
- 2 (CF3COO)2Pd + 2 CH2=CHCH3 → [(η3-C3H5)Pd(CF3COO)]2
- [(η3-C3H5)Pd(CF3COO)]2 + 2 Cl− → [(η3-C3H5)PdCl]2 + 2 CF3COO−
Reactions
APC reacts with sources of cyclopentadienyl anion to give the corresponding 18e− complex cyclopentadienyl allyl palladium:
- [(η3-C3H5)PdCl]2 + 2 NaC5H5 → 2 [(η5-C5H5)Pd(η3-C3H5)] + 2 NaCl
The dimer reacts with a variety of Lewis bases (:B) to form adducts (η3-C3H5)PdCl:B. Its reaction with pyridine and the corresponding enthalpy are:
This enthalpy corresponds to the enthalpy change for a reaction forming one mole of the product, (η3-C3H5)PdCl:NC5H5, from the acid dimer. The dissociation energy for the Pd dimer, which is an energy contribution prior to reaction with the donor,
has been determined by the ECW model to be 28 kJ mol−1.
APC catalyzes many organic reactions, such as cross-coupling, nucleophilic addition to dienes, and decomposition of diazo compounds to reactive carbenes. It is also a useful precursor of other Pd catalysts.[3]
References
- Smith, A. E. (1965). "The structure of the allylpalladium chloride complex (C3H5PdCl)2 at –140°C". Acta Crystallographica. 18 (3): 331–340. doi:10.1107/S0365110X65000774. ISSN 0365-110X.
- Tatsuno, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Otsuka, S. "(η3-allyl)palladium(II) Complexes" Inorganic Syntheses, 1990, volume 28, pages 342-345. ISBN 0-471-52619-3
- Godleski, Stephen A.; Michelet, Véronique; Genêt, Jean-Pierre (2006), "Bis(allyl)di-μ-chlorodipalladium", Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, doi:10.1002/047084289x.rb098s.pub2, ISBN 978-0-471-93623-7, retrieved 2020-09-06