Pentagonal bifrustum
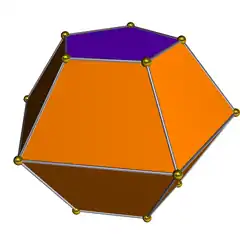
The pentagonal bifrustum or truncated pentagonal bipyramid is the third in an infinite series of bifrustum polyhedra. It has 10 trapezoid and 2 pentagonal faces.
| Pentagonal Bifrustum | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Bifrustum |
| Faces | 10 trapezoids, 2 pentagons |
| Edges | 20 |
| Vertices | 15 |
| Symmetry group | D5h |
| Dual polyhedron | elongated pentagonal dipyramid |
| Properties | convex |
Net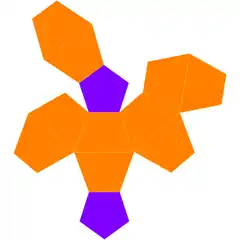 | |
Constructions
The pentagonal bifrustum is the dual polyhedron of a Johnson solid, the elongated pentagonal bipyramid. A Johnson solid is one of 92 strictly convex polyhedra that is composed of regular polygon faces but are not uniform polyhedra (that is, they are not Platonic solids, Archimedean solids, prisms, or antiprisms). They were named by Norman Johnson, who first listed these polyhedra in 1966.[1]
This polyhedron can be constructed by taking a pentagonal bipyramid and truncating the polar axis vertices. In Conway's notation for polyhedra, it can be represented as the polyhedron "t5dP5", meaning the truncation of the degree-five vertices of the dual of a pentagonal prism.[2]
Alternatively, it can be constructed by gluing together two end-to-end pentagonal frustums, or (if coplanar faces are allowed) by gluing together two pentagonal prisms on their pentagonal faces.
Application
In the formation of quasicrystals, a 15-site truncated pentagonal bipyramid structure may form the nucleus of larger structures with five-fold or icosahedral symmetry.[3]
References
- Johnson, Norman W. (1966), "Convex polyhedra with regular faces", Canadian Journal of Mathematics, 18: 169–200, doi:10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8, MR 0185507, Zbl 0132.14603.
- Conway Notation for Polyhedra, George W. Hart, accessed 2014-12-20.
- Hofmeister, Herbert (1999), "Fivefold twinning in nanosized particles and nanocrystalline thin films – ubiquitous metastable structures" (PDF), Materials Science Forum, 312–314: 325–332, doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.312-314.325, S2CID 136620837.