Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) is a pentosephosphate.
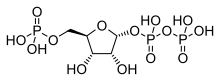 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| MeSH | Phosphoribosyl+pyrophosphate |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H13O14P3 | |
| Molar mass | 390.07 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is formed from ribose 5-phosphate by the enzyme ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase.
It plays a role in transferring phospho-ribose groups in several reactions:
In de novo generation of purines, the enzyme amidophosphoribosyltransferase acts upon PRPP to create phosphoribosylamine.
Increased PRPP
Increased levels of PRPP is characterized by the overproduction and accumulation of uric acid leading to hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria. It is one of the causes of gout.
Increased levels of PRPP are present in Lesch–Nyhan Syndrome. Decreased levels of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT) causes this accumulation, as PRPP is a substrate used by HGPRT during purine salvage.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.