Rclone
Rclone is an open source, multi threaded, command line computer program to manage content on cloud and other high latency storage. Its capabilities include sync, transfer, crypt, cache, union, compress and mount. The rclone website lists fifty supported backends including S3 services and Google Drive.[5]
 | |
 | |
| Original author(s) | Nick Craig-Wood[1] |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Nick Craig-Wood[2] |
| Initial release | July 3, 2014[3] |
| Stable release | |
| Repository | github |
| Written in | Go[5] |
| Operating system | Linux, Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, Plan9, Solaris[5] |
| Platform | Intel/AMD-64, Intel/AMD-32, ARM-32, ARM-64, MIPS-Big-Endian, MIPS-Little-Endian[5] |
| Licence | MIT |
| Website | rclone |
Descriptions of rclone often carry the strapline Rclone syncs your files to cloud storage.[5] Those prior to 2020 include the alternative Rsync for Cloud Storage.[6] Users have called rclone The Swiss Army Knife of cloud storage.[7]
Rclone is well known for its rclone sync and rclone mount commands.[8] It provides further management functions analogous to those ordinarily used for files on local disks, but which tolerate some intermittent and unreliable service. Transfers are optimised for high latency networks. Rclone is commonly a front-end for media servers such as Plex,[9] Emby or Jellyfin[10] to stream content direct from consumer file storage services.[9]
Rclone is widely used at HPC sites to transfer research datasets.
Official Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, Gentoo, Arch, Brew, Chocolatey, and other package managers include rclone.[11]
History
Nick Craig-Wood was inspired by rsync.[12][6] Concerns about the noise and power costs arising from home computer servers prompted him to embrace cloud storage. He began developing rclone as open source software in 2012 under the name swiftsync.[13][14][1]
Rclone was promoted to stable version 1.00 in July 2014.[3]
In May 2017 Amazon barred new rclone users from its consumer Amazon Drive file storage product. Amazon Drive had been advertised as offering unlimited storage for £55 per year. Amazon blamed security concerns and also banned other upload utilities.[15] Amazon's AWS S3 service continues to support new rclone users.
The original rclone logo was retired to be replaced with the present one in September 2018.[16]
In March 2020 Nick Craig-Wood resigned from Memset Ltd, a cloud hosting company he founded, to focus on open source software.[17][14][18][19]
Amazon's AWS April 2020 public sector blog explained how the Fred Hutch Cancer Research Center were using rclone in their Motuz tool to migrate very large biomedical research datasets in and out of AWS S3 object stores.[20]
May 2020 reports stated rclone had been used by hackers to exploit Diebold Nixdorf ATMs with ProLock ransomware.[21][22] The FBI issued a Flash Alert MI-000125-MW on 4 May 2020 in relation to the compromise.[23] They issued a further, related alert 20200901–001 in September 2020. Attackers had exfiltrated / encrypted data from organisations involved in healthcare, construction, finance, and legal services. Multiple US government agencies, and industrial entities were affected. Researchers established the hackers spent about a month exploring the breached networks, using rclone to archive stolen data to cloud storage, before encrypting the target system.[23][24][25] Reported targets included LaSalle County, and the city of Novi Sad.[26][27]
In November 2020 rclone was updated to correct a weakness in the way it generated passwords. Passwords for encrypted remotes can be generated randomly by rclone or supplied by the user. In all versions of rclone from 1.49.0 to 1.53.2 the seed value for generated passwords was based on the number of seconds elapsed in the day, and therefore not truly random. CVE-2020-28924 recommended users upgrade to the latest version of rclone and check the passwords protecting their encrypted remotes.[28]
The FBI warned January 2021, in Private Industry Notification 20210106–001, of extortion activity using Egregor ransomware and rclone. Organisations worldwide had been threatened with public release of exfiltrated data. In some cases rclone had been disguised under the name svchost.[29] Bookseller Barnes & Noble, US retailer Kmart, games developer Ubisoft and the Vancouver metro system have been reported as victims.[30]
Backends and Commands
Rclone supports the following services as backends. There are others, built on standard protocols such as WebDAV or S3, that work.[5] WebDAV backends do not directly support server side checksum or modtime.[31]
- 1Fichier
- Alibaba (Aliyun) Object Storage System (OSS)
- Amazon Drive (See note)
- Amazon S3
- Aruba COS[32]
- Backblaze B2
- Box
- C14
- Ceph
- Citrix ShareFile
- Cloudian[33]
- Dell-EMC ECS[34]
- DigitalOcean Spaces
- Dreamhost
- Dropbox
- Enterprise File Fabric[4]
- FTP
- Google Cloud Storage
- Google Drive
- Google Photos
- HDFS[4]
- HTTP
- Hubic
- IBM COS S3
- Jottacloud
- Koofr
- Mail.ru Cloud
- Memset Memstore
- Mega
- Microsoft Azure Blob Storage
- Microsoft OneDrive
- MinIO
- NetApp StorageGRID[35]
- Nextcloud
- OVH
- OpenDrive
- OpenIO[36]
- OpenStack Swift
- Oracle Cloud Storage
- ownCloud
- pCloud
- premiumize.me
- put.io
- QingStor
- Rackspace Cloud Files
- rsync.net
- Scaleway
- Scality[37]
- Seafile
- Selectel[38][39]
- SFTP
- StackPath
- SugarSync
- Tardigrade
- Tencent COS
- Wasabi
- WebDAV
- Yandex Disk
- Zoho Workdrive[4]
Remotes are usually defined interactively from these backends, local disk, or memory (as S3), with rclone config. Rclone can further wrap those remotes with one or more of alias, chunk, compress, crypt or union, remotes.
Once defined, the remotes are referenced by other rclone commands interchangeably with the local drive. Remote names are followed by a colon to distinguish them from local drives. For example, a remote example_remote containing a folder, or pseudofolder, myfolder is referred to within a command as a path example_remote:/myfolder.[40]
Rclone commands directly address remotes, or mount them for file access or streaming. With appropriate cache options the mount behaves as if a conventional, block level disk. Commands are provided to serve remotes over SFTP, HTTP, WebDAV, FTP and DLNA.[5] Commands can have sub-commands and flags. Filters determine which files on a remote rclone commands are applied to.[41]
rclone rc passes commands or new parameters to existing rclone sessions and has an experimental web browser interface.[42]
Crypt remotes
Rclone's crypt implements encryption of files at rest in cloud storage. It layers an encrypted remote over a pre-existing, cloud or other remote. Crypt is commonly[9] used to encrypt / decrypt media, for streaming, on consumer storage services such as Google Drive.
Rclone's configuration file contains the crypt password. The password can be lightly obfuscated, or the whole rclone.conf file can be encrypted.[43]
Crypt can either encrypt file content and name, or additionally full paths. In the latter case there is a potential clash with encryption for cloud backends, such as Microsoft OneDrive, having limited path lengths.[44] Crypt remotes do not encrypt object modification time or size. The encryption mechanism for content, name and path is available, for scrutiny, on the rclone website. Key derivation is with scrypt.[43]
Available commands
about Get quota information from the remote.
authorize Remote authorization.
backend Run a backend specific command.
cat Concatenates any files and sends them to stdout.
check Checks the files in the source and destination match.
cleanup Clean up the remote if possible.
config Enter an interactive configuration session.
copy Copy files from source to dest, skipping already copied.
copyto Copy files from source to dest, skipping already copied.
copyurl Copy url content to dest.
cryptcheck Cryptcheck checks the integrity of a crypted remote.
cryptdecode Cryptdecode returns unencrypted file names.
dedupe Interactively find duplicate filenames and delete/rename them.
delete Remove the files in path.
deletefile Remove a single file from remote.
genautocomplete Output completion script for a given shell.
gendocs Output markdown docs for rclone to the directory supplied.
hashsum Produces a hashsum file for all the objects in the path.
help Show help for rclone commands, flags and backends.
link Generate public link to file/folder.
listremotes List all the remotes in the config file.
ls List the objects in the path with size and path.
lsd List all directories/containers/buckets in the path.
lsf List directories and objects in remote:path formatted for parsing.
lsjson List directories and objects in the path in JSON format.
lsl List the objects in path with modification time, size and path.
md5sum Produces an md5sum file for all the objects in the path.
mkdir Make the path if it doesn't already exist.
mount Mount the remote as file system on a mountpoint.
move Move files from source to dest.
moveto Move file or directory from source to dest.
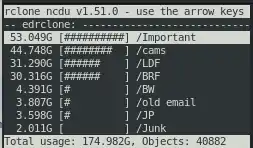
ncdu Explore a remote with a text based user interface.
obscure Obscure password for use in the rclone config file.
purge Remove the path and all of its contents.
rc Run a command against a running rclone.
rcat Copies standard input to file on remote.
rcd Run rclone listening to remote control commands only.
rmdir Remove the empty directory at path.
rmdirs Remove empty directories under the path.
serve Serve a remote over a protocol.
settier Changes storage class/tier of objects in remote.
sha1sum Produces an sha1sum file for all the objects in the path.
size Prints the total size and number of objects in remote:path.
sync Make source and dest identical, modifying destination only.
touch Create new file or change file modification time.
tree List the contents of the remote in a tree like fashion.
version Show the version number.[45]
Example syntax (Linux)
These examples describe paths and file names but object keys behave similarly.
To install the latest stable rclone version:-[46]
$ curl https://rclone.org/install.sh | sudo bash
To interactively configure xmpl: remote from a backend such as S3, Google Drive, or an sftp server:-
$ rclone config
To test the remote and obtain information about it:-
$ rclone about xmpl:
To recursively copy files from directory remote_stuff, at the remote, to directory stuff in the home folder:-
$ rclone copy -v -P xmpl:/remote_stuff ~/stuff
-v enables logging and -P, progress information. By default rclone checks the file integrity (hash) after copy; can retry each file up to three times if the operation is interrupted; uses up to four parallel transfer threads, and does not apply bandwidth throttling.
Running the above command again copies any new or changed files at the remote to the local folder but, like default rsync behaviour, will not delete from the local directory, files which have been removed from the remote.
To additionally delete files from the local folder which have been removed from the remote - more like the behaviour of rsync with a --delete flag:-
$ rclone sync xmpl:/remote_stuff ~/stuff
And to delete files from the source after they have been transferred to the local directory - more like the behaviour of rsync with a --remove-source-file flag:-
$ rclone move xmpl:/remote_stuff ~/stuff
To mount the remote directory at a mountpoint in the pre-existing, empty stuff directory in the home directory (the ampersand at the end makes the mount command run as a background process):-
$ rclone mount xmpl:/remote_stuff ~/stuff &
Default rclone syntax can be modified. Alternative transfer, filter, conflict and backend specific flags are available. Performance choices include number of concurrent transfer threads; chunk size; bandwidth limit profiling, and cache aggression.[41]
Example syntax (Windows)
These examples describe paths and file names but object keys behave similarly.
To install the latest stable release download the rclone installer archive, from the rclone website, and extract it.[46]
To interactively configure xmpl: remote from a backend such as S3, Google Drive, or an sftp server:-
>rclone config
To test the remote and obtain information about it:-
>rclone about xmpl:
To recursively copy files from directory remote_stuff, at the remote, to directory stuff on E drive:-
>rclone copy -v -P xmpl:remote_stuff E:\stuff
-v enables logging and -P, progress information. By default rclone checks the file integrity (hash) after copy; can retry each file up to three times if the operation is interrupted; uses up to four parallel transfer threads, and does not apply bandwidth throttling.
Running the above command again copies any new or changed file at the remote to the local directory but will not delete from the local directory.
To additionally delete files removed from the remote also from the local directory:-
>rclone sync xmpl:remote_stuff E:\stufff
And to delete files from the source after they have been transferred to the local directory:-
>rclone move xmpl:remote_stuff E:\stuff
To mount the remote directory from an unused drive letter, or at a mountpoint in a non existent directory:-
>rclone mount xmpl:remote_stuff X:
>rclone mount xmpl:remote_stuff E:\stuff
Default rclone syntax can be modified. Alternative transfer, filter, conflict and backend specific options are available. Performance choices include number of concurrent transfer threads; chunk size; bandwidth limit profiling, and cache aggression.[41]
Academic evaluation
In 2018, University of Kentucky researchers published a conference paper comparing use of rclone and other command line, cloud data transfer agents for big data.[47] The paper was published as a result of funding by the National Science Foundation.[48]
Later that year the University of Utah Center for High Performance Computing examined the impact of rclone options on data transfer rates.[49]
Rclone use at HPC research sites
Examples are University of Maryland,[50] Iowa State University,[51] Trinity College Dublin,[52] NYU,[53] BYU,[54] Indiana University,[55] CSC Finland,[56] Utrecht University,[57] University of Nebraska,[58] University of Utah,[59] North Carolina State University,[60] Stony Brook,[61] Tulane University,[62] Washington State University,[63] Georgia Tech,[64] National Institutes of Health,[65] Wharton,[66] Yale,[67] Harvard,[68] Minnesota,[69] Michigan State,[70] Case Western Reserve University,[71] University of South Dakota,[72] Northern Arizona University,[73] University of Pennsylvania,[74] Stanford,[75] University of Southern California,[76] UC Santa Barbara,[77][78] UC Irvine[79] and UC Berkeley.[80][81]
Rclone and rsync
Rsync transfers files with other computers that have rsync installed.[82] Rsync operates at the block, rather than file, level and has a delta algorithm so that it only needs to transfer changes in files. Rsync preserves file attributes and permissions. Rclone has a wider range of content management capabilities, and types of backend it can address, but only works at a whole file / object level.[83][1] It does not currently preserve permissions and attributes.[84] Rclone is designed to have some tolerance of intermittent and unreliable connections or remote services. Its transfers are optimised for high latency networks. Rclone decides which of those whole files / objects to transfer after obtaining checksums, to compare, from the remote server. Where checksums are not available, rclone can use object size and timestamp.[85]
Rsync is single threaded.[86] Rclone is multi threaded with a user definable number of simultaneous transfers.[87][88]
Rclone can pipe data between two completely remote locations, sometimes without local download. During an rsync transfer, one side must be a local drive.[82][88]
Rclone ignores trailing slashes. Rsync requires their correct use.[89] Rclone filters require the use of ** to refer to the contents of a directory. Rsync does not.[90]
Rsync enthusiasts can be rclone enthusiasts too.[91] Rsync continued to influence rclone at September 2020.[12]
Eponymous cloud storage service rsync.net provides remote unix filesystems so that customers can run rsync and other standard Unix tools.[92] They also offer rclone only accounts.[93]
In 2016 a poster on Hacker News summarised rclone's relationship to rsync as:- (rclone) exists to give you rsync to things that aren't rsync. If you want to rsync to things that are rsync, use rsync.[94]
Rclone and AWS CLI
AWS CLI is part of a suite of tools for managing Amazon's object storage service. It is built upon an AWS, python API.[95] Rclone supports storage from a range of suppliers. Both can be used to manipulate AWS storage objects in a way comparable to local files at the command line.
A contributor to an rclone forum summarised the difference between using AWS CLI and rclone as:- rclone works with many cloud providers. so learn rclone once and use it again and again.[96]
See also
References
- Craig-Wood, Nick (November 21, 2018). "Rclone "rsync for cloud storage"" (PDF). craig-wood.com. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- Craig-Wood, Nick (September 3, 2020). "Rclone 1.53 release". rclone. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Changelog". rclone. Retrieved July 29, 2020.
- Craig-Wood, Nick (February 2, 2021). "Rclone 1.54 release". rclone forum. Retrieved February 2, 2021.
- "Rclone". rclone. Archived from the original on June 17, 2020. Retrieved July 29, 2020.
- "rclone/rclone". July 31, 2020. Archived from the original on June 30, 2020. Retrieved July 29, 2020 – via GitHub.
- Massey, Jon (November 19, 2019). "Mounting Sharepoint Libraries On Linux Using Rclone". jonmassey.co.uk. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Tozzi, Christopher (September 25, 2020). "How to Access S3 Buckets from Windows or Linux". IT Pro. Retrieved September 27, 2020.
- "Recommended Google Drive and Plex Mount Settings". rclone forum. July 10, 2018. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Storage | Documentation - Jellyfin Project". jellyfin.org. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- "rclone package versions - Repology". repology.org. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Craig-Wood, Nick (September 9, 2020). "Rclone --links gets tripped up by existing .rclonelink files". rclone forum. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Craig-Wood, Nick (June 10, 2020). "Is rclone more efficient than an nfs mount". rclone forum. Retrieved July 29, 2020.
- "Meet The Team". Memset. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Claburn, Thomas (May 23, 2017). "Amazon Drive bans rclone storage client". theregister.com. The Register.
- "A New Logo for rclone". rclone forum. September 30, 2018.
- Craig-Wood, Nick (May 27, 2020). "Rclone 1.52 release". rclone forum. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "MEMSET LTD - Officers (free information from Companies House)". beta.companieshouse.gov.uk. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Trading Update, Iomart Group PLC, 2020-04-03". AIM-Watch. April 3, 2020. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Rogers, Ray (April 16, 2020). "How Fred Hutch unlocks siloed data with AWS and open-source software". Amazon Web Services. Archived from the original on July 12, 2020. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- Millman, Rene (May 23, 2020). "Diebold Nixdorf ATM attack by ProLock ransomware used QakBot trojan to access networks". Archived from the original on June 9, 2020. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- Ilascu, Ionut (May 14, 2020). "ProLock Ransomware teams up with QakBot trojan for network access". BleepingComputer. Archived from the original on June 13, 2020. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- Gatlan, Sergiu (September 5, 2020). "FBI issues second alert about ProLock ransomware stealing data". Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Ilascu, Ionut (September 10, 2020). "ProLock ransomware increases payment demand and victim count". BleepingComputer. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Skulkin, Oleg (May 14, 2020). "ATT&CKing ProLock Ransomware". group-ib.com. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "ProLock Ransomware" (PDF). sisainfosec.com. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- Abrams, Lawrence (March 2, 2020). "New PwndLocker Ransomware Targeting U.S. Cities, Enterprises". BleepingComputer. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "CVE - CVE-2020-28924". cve.mitre.org. November 19, 2020. Retrieved November 20, 2020.
- "FBI Private Industry Notification 20210106-001" (PDF). FBI. January 6, 2021.
- Montalbano, Elizabeth (January 8, 2021). "FBI Warns of Egregor Attacks on Businesses Worldwide". Threatpost. Retrieved January 21, 2021.
- Winokur, Justin (October 5, 2020). "iDrive.com Support". rclone forum. Retrieved October 5, 2020.
- "Aruba Cloud Object Storage". rclone forum. October 10, 2020. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
- Roetert, Niels (August 28, 2019). "S3 Bucket migration with metadata issues". rclone forum. Retrieved September 26, 2020.
- "Is anybody using Dell EMC Object Storage successfully with rclone?". rclone forum. September 23, 2020. Retrieved September 25, 2020.
- "Can't ls to sub directory? sorry, total newbie here". rclone forum. November 11, 2019. Retrieved September 22, 2020.
- "RClone". openio.io. Retrieved September 22, 2020.
- "OOM with big buckets". rclone forum. September 16, 2020. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Cloud Object Storage that supports an Amazon S3-compatible API". selectel.ru. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Add Selectel.com Storage support · Issue #4472 · rclone/rclone". GitHub. July 30, 2020. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- McKay, Dave. "How to Use rclone to Back Up to Google Drive on Linux". How-To Geek.
- "Documentation". rclone. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "GUI". rclone. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Crypt". rclone.org. September 2, 2020. Retrieved October 5, 2020.
- "Crypt backend, and path lengths". rclone forum. June 14, 2020. Retrieved October 5, 2020.
- "Commands". rclone.
- "Install". rclone. August 8, 2020. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Navigating the Unexpected Realities of Big Data Transfers in a Cloud-based World" (PDF). par.nsf.gov. National Science Foundation. Retrieved August 1, 2020.
- "NSF Award Search: Award#1541380 - CC*DNI Networking Infrastructure: An Software Defined Networking-Enabled Research Infrastructure". National Science Foundation. May 9, 2018. Archived from the original on September 28, 2018. Retrieved August 1, 2020.
- "rclone - Center for High Performance Computing - The University of Utah". chpc.utah.edu. The University of Utah. Retrieved August 1, 2020.
- "HPC Software Rclone". hpcc.umd.edu. University of Maryland. Archived from the original on October 24, 2019. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- "Rclone - High Performance Computing". hpc.iastate.edu. Iowa State University.
- "rclone". tchpc.tcd.ie. Trinity College Dublin. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Deng, Wensheng (September 30, 2018). "Transferring files between the HPC Prince Cluster and Google Drive - High Performance Computing at NYU - NYU Wikis". wikis.nyu.edu. New York University. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Office of Research Computing - BYU". rc.byu.edu. Brigham Young University. August 19, 2020. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Henderson, Rob (March 4, 2019). "Using Box under Linux - Luddy School of Informatics, Computing, and Engineering KB - Indiana University Enterprise Confluence". uisapp2.iu.edu. Indiana University Bloomington. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Using Allas with Rclone on CSC supercomputers - Docs CSC". docs.csc.fi. CSC – IT Center for Science. August 11, 2020. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "How to synchronize data with HPC platforms - News - Universiteit Utrecht". uu.nl. Utrecht University. February 18, 2019. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "HCC-DOCS". hcc.unl.edu. University of Nebraska–Lincoln. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "rclone - Center for High Performance Computing - The University of Utah". chpc.utah.edu. The University of Utah.
- "High Powered Computing Cluster – Mathematics IT". North Carolina State University. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Using rclone to backup data". it.stonybrook.edu. Stony Brook University. August 11, 2020. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "cypress/FileTransfer – hpc". wiki.hpc.tulane.edu. Tulane University. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "The Forbes Group". swan.physics.wsu.edu. Washington State University. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Dropbox, HPC, and Rclone". bioit.biology.gatech.edu. Georgia Tech. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Rclone on Helix and Biowulf". hpc.nih.gov. National Institute of Health. Archived from the original on January 8, 2017. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- "Rclone". research-it.wharton.upenn.edu. University of Pennsylvania. Archived from the original on December 18, 2019. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- "Rclone - Yale Center for Research Computing". docs.ycrc.yale.edu. Yale University. Archived from the original on May 16, 2020. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- "rclone – transfer files to/from cloud storage – FASRC DOCS". Harvard University. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "rclone - The Minnesota Supercomputing Institute". msi.umn.edu. University of Minnesota. Retrieved August 1, 2020.
- "Rclone on HPCC - Institute for Cyber-Enabled Research - Michigan State University". icer.msu.edu. Michigan State University. Retrieved August 1, 2020.
- "Rclone - Google Drive - hpc". Case Western Reserve University. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "rclone for Google Drive". University of South Dakota. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- "Cloud Storage Management". Northern Arizona University. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "HPC Software Rclone". hpcwiki.pmacs.upenn.edu/. Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- "Rclone - Sherlock". sherlock.stanford.edu. Stanford University. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "USC Research Computing, New Faculty Orientation Presentation" (PDF). University of Southern California. August 1, 2019. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- "Introduction to HPC Resources and Linux" (PDF). hpcc.umd.edu. University of California, Santa Barbara. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- "Copying files to Google (Google Drive)". csc.cnsi.ucsb.edu/. University of California, Santa Barbara. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- Mangalam, Harry (March 23, 2018). "Pushing data with rclone". moo.nac.uci.edu. University of California, Irvine. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Transferring Data Between Savio and Your bDrive (Google Drive) Account". research-it.berkeley.edu. University of California, Berkeley. Archived from the original on April 13, 2019. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- "Take advantage of unlimited bDrive (and Box) storage using rclone". research-it.berkeley.edu. University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "rsync(1) - Linux man page". linux.die.net. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Difference between Rclone and Rsync when syncing to the Local Filesystem?". rclone forum. July 9, 2017. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Rclone instead of rsync". rclone forum. September 11, 2019. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "SFTP". rclone. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Riel, Manuel (June 5, 2020). "bash - Speed up rsync with Simultaneous/Concurrent File Transfers?". Stack Overflow. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Documentation". rclone. August 9, 2020. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Winokur, Justin (September 12, 2020). "Nick giving a talk about Rclone and Backblaze". rclone forum. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Levens, Skip; Craig-Wood, Nick (September 17, 2020). "Tapping the Power of Cloud Copy & Sync with Rclone". brighttalk.com. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- Krajnik, Daniel (February 1, 2021). "How to exclude from directory ?! why is exclude not working? why is it even complicated at all?!". rclone forum. Retrieved February 2, 2021.
- Bruchanov, Martin (October 5, 2018). "BruXy: File synchronization with rsync and rclone". bruxy.regnet.cz. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "rsync.net Cloud Storage for Offsite Backups". rsync.net. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Cloud Storage for Offsite Backups - rclone support". rsync.net. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "Rclone: rsync for cloud storage". Hacker News. August 31, 2016. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- "aws/aws-cli". February 6, 2021. Retrieved February 6, 2021.
- "New user - rclone source ssh to remote s3". rclone forum. January 30, 2021. Retrieved February 2, 2021.