San Juan de Ulúa
San Juan de Ulúa, also known as Castle of San Juan de Ulúa, is a large complex of fortresses, prisons and one former palace on an island of the same name in the Gulf of Mexico overlooking the seaport of Veracruz, Mexico. Juan de Grijalva's 1518 expedition named the island. On Easter Sunday 1519, Hernan Cortés met with Tendile and Pitalpitoque, emissaries from Moctezuma II's Aztec Empire.[1]
| Fortaleza de San Juan de Ulúa | |
|---|---|
Fortress of San Juan de Ulúa | |
| Veracruz, Veracruz, Mexico | |
 View of the fortress facilities | |
| Coordinates | 19°12′33″N 96°7′53″W |
| Type | Fortress |
| Site information | |
| Controlled by | Instituto Nacional de Antropología e Historia |
| Open to the public | Yes |
| Condition | Deteriorated |
| Website | Official website |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1535 |
| Built by | Spanish Empire |
| Materials | Stone |
| Battles/wars | Spanish attempts to reconquer Mexico Mexican-American War French intervention in Mexico |
| Garrison information | |
| Past commanders | Francisco Luján (1568) José Coppinger (1825) Mariano Arista (1838) Juan Morales (1847) |
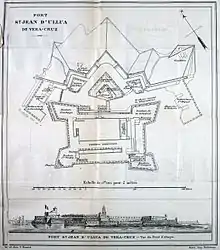
It was built between 1535 and 1769.[2] There is a local museum of the fortress, inaugurated in 1984.[3]
History

The fort was constructed during the period of Spanish colonial rule, with construction being initiated in 1535 by the Spanish authorities. The boundaries of the fort were repeatedly expanded several times during its existence. In 1568, the Spanish forces stationed on the fortress succeeded in trapping a privateer fleet under the command of John Hawkins in the fortress's harbour. The commanders under Hawkins included his cousin, the young Francis Drake. Although Hawkins and Drake both managed to escape the organized entrapment on their respective warships, many of the trapped sailors aboard the ships were killed by Spanish cannon fire. Several of the privateer warships present were sunk, and several more were damaged beyond repair, and scuttled along the Mexican coastline. The shipwrecked sailors were abandoned by Hawkins, who chose to cut his losses and venture elsewhere on the Spanish Main.
Trapped, and with no rescue in sight, these sailors ventured further inland, where they eventually settled among the local population and integrated into the Mexican populace at large, becoming part of the European diaspora in Mexico. Hawkins, along with Drake, continued his attacks on Spanish shipping transporting valuable cargo such as gold and silver from Spanish colonies in Latin America to Spain. The attack by the Spaniards at San Juan de Ulúa is credited as marking Drake's first feelings of intense hatred of both Catholicism and the Spanish, which would both go on to have an influence on his later career. After the repulse of the privateers, the fortress saw no further action under Spanish control, becoming an isolated outpost of the Spanish Army in New Spain. It saw no action during the Mexican War of Independence, being too far away from the main areas of fighting to see any real action.
Post-Spanish era
After Mexico's independence in 1821, a large body of Spanish troops continued to occupy San Juan de Ulúa as late as 1825. It was the last site in the former colony of New Spain to be held by the Spanish and was surrendered to Mexican General Miguel Barragán in November 1825. The justification for the order of expulsion issued by President Vicente Guerrero was their failed attempt at re-conquering Mexico. Since then, San Juan de Ulúa served as a military and political symbol of Mexican resistance to foreign invasions and occupations, thanks to several of which took place during the nineteenth century. In 1836 the French bombarded the fortress in the Battle of Veracruz during the Pastry War, a conflict resulting from a French citizen in Mexico seeking reparations for his allegedly damaged pastry shop; during the Mexican–American War, the United States laid siege to the fortress during the war, a conflict which resulted from disputes over the nascent Republic of Texas, and in 1863 the French briefly occupied the city when installing Maximilian I as emperor of Mexico. For much of the nineteenth century, the fort served as a prison, especially for political prisoners judged to be opposition to the government. Many prominent Mexican politicians spent time here while they were not in power.
The last foreign incursion came in 1914, on the eve of the First World War, when an American expedition captured and occupied Veracruz as a response to the Tampico Affair against the background of the Mexican Revolution; which threatened the regional oil industry in which Americans were heavily invested. After a short but bloody firefight the Americans captured the city, including San Juan de Ulúa. After seven months of U.S. occupation, the Americans departed and handed back the city to the Mexicans. The national legislature awarded the port and city of Veracruz the title of Heroic for the fourth time following this incident. A portion of San Juan de Ulúa also served several times as the presidential palace, housing presidents such as Benito Juárez and Venustiano Carranza. The citadel was also used as a prison, especially during the early 20th-century regime of President Porfirio Díaz. It was alleged by some sources that in order to prevent prisoners from escaping, sharks were placed into the waters surrounding the island, so that they would kill anyone attempting to escape.
Modern times
The fortress was ultimately closed ("decommisioned") when it was no longer required for the defence of Mexico, being too impractical to serve as a modern naval base. After several years of decay, renovations were begun on the complex in the late 20th century. Some of the renovation projects are still under construction today. San Juan de Ulúa has been preserved in a somewhat deteriorated form and has been transformed into a museum open to the public. The prison, along with the remaining fortress complex are all open to the public, with the exception of the former presidential palace, which suffered severe decay and is still undergoing renovations as of 2020. The complex is a very popular tourist attraction among the Mexican public. The fortress has also been featured in Hollywood movies, with San Juan de Ulúa was used to depict the fortress in Cartagena, Colombia, in the climax of the 1984 film Romancing the Stone.
See also
References
- Diaz, B., 1963, The Conquest of New Spain, London: Penguin Books, ISBN 0140441239 :89 :36,38,89
- "FORTALEZA DE SAN JUAN DE ULÚA". fortalezas.org (in Spanish).
- "Museo Local Fuerte de San Juan de Ulúa (SJU) Veracruz, México". ILAM Foundation (in Spanish).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to San Juan de Ulua Fort, Veracruz. |