Serine racemase
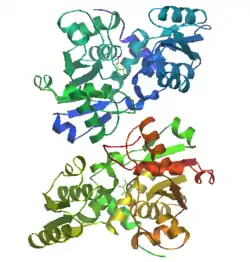
Serine racemase is an enzyme which generates D-serine from L-serine. D-serine acts as a neuronal signaling molecule by activating NMDA receptors in the brain. In humans, the serine racemase protein is encoded by the SRR gene.[5]
Mammalian serine racemase is a pyridoxal 5'-phosphate dependent enzyme that catalyzes both the racemization of L-serine to D-serine and also the elimination of water from L-serine, generating pyruvate and ammonia.[6] The enzyme is physiologically stimulated by divalent cations (e.g., magnesium) and is allosterically activated by the magnesium/ATP complex.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000167720 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000001323 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- De Miranda J, Santoro A, Engelender S, Wolosker H (Oct 2000). "Human serine racemase: moleular cloning, genomic organization and functional analysis". Gene. 256 (1–2): 183–8. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00356-5. PMID 11054547.
- De Miranda J, Panizzutti R, Foltyn VN, Wolosker H (Oct 2002). "Cofactors of serine racemase that physiologically stimulate the synthesis of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor coagonist D-serine". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99 (22): 14542–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.222421299. PMC 137919. PMID 12393813.
Further reading
- Morita Y, Ujike H, Tanaka Y, Otani K, Kishimoto M, Morio A, Kotaka T, Okahisa Y, Matsushita M, Morikawa A, Hamase K, Zaitsu K, Kuroda S (May 2007). "A genetic variant of the serine racemase gene is associated with schizophrenia". Biological Psychiatry. 61 (10): 1200–3. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.07.025. PMID 17067558. S2CID 8142062.
- Steffek AE, Haroutunian V, Meador-Woodruff JH (Jul 2006). "Serine racemase protein expression in cortex and hippocampus in schizophrenia". NeuroReport. 17 (11): 1181–5. doi:10.1097/01.wnr.0000230512.01339.72. PMID 16837850. S2CID 35663584.
- Fujii K, Maeda K, Hikida T, Mustafa AK, Balkissoon R, Xia J, Yamada T, Ozeki Y, Kawahara R, Okawa M, Huganir RL, Ujike H, Snyder SH, Sawa A (Feb 2006). "Serine racemase binds to PICK1: potential relevance to schizophrenia". Molecular Psychiatry. 11 (2): 150–7. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001776. PMID 16314870.
- Dumin E, Bendikov I, Foltyn VN, Misumi Y, Ikehara Y, Kartvelishvily E, Wolosker H (Jul 2006). "Modulation of D-serine levels via ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of serine racemase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (29): 20291–302. doi:10.1074/jbc.M601971200. PMID 16714286.
- Strísovský K, Jirásková J, Barinka C, Majer P, Rojas C, Slusher BS, Konvalinka J (Jan 2003). "Mouse brain serine racemase catalyzes specific elimination of L-serine to pyruvate". FEBS Letters. 535 (1–3): 44–8. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03855-3. PMID 12560076. S2CID 43772379.
- Hoffman HE, Jirásková J, Ingr M, Zvelebil M, Konvalinka J (Jan 2009). "Recombinant human serine racemase: enzymologic characterization and comparison with its mouse ortholog". Protein Expression and Purification. 63 (1): 62–7. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2008.09.003. PMID 18812225.
- Sarras H, Semeralul MO, Fadel MP, Feldcamp LA, Labrie V, Wong AH (Jul 2010). "Elevated PICK1 mRNA in schizophrenia increased SRR mRNA in suicide". Schizophrenia Research. 120 (1–3): 236–7. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2010.03.002. PMID 20385472. S2CID 21820692.
- Yamada K, Ohnishi T, Hashimoto K, Ohba H, Iwayama-Shigeno Y, Toyoshima M, Okuno A, Takao H, Toyota T, Minabe Y, Nakamura K, Shimizu E, Itokawa M, Mori N, Iyo M, Yoshikawa T (Jun 2005). "Identification of multiple serine racemase (SRR) mRNA isoforms and genetic analyses of SRR and DAO in schizophrenia and D-serine levels". Biological Psychiatry. 57 (12): 1493–503. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.03.018. PMID 15953485. S2CID 22811942.
- Xia M, Liu Y, Figueroa DJ, Chiu CS, Wei N, Lawlor AM, Lu P, Sur C, Koblan KS, Connolly TM (Jun 2004). "Characterization and localization of a human serine racemase". Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research. 125 (1–2): 96–104. doi:10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.03.007. PMID 15193426.
External links
- Serine+racemase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: Q9GZT4 (Serine racemase) at the PDBe-KB.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.