Sigma
Sigma /ˈsɪɡmə/[1] (uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς; Greek: σίγμα) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase ∑ is used as an operator for summation. When used at the end of a letter-case word (one that does not use all caps), the final form (ς) is used. In Ὀδυσσεύς (Odysseus), for example, the two lowercase sigmas (σ) in the center of the name are distinct from the word-final sigma (ς) at the end.
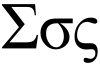 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greek alphabet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Use in other languages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related topics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History
The shape (Σς) and alphabetic position of sigma is derived from the Phoenician letter ![]() (shin).
(shin).
Sigma's original name may have been san, but due to the complicated early history of the Greek epichoric alphabets, san came to be identified as a separate letter in the Greek alphabet, represented as Ϻ.[2] Herodotus reports that "san" was the name given by the Dorians to the same letter called "sigma" by the Ionians.[lower-roman 1][3]
According to one hypothesis,[4] the name "sigma" may continue that of Phoenician samekh (![]() ), the letter continued through Greek xi, represented as Ξ. Alternatively, the name may have been a Greek innovation that simply meant 'hissing', from the root of σίζω (sízō, from Proto-Greek *sig-jō 'I hiss').[2]
), the letter continued through Greek xi, represented as Ξ. Alternatively, the name may have been a Greek innovation that simply meant 'hissing', from the root of σίζω (sízō, from Proto-Greek *sig-jō 'I hiss').[2]
Lunate sigma


In handwritten Greek during the Hellenistic period (4th–3rd century BC), the epigraphic form of Σ was simplified into a C-like shape,[5] which has also been found on coins from the 4th century BC onward.[6] This became the universal standard form of sigma during late antiquity and the Middle Ages.
Today, it is known as lunate sigma (uppercase Ϲ, lowercase ϲ), because of its crescent-like shape, and is still widely used in decorative typefaces in Greece, especially in religious and church contexts, as well as in some modern print editions of classical Greek texts.
A dotted lunate sigma (sigma periestigmenon, Ͼ) was used by Aristarchus of Samothrace (220–143 BC) as an editorial sign indicating that the line marked as such is at an incorrect position. Similarly, a reversed sigma (antisigma, Ͻ), may mark a line that is out of place. A dotted antisigma (antisigma periestigmenon, Ͽ) may indicate a line after which rearrangements should be made, or to variant readings of uncertain priority.
In unicode, the above variations of lunate sigma are encoded as U+03F9 Ϲ ; U+03FD Ͻ ; U+03FE Ͼ ; and U+03FF Ͽ
Derived alphabets
Sigma was adopted in the Old Italic alphabets beginning in the 8th century BC. A simplified three-stroke version, omitting the lowermost stroke, is found already in Western Greek alphabets, and becomes current in classical Etruscan and in Oscan, as well as in the earliest Latin epigraphy (early Latin S), such as the Duenos inscription. The alternation between three and four (and occasionally more than four) strokes is also adopted into the early runic alphabet (early form of the s-rune). Both the Anglo-Saxon runes and the Younger Futhark consistently use the simplified three-stroke version.
The forms of the Coptic letter sima (Ⲥ; 2nd century BC) and of Cyrillic letter es (С; 9th century AD) are derived from lunate sigma.
Uses
Language and linguistics
- In both Ancient and Modern Greek, the sigma represents the voiceless alveolar fricative /s/. In Modern Greek, this sound is voiced to /z/ before /m/, /n/, /v/, /ð/ or /ɣ/.
- The uppercase form of sigma (Σ) was re-borrowed into the Latin alphabet—more precisely, the International African Alphabet—to serve as the uppercase of modern esh (lowercase: ʃ).
- In phonology, σ is used to represent syllables.
- In linguistics, Σ represents the set of symbols that form an alphabet (see also computer science).
Mathematics
- In general mathematics, lowercase σ is commonly used to represent unknown angles, as well as serving as a shorthand for "countably", whereas ∑ is regularly used as the operator for summation, e.g.:
- In mathematical logic, is used to denote the set of formulae with bounded quantifiers beginning with existential quantifiers, alternating times between existential and universal quantifiers. This notation reflects an indirect analogy between the relationship of summation and products on one hand, and existential and universal quantifiers on the other. See the article on the arithmetic hierarchy.
- In statistics, σ represents the standard deviation of population or probability distribution (where mu or μ is used for the mean).
- In topology, σ-compact topological space is one that can be written as a countable union of compact subsets.
- In mathematical analysis and in probability theory, there is a type of algebra of sets known as σ-algebra (aka σ-field). Sigma algebra also includes terms such as:
- σ(A), denoting the generated sigma-algebra of a set A
- σ-finite measure (see measure theory)
- In number theory, σ is included in various divisor functions, especially the sigma function or sum-of-divisors function.
- In applied mathematics, σ(T) denotes the spectrum of a linear map T.
- In complex analysis, σ is used in the Weierstrass sigma-function.
- In probability theory and statistics, Σ denotes the covariance matrix of a set of random variables, sometimes in the form to distinguish it from the summation operator.
- Theoretical spectral analysis uses σ as standard deviation opposed to lowercase mu as the absolute mean value.
Biology, physiology, and medicine
- In biology, the sigma receptor (σ–receptors) is a type of cell surface receptor.
- In biochemistry, the σ factor (or specificity factor) is a protein found in RNA polymerase.
- In bone physiology, the bone remodeling period—i.e., the life span of a basic multicellular unit—has historically been referred to as the sigma period
- In early 20th-century physiology literature, σ had been used to represent milliseconds[7]
Business, finance, and economics
- In finance, σ is the symbol used to represent volatility of stocks, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns.
- In accounting, Σ indicates the balance of invoice classes and the overall amount of debts and demands.
- In macroeconomics, σ is used in equations to represent the elasticity of substitution between two inputs
- In the machine industry, Six Sigma (6σ) is a quality model based on the standard deviation
Chemistry
- Sigma bonds (σ bonds) are the strongest type of covalent chemical bond
- In organic chemistry, σ symbolizes the sigma constant of Hammett equation
Engineering and computer science
- In computer science, Σ represents the set of symbols that form an alphabet (see also linguistics)
- Relational algebra uses the values and to denote selections, which are a type of unary operation.
- In machine learning, σ is used in the formula that derives the Sigmoid function.
- In radar jamming or electronic warfare, radar cross-sections (RCS) are commonly represented as σ when measuring the size of a target's image on radar.
- In signal processing, σ denotes the damping ratio of a system parameter.
- In theoretical computer science, Σ serves as the busy beaver function.
Physics
- In nuclear and particle physics, σ is used to denote cross sections in general(see also RCS), while Σ represents macroscopic cross sections [1/length].
- The symbol is to denote the Stefan–Boltzmann constant.
- In relation to fundamental properties of material, σ is often used to signify electrical conductivity.
- In electrostatics, σ represents surface charge density.
- in continuum mechanics, σ is used to signify stress.
- In condensed matter physics, Σ denotes self-energy.
- The symbol can be used to signify surface tension (alternatively, γ or T are also used instead).
- In quantum mechanics, σ is used to indicate Pauli matrices.
- In astronomy, σ represents velocity dispersion
- In particle physics, Σ represents a class of baryons.
Organizations
- During the 1930s, an uppercase Σ was in use as the symbol of the Ação Integralista Brasileira, a fascist political party in Brazil.
- Sigma Corporation uses the name of the letter but not the letter itself, but in many Internet forums, photographers refer to the company or its lenses using the letter.
- Sigma Aldrich incorporate both the name and the character in their logo.
Character encoding
Greek sigma
| Preview | Σ | σ | ς | Ϲ | ϲ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | GREEK CAPITAL LETTER SIGMA | GREEK SMALL LETTER SIGMA | GREEK SMALL LETTER FINAL SIGMA | GREEK CAPITAL LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL | GREEK LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL | |||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 931 | U+03A3 | 963 | U+03C3 | 962 | U+03C2 | 1017 | U+03F9 | 1010 | U+03F2 |
| UTF-8 | 206 163 | CE A3 | 207 131 | CF 83 | 207 130 | CF 82 | 207 185 | CF B9 | 207 178 | CF B2 |
| Numeric character reference | Σ | Σ | σ | σ | ς | ς | Ϲ | Ϲ | ϲ | ϲ |
| Named character reference | Σ | σ | ς, ς, ς | |||||||
| DOS Greek | 145 | 91 | 169 | A9 | 170 | AA | ||||
| DOS Greek-2 | 207 | CF | 236 | EC | 237 | ED | ||||
| Windows 1253 | 211 | D3 | 243 | F3 | 242 | F2 | ||||
| TeX | \Sigma | \sigma | \varsigma | |||||||
| Preview | Ͻ | ͻ | Ͼ | ͼ | Ͽ | ͽ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | GREEK CAPITAL REVERSED LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL | GREEK SMALL REVERSED LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL | GREEK CAPITAL DOTTED LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL | GREEK SMALL DOTTED LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL | GREEK CAPITAL REVERSED DOTTED LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL | GREEK SMALL REVERSED DOTTED LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL | ||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 1021 | U+03FD | 891 | U+037B | 1022 | U+03FE | 892 | U+037C | 1023 | U+03FF | 893 | U+037D |
| UTF-8 | 207 189 | CF BD | 205 187 | CD BB | 207 190 | CF BE | 205 188 | CD BC | 207 191 | CF BF | 205 189 | CD BD |
| Numeric character reference | Ͻ | Ͻ | ͻ | ͻ | Ͼ | Ͼ | ͼ | ͼ | Ͽ | Ͽ | ͽ | ͽ |
Coptic sima
| Preview | Ⲥ | ⲥ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | COPTIC CAPITAL LETTER SIMA | COPTIC SMALL LETTER SIMA | ||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 11428 | U+2CA4 | 11429 | U+2CA5 |
| UTF-8 | 226 178 164 | E2 B2 A4 | 226 178 165 | E2 B2 A5 |
| Numeric character reference | Ⲥ | Ⲥ | ⲥ | ⲥ |
Mathematical sigma
These characters are used only as mathematical symbols. Stylized Greek text should be encoded using the normal Greek letters, with markup and formatting to indicate text style.
| Preview | ∑ | 𝚺 | 𝛔 | 𝛓 | 𝛴 | 𝜎 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | N-ARY SUMMATION | MATHEMATICAL BOLD CAPITAL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL BOLD SMALL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL BOLD SMALL FINAL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL ITALIC CAPITAL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL ITALIC SMALL SIGMA | ||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 8721 | U+2211 | 120506 | U+1D6BA | 120532 | U+1D6D4 | 120531 | U+1D6D3 | 120564 | U+1D6F4 | 120590 | U+1D70E |
| UTF-8 | 226 136 145 | E2 88 91 | 240 157 154 186 | F0 9D 9A BA | 240 157 155 148 | F0 9D 9B 94 | 240 157 155 147 | F0 9D 9B 93 | 240 157 155 180 | F0 9D 9B B4 | 240 157 156 142 | F0 9D 9C 8E |
| UTF-16 | 8721 | 2211 | 55349 57018 | D835 DEBA | 55349 57044 | D835 DED4 | 55349 57043 | D835 DED3 | 55349 57076 | D835 DEF4 | 55349 57102 | D835 DF0E |
| Numeric character reference | ∑ | ∑ | 𝚺 | 𝚺 | 𝛔 | 𝛔 | 𝛓 | 𝛓 | 𝛴 | 𝛴 | 𝜎 | 𝜎 |
| Named character reference | ∑, ∑ | |||||||||||
| Preview | 𝜍 | 𝜮 | 𝝈 | 𝝇 | 𝝨 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | MATHEMATICAL ITALIC SMALL FINAL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL BOLD ITALIC CAPITAL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL BOLD ITALIC SMALL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL BOLD ITALIC SMALL FINAL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD CAPITAL SIGMA | |||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 120589 | U+1D70D | 120622 | U+1D72E | 120648 | U+1D748 | 120647 | U+1D747 | 120680 | U+1D768 |
| UTF-8 | 240 157 156 141 | F0 9D 9C 8D | 240 157 156 174 | F0 9D 9C AE | 240 157 157 136 | F0 9D 9D 88 | 240 157 157 135 | F0 9D 9D 87 | 240 157 157 168 | F0 9D 9D A8 |
| UTF-16 | 55349 57101 | D835 DF0D | 55349 57134 | D835 DF2E | 55349 57160 | D835 DF48 | 55349 57159 | D835 DF47 | 55349 57192 | D835 DF68 |
| Numeric character reference | 𝜍 | 𝜍 | 𝜮 | 𝜮 | 𝝈 | 𝝈 | 𝝇 | 𝝇 | 𝝨 | 𝝨 |
| Preview | 𝞂 | 𝞁 | 𝞢 | 𝞼 | 𝞻 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD SMALL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD SMALL FINAL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD ITALIC CAPITAL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD ITALIC SMALL SIGMA | MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD ITALIC SMALL FINAL SIGMA | |||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 120706 | U+1D782 | 120705 | U+1D781 | 120738 | U+1D7A2 | 120764 | U+1D7BC | 120763 | U+1D7BB |
| UTF-8 | 240 157 158 130 | F0 9D 9E 82 | 240 157 158 129 | F0 9D 9E 81 | 240 157 158 162 | F0 9D 9E A2 | 240 157 158 188 | F0 9D 9E BC | 240 157 158 187 | F0 9D 9E BB |
| UTF-16 | 55349 57218 | D835 DF82 | 55349 57217 | D835 DF81 | 55349 57250 | D835 DFA2 | 55349 57276 | D835 DFBC | 55349 57275 | D835 DFBB |
| Numeric character reference | 𝞂 | 𝞂 | 𝞁 | 𝞁 | 𝞢 | 𝞢 | 𝞼 | 𝞼 | 𝞻 | 𝞻 |
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to the letter sigma. |
| Look up Σ, σ, or ς in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Antisigma
- Greek letters used in mathematics, science, and engineering
- Sampi
- Sho (letter)
- {{sigma}} − Template to produce the 𝜎 character
- Stigma (letter)
- Sibilant consonant
- Summation (∑)
- Combining form "sigm-" (e.g. sigmodon, sigmurethra, etc.)
- Derivative "sigmoid" (e.g. sigmoid sinus, sigmoid colon, sigmoidoscopy, etc.)
References
Notes
- "the same letter, which the Dorians call "san", but the Ionians 'sigma'…" [translated from Ancient Greek: "τὠυτὸ γράμμα, τὸ Δωριέες μὲν σὰν καλέουσι ,Ἴωνες δὲ σίγμα"] (Herodotus 1.139)
Citations
- "sigma". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- Woodard, Roger D. (2006). "Alphabet". In Wilson, Nigel Guy (ed.). Encyclopedia of Ancient Greece. London: Routledge. p. 38.
- Herodotus, Histories 1.139 — Everson, Michael and Nicholas Sims-Williams. 2002. "Non-Attic letters," transcribed by N. Nicholas. Archived from the original 2020-06-28.
- Jeffery, Lilian H. (1961). The Local Scripts of Archaic Greece. Oxford: Clarendon. pp. 25–7.
- Thompson, Edward M. (1912). Introduction to Greek and Latin Paleography. Oxford: Clarendon. p. 108, 144.
- Hopkins, Edward C. D. (2004). "Letterform Usage | Numismatica Font Projects" Parthia.
- Hill, A. V. (1935). "Units and Symbols". Nature. 136 (3432): 222. Bibcode:1935Natur.136..222H. doi:10.1038/136222a0. S2CID 4087300.
- Unicode Code Charts: Greek and Coptic (Range: 0370-03FF)
