Su Tseng-chang
Su Tseng-chang (Chinese: 蘇貞昌; born 28 July 1947) is a Taiwanese politician serving as premier of the Republic of China (Taiwan) since 2019, and previously from 2006 to 2007. He was the chairman of the Democratic Progressive Party in 2005 and from 2012 to 2014. Su served as Chief of Staff to President Chen Shui-bian in 2004.[2] He leads the second-largest faction in the DPP, after New Tide faction.
Su Tseng-chang | |
|---|---|
蘇貞昌 | |
 | |
| Premier of the Republic of China | |
| Assumed office 14 January 2019 | |
| President | Tsai Ing-wen |
| Vice Premier | Chen Chi-mai Shen Jong-chin |
| Preceded by | Lai Ching-te |
| In office 25 January 2006 – 21 May 2007 | |
| President | Chen Shui-bian |
| Vice Premier | Tsai Ing-wen |
| Preceded by | Frank Hsieh |
| Succeeded by | Chang Chun-hsiung |
| Chairman of the Democratic Progressive Party | |
| In office 30 May 2012[1] – 28 May 2014 | |
| Preceded by | Tsai Ing-wen |
| Succeeded by | Tsai Ing-wen |
| In office 15 February 2005 – 3 December 2005 | |
| Preceded by | Ker Chien-ming (acting) |
| Succeeded by | Annette Lu (acting) |
| Magistrate of Taipei County | |
| In office 20 December 1997 – 20 May 2004 | |
| Preceded by | You Ching |
| Succeeded by | Lin Hsi-yao (acting) Chou Hsi-wei |
| Magistrate of Pingtung County | |
| In office 20 December 1989 – 20 December 1993 | |
| Preceded by | Shih Meng-hsiung |
| Succeeded by | Wu Tse-yuan |
| Personal details | |
| Born | 28 July 1947 Pingtung County, Taiwan Province, Republic of China |
| Nationality | Republic of China |
| Political party | Democratic Progressive Party |
| Spouse(s) | Chan Hsiu-ling |
| Children | 3, including Su Chiao-hui |
| Alma mater | National Taiwan University (LL.B.) |
| Profession | Lawyer |
| Su Tseng-chang | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 蘇貞昌 | ||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 苏贞昌 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Su actively campaigned for the DPP presidential nomination in 2008, but finished second to Frank Hsieh. Su eventually teamed with Hsieh as the vice presidential nominee; the DPP lost to the Kuomintang ticket of Ma Ying-jeou and Vincent Siew. Su ran for Taipei City Mayor in November 2010, but lost to the incumbent Hau Lung-pin by a 12-point margin. Su campaigned for the 2012 presidential candidacy of the DPP in 2011, but lost to Tsai Ing-wen by a very narrow margin. Following the loss of Tsai to Ma Ying-jeou, Su was elected to succeed Tsai as DPP chairman in 2012.
Su, along with politicians Annette Lu, Frank Hsieh and Yu Shyi-kun, are collectively known as the "Big Four of the Democratic Progressive Party". Su is nicknamed the "Lightbulb" (電火球) by the Taiwanese media and DPP voters, a nickname he earned in the 1980s for his charismatic approach to campaigning during election season, in addition to being an affectionate reference to the balding Su.
Personal background
Su was born at Ministry of Health and Welfare Pingtung Hospital in Pingtung, in Taiwan Province on 28 July 1947. He studied at the National Taiwan University. During his college years, he was vice captain of the rugby team.[3] He was a practicing lawyer from 1973 to 1983 and became a defense lawyer in the Kaohsiung Incident trials.[4][5] In September 1986, Su and seventeen others founded the Democratic Progressive Party.[6][7]
He was previously the magistrate of Pingtung County (1989–1993) and magistrate of Taipei County (1997–2004).[6] His first election as the Taipei magistrate was aided by a split between the New Party and the Kuomintang. His subsequent reelection occurred by a wide margin despite the ability of the Pan-Blue Coalition to present a united candidate, Wang Chien-shien.[8][9] He was Secretary-General (Chief of Staff) to the Office of the President of the Republic of China under President Chen Shui-bian (2004–2005). After President Chen resigned as DPP chairman following the 2004 legislative elections, he was elected the 10th-term DPP chairman.[6] Following DPP losses in the 2005 municipal elections on December 3, Su announced that he would, pursuant to a pre-election promise, resign from the chairmanship.[10]
Su is married to Chan Hsiu-ling (詹秀齡) with whom he has three daughters, one of which is Su Chiao-hui.[11]
First premiership: 2006–2007
| The First Su Cabinet | ||
|---|---|---|
| Office | Name | Term |
| Premier | Su Tseng-chang | 2006–2007 |
| Vice Premier | Tsai Ing-wen | 2006–2007 |
| Minister of the Interior | Lee I-yang | 2006–2008 |
| Minister of Foreign Affairs | James C. F. Huang | 2006–2008 |
| Minister of National Defense | Lee Jye | 2006–2007 |
| Minister of Finance | Joseph Lyu | 2006–2006 |
| Ho Chih-chin | 2006–2008 | |
| Minister of Justice | Shih Mao-lin | 2005–2008 |
| Minister of Economic Affairs | Morgan Huang | 2006–2006 |
| Steve Chen | 2006–2008 | |
| Minister of Transportation and Communications | Kuo Yao-chi | 2006–2006 |
| Tsai Duei | 2006–2008 | |
| Minister of Education | Tu Cheng-sheng | 2006–2008 |
Su was announced as the new premier on January 19, 2006 and took his oath of office, along with his cabinet, on January 25, 2006. Soon after, Su promised to step down if the people's welfare (referring to crime and other civil problems) did not improve within six months.[12] Su faced calls for his resignation after the Rebar Chinese Bank run, but refused to leave his post at the time.[13][14]
Su was a contender for the DPP nomination in the 2008 presidential election.[15][16] He formally announced his candidacy on Feb. 25. In the DPP primary vote on May 6, 2007, Su received 46,994 votes, coming in second to former Premier Frank Hsieh. Conceding defeat in the primary, Su announced that he had withdrawn from the race.[17]
On May 12, 2007, Su submitted his letter of resignation to President Chen Shui-bian, ending his tenure on May 21.[18] With the resignation of Su and with ten months left in Chen's presidency, that would mean Chen's eight years as President will have seen at least six Premiers (with Chang Chun-Hsiung serving two separate tenures).[19] Su also stated that he previously submitted resignations numerous times over his sixteen-month tenure, but all were rejected by President Chen.[20]
2008 presidential campaign
Su ran for Vice President alongside Frank Hsieh, who was the DPP Nomination. Together, Su and Hsieh ran against Ma and Siew. On March 22, they lost in a landslide to Ma and Siew's 7,659,014 (58.45%) votes with their 5,444,949 (41.55%) votes.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | Percentage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| President | Vice president | ||||
| Ma Ying-Jeou | Vincent Siew | 7,659,014 | 58.45% | ||
| Democratic Progressive Party | Frank Hsieh | Su Tseng-chang | 5,444,949 | 41.55% | |
| Total | 13,103,963 | 100.00% | |||
2010 Taipei mayoral race
Although Su had been considered a strong candidate to helm the newly created New Taipei City, because he had previously served the area as Taipei County Magistrate, he instead ran for the mayoralty of Taipei City.[21][22] Su vowed that should he win, he would serve out the entire term (through 2014) effectively ending any talks of a presidential run in 2012.[23] Su eventually lost the race to the incumbent mayor Hau Lung-pin.
| 2010 Taipei City Mayoral Election Result | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | # | Candidate | Votes | Percentage | ||
| 1 | Wu Yen-cheng (吳炎成) | 1,832 | 0.13% | |||
| 2 | 797,865 | 55.65% | ||||
| 3 | Helen Hsiao (蕭淑華) | 2,238 | 0.16% | |||
| 4 | Francis Wu (吳武明) | 3,672 | 0.26% | |||
| Democratic Progressive Party | 5 | Su Tseng-chang | 628,129 | 43.81% | ||
| Total | 1,433,736 | 100.00% | ||||
| Voter turnout | 70.65% | |||||
2012 campaigns
Su declared his candidacy for the 2012 presidential candidacy, but lost a DPP party primary held in April 2011 to Tsai Ing-wen and Hsu Hsin-liang, by a margin of 1.35 percent.[24] He was subsequently elected DPP chairman in May 2012,[7] and was succeeded by Tsai in 2014, after dropping out of the chairmanship election in the wake of the Sunflower Student Movement.[25][26]
2018 New Taipei mayoral race
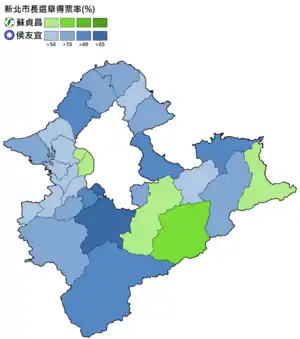
| 2018 New Taipei City mayoral results[27] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Candidate | Party | Votes | Percentage | |
| 1 | Su Tseng-chang | Democratic Progressive Party | 873,692 | 42.85% | |
| 2 | Hou You-yi | 1,165,130 | 57.15% | ||
| Total voters | 3,264,128 | ||||
| Valid votes | 2,038,822 | ||||
| Invalid votes | |||||
| Voter turnout | 62.46% | ||||
Second premiership: 2019–present
| The Second Su Cabinet | ||
|---|---|---|
| Office | Name | Term |
| Premier | Su Tseng-chang | 2019–present |
| Vice Premier | Chen Chi-mai | 2019–2020 |
| Shen Jong-chin | 2020–present | |
| Secretary-General | Li Meng-yen | 2019–present |
| Minister of the Interior | Hsu Kuo-yung | 2019–present |
| Minister of Foreign Affairs | Joseph Wu | 2019–present |
| Minister of National Defense | Yen Teh-fa | 2019–present |
| Minister of Finance | Su Jain-rong | 2019–present |
| Minister of Education | Pan Wen-chung | 2019–present |
| Minister of Justice | Tsai Ching-hsiang | 2019–present |
| Minister of Economic Affairs | Shen Jong-chin | 2019–2020 |
| Wang Mei-hua | 2020–present | |
| Minister of Transportation and Communications | Lin Chia-lung | 2019–present |
| Minister of Labor | Hsu Ming-chun | 2019–present |
| Minister of Health and Welfare | Chen Shih-chung | 2019–present |
| Minister of Culture | Cheng Li-chun | 2019–2020 |
| Lee Yung-te | 2020–present | |
| Minister of Science and Technology | Chen Liang-gee | 2019–2020 |
| Wu Tsung-tsong | 2020–present | |
Su was appointed to the premiership on January 14, 2019 by President Tsai Ing-wen.[28] He succeeded William Lai, who had resigned in response to the Democratic Progressive Party's poor performance in the 2018 Taiwanese local elections. Aged 71, when he returned to the premiership, Su became one of the oldest to hold the office. Soon after Su assumed office, approval ratings for Tsai's presidential administration rose.[29] Su and his second cabinet resigned en masse following the 2020 Taiwanese legislative election, as stipulated in the constitution, but Tsai, who won reelection to the presidency, asked him to remain in his post.[30]
See also
References
- (Taiwan), Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of China (31 May 2012). "Former Premier Su takes over as DPP leader - Taiwan Today".
- About Executive Yuan: Premier, Executive Yuan, Republic of China (Taiwan), Updated 2006-02-24
- "台大橄欖球隊友會蘇貞昌 聊趣事笑料橫生".
- Hwang, Jim (1 March 2008). "Finding Common Ground". Taiwan Today. Archived from the original on 9 May 2016. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- Lin, Irene (9 December 1999). "Kaohsiung Eight trial pointed way to Taiwan's future". Taipei Times. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- "Su Tseng-chang's political fortunes change rapidly". Taipei Times. Agence France Presse. 13 May 2007. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- Hsu, Jenny W. (27 May 2012). "Taiwan Ex-Premier Su Tseng-Chang Elected Head of Opposition Party". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- Copper, John Franklin (2005). Consolidating Taiwan's Democracy. University Press of America. p. 128. ISBN 9780761829775.
- Sheng, Virginia (2 February 2002). "The Voters Speak". Taiwan Today. Archived from the original on 2 February 2002. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- Grauwels, Stephan (3 December 2005). "Taiwan Opposition Wins Local Elections". Washington Post. Associated Press. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- Huang, Jewel (1 January 2005). "Su Tseng-chang enters race for DPP chairman". Taipei Times. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- Chang, S.C. / CNA, "PREMIER TO QUIT POLITICS IF SOCIAL ORDER NOT IMPROVED WITHIN 6 MONTHS" Archived 2007-09-29 at the Wayback Machine, Government Information Office, 2006-03-15
- Hille, Kathrin (14 January 2007). "Taiwan PM under pressure to quit". Financial Times. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- "FSC chief steps down over recent bank runs". China Post. 13 January 2007. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- CNA, WASHINGTON, "Adviser predicts a Su-Tsai DPP ticket for 2008", Taipei Times, 2006-02-06
- AFP, TAIPEI, "Su Tseng-chang excels at rebounding from defeat", Taipei Times, 2006-01-20
- "Frank Hsieh wins DPP presidential primary". China Post. 7 May 2007. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- "Taiwanese prime minister resigns". BBC News. 12 May 2007. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- "News".
- http://ettoday.com/2007/05/12/91-2095535.htm
- Chao, Vincent Y. (11 May 2010). "Su Tseng-chang rebuffs call to run in Sinbei City". Taipei Times. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- "Taiwan Ex-Premier Su Tseng-chang to run for Taipei City Mayor: Reports". Taiwan News. 2 March 2010. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- Chao, Vincent Y.; Mo, Yan-chih (26 November 2010). "Tsai downplays DPP official's comments". Taipei Times. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- Chao, Vincent Y. (28 April 2011). "Su concedes defeat in DPP primaries". Taipei Times. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- Wang, Chris (26 May 2014). "Tsai Ing-wen elected as DPP chair". Taipei Times. Retrieved 1 June 2014.
- Chang, Jung-hsiang; Hsu, Elizabeth (May 25, 2014). "Tsai Ing-wen wins DPP chair election (update)". Central News Agency. Retrieved June 2, 2014.
- https://www.cec.gov.tw/pc/en/TC/nm65000000000000000.html
- "Former premier Su to regain position". Taipei Times. 12 January 2019.
- Pan, Jason. (May 20, 2019). "Tsai’s approval rating rising, poll shows." Taipei Times. Retrieved May 30, 2019.
- Hsieh, Chun-ling (14 January 2020). "Su and Cabinet resign, but Su to stay on". Taipei Times. Retrieved 14 January 2020.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Su Tseng-chang. |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Su Tseng-chang |
- Su Tseng-chang on Facebook
- Premier biography timeline at the Government Information Office, Republic of China (Taiwan)
| Government offices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Shih Meng-hsiung |
Magistrate of Pingtung County 1989–1993 |
Succeeded by Wu Tse-yuan |
| Preceded by You Ching |
Magistrate of Taipei County 1997–2003 |
Succeeded by Lin Hsi-yao |
| Preceded by Frank Hsieh |
Premier of the Republic of China 2006–2007 |
Succeeded by Chang Chun-hsiung |
| Preceded by William Lai |
Premier of the Republic of China 2019–present |
Succeeded by incumbent |
| Party political offices | ||
| Preceded by Ker Chien-ming Acting |
Chairperson of the Democratic Progressive Party 2005 |
Succeeded by Annette Lu Acting |
| Preceded by Chen Chu Acting |
Chairperson of the Democratic Progressive Party 2012–2014 |
Succeeded by Tsai Ing-wen |
