Sulfonium
A sulfonium ion, also known as sulphonium ion or sulfanium ion, is a positively charged ion (a "cation") featuring three organic substituents attached to sulfur. These organosulfur compounds have the formula [SR3]+. Together with a negatively charged counterion, they give sulfonium salts. They are typically colorless solids that are soluble in organic solvent.
3S%252B_in_the_BPh4-_salt_(code_HEYZAM).png.webp)
Synthesis
Sulfonium compounds are usually synthesized by the reaction of thioethers with alkyl halides. For example, the reaction of dimethyl sulfide with iodomethane yields trimethylsulfonium iodide:
- CH
3–S–CH
3 + CH
3–I → (CH
3)
3S+
I−
The reaction proceeds by a nucleophilic substitution mechanism (SN2). Iodide is the leaving group departs. The rate of methylation is faster with more electrophilic methylating agents, such as methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate.
The compounds are pyramidal at sulfur. Thus, Me3S+ is isostructural and isoelectronic to trimethylphosphine. Sulfonium compounds wherein the three substituents differ are chiral and optically stable.[3] [Me(Et)SCH2CO2H]+ is the first chiral sulfonium cation to be resolved into enantiomers.[4]
Applications and occurrence
Biochemistry
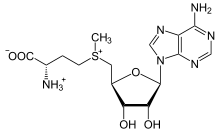
The sulfonium (more specifically methioninium) species S-adenosylmethionine occurs widely in nature, where it is used as a source of the adenosoyl radical. This radical participates in the biosynthesis of various compounds.[5][6]
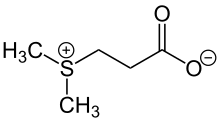
Another, sulfonium (methioninium) species found in nature is S-methylmethionine.
Organic synthesis
Sulfonium salts are precursor to sulfur ylides, which are useful in C-C forming reactions. In a typical application, a R2S+CH2R′ center is deprotonated to give the ylide R2S+CHR−.[7]
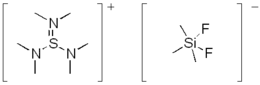
Tris(dimethylamino)sulfonium difluorotrimethylsilicate [((CH3)2N)3S]+[F2Si(CH3)3]− is a popular fluoridation agent.[8]
Some azo dyes are modified with sulfonium groups to give them a positive charge. The compound triphenylsulfonium triflate is a photoacid, a compound that under light converts to an acid.
See also
References
- Knop, Osvald; Cameron, T. Stanley; Bakshi, Pradip K.; Linden, Antony; Roe, Stephen P. (1994). "Crystal chemistry of tetraradial species. Part 5. Interaction Between Cation Lone Pairs and Phenyl Groups in Tetraphenylborates: Crystal Structures of Me3S+,Et3S+, Me3SO+, Ph2I+, and 1-Azoniapropellane Tetraphenylborates". Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 72 (8): 1870–1881. doi:10.1139/v94-238.
- DeBose, Jennifer L.; Sean C. Lema; Gabrielle A. Nevitt (2008-03-07). "Dimethylsulfoniopropionate as a foraging cue for reef fishes". Science. 319 (5868): 1356. doi:10.1126/science.1151109. PMID 18323445.
- March, J. “Advanced Organic Chemistry” 5th Ed. J. Wiley and Sons, 1992: New York. ISBN 0-471-60180-2
- Barbachyn, Michael R.; Johnson, Carl R. (1984). "Optical Activation and Utilization of Compounds Containing Chiral Sulfur Centers". Asymmetric Synthesis. pp. 227–261. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-507704-0.50007-6.
- Layer, G.; Heinz, D. W.; Jahn, D.; Schubert, W.-D. "Structure and function of radical SAM enzymes" Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 2004, volume 8, 468-476. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2004.08.001
- Perry A. Frey, Olafur Th. Magnusson "S-Adenosylmethionine: A Wolf in Sheep's Clothing, or a Rich Man's Adenosylcobalamin?" Chem. Rev., 2003, 103 (6), pp 2129–2148. doi:10.1021/cr020422m
- Mitchell J. Bogdanowicz, Barry M. Trost (1988). "Cyclopropylphenylsulfonium Tetrafluoroborate". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 6, p. 364
- W. J. Middleton (1990). "Tris(dimethylamino)sulfonium difluorotrimethylsilicate". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 7, p. 528
External links
- IUPAC definition (short pdf)