TMEM101
Transmembrane protein 101 (TMEM101) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMEM101 gene.[5] The TMEM101 protein has been demonstrated to activate the NF-κB signaling pathway.[6] High levels of expression of TMEM101 have been linked to breast cancer.[7]
| TMEM101 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | TMEM101, transmembrane protein 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1923797 HomoloGene: 12649 GeneCards: TMEM101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 17: 44.01 – 44.02 Mb | Chr 11: 102.15 – 102.16 Mb | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene
Aliases
Known aliases of TMEM101 include Putative NF-Kappa-B-Activating Protein 130, FLJ23987, and MGC4251.[8]
Location
TMEM101 is located on the minus strand of the long arm of human chromosome 17 at the locus 17q21.31.[5] The gene is 12,758 bp long, and it ranges from position 44,011,188 to position 44,023,946 on chromosome 17.[5] TMEM101 is located between the genes NAGS and LSM12.[5]
Transcript Variants
NCBI RefSeq contains five mRNA transcript variants for TMEM101.[5] Transcript variants 1, 2, and 3 have been found experimentally, while transcript variants X1 and X2 have been predicted computationally.[5] The last three exons of all five transcript variants are identical. The second exon is identical in transcript variants 2 and 3. The first exon of variant X1 and the second exon of variant X2 are nearly identical to the second exon of variants 2 and 3, but both contain an additional segment of bases at the 3’ end of this exon, and the first exon of variant X1 has 6 extra bases on the 5’ end. The first exon differs considerably in length between variants 2, X2, and 3.
| Name | Accession Number | Number of Exons | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transcript Variant 1 | NM_032376.4 | 4 | 1525 |
| Transcript Variant X1 | XM_024451006.1 | 4 | 1602 |
| Transcript Variant 2 | NM_001304813.2 | 5 | 1726 |
| Transcript Variant X2 | XM_011525353.2 | 5 | 4604 |
| Transcript Variant 3 | NM_001304814.2 | 5 | 1759 |
Protein

Isoforms
There are two known isoforms of the TMEM101 protein. Isoform a is encoded by transcript variant 1, while isoform b is encoded by transcript variants 2 and 3.[5] Transcript variants X1 and X2 are also predicted to encode isoform b. Isoform b lacks the first 58 amino acids following the N-terminus of isoform a, but the remaining 199 amino acids are identical to isoform a.
| Name | Accession Number | Size (aa) | Predicted molecular weight (kDa)[9] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isoform a | NP_115752.1 | 257 | 29 |
| Isoform b | NP_001291742.1 | 199 | 22 |
Protein Characteristics

Isoform a of the TMEM101 protein has a predicted molecular weight of about 29 kDa and a theoretical isoelectric point of about 9.6.[9] In terms of amino acid composition, TMEM101 is relatively rich in the hydrophobic amino acids leucine and tyrosine, and relatively poor in the hydrophilic amino acids asparagine and threonine.[10] It is also relatively poor in the sum of the two negatively charged amino acids, aspartic acid and glutamic acid.[10]
Transmembrane Domains
Isoform a of the TMEM101 protein contains 8 transmembrane domains.[11]
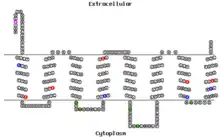
| Transmembrane Domain | Amino Acids |
|---|---|
| 1 | 21-40 |
| 2 | 52-72 |
| 3 | 77-97 |
| 4 | 110-130 |
| 5 | 139-159 |
| 6 | 182-202 |
| 7 | 206-226 |
| 8 | 233-257 |
Secondary Structure
.png.webp)
The Ali2D, I-TASSER, and Phyre2 models all predict that the secondary structure of TMEM101 is predominately composed of alpha helices.[12][13][14] The Phyre2 prediction is presented in the figure to the right.
Tertiary Structure
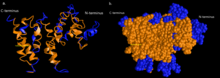
The I-TASSER highest confidence model for the predicted tertiary structure for the TMEM101 protein resembles the structure of a polytopic transmembrane alpha-helical protein.[13]
Acetylation
The lysine at position 4 in the TMEM101 protein is predicted to be acetylated by the EP300 acetyltransferase enzyme.[15]
Phosphorylation
There are five predicted phosphorylation sites located outside of transmembrane domains on the cytoplasmic side of the TMEM101 protein, which are listed in the table below.[16]
| Position | Amino Acid |
|---|---|
| 98 | Tyrosine |
| 101 | Tyrosine |
| 162 | Serine |
| 169 | Tyrosine |
| 228 | Threonine |
Subcellular Localization
Immunofluorescent staining experiments have detected the TMEM101 protein in the plasma membrane and the nucleoplasm.[17]
Regulation and Expression
Promoters
The Genomatix Gene2Promoter tool lists 7 promoter regions for the Homo sapiens TMEM101 gene.[18] The promoter that is supported by the greatest number of mRNA transcripts is 1525 bp long and spans the base pairs 44014913–44016437 on the negative strand of human chromosome 17. This promoter overlaps the start of transcription of mRNA transcript variant 1.
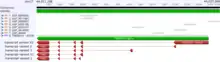
| Number | Promoter ID | Start position | End position | Length (bp) | Number of supporting transcripts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GXP_8985856 | 44014913 | 44016437 | 1525 | 5 |
| 2 | GXP_9511469 | 44015003 | 44016042 | 1040 | 1 |
| 3 | GXP_8985857 | 44026007 | 44027046 | 1040 | 1 |
| 4 | GXP_6035198 | 44023907 | 44024946 | 1040 | 1 |
| 5 | GXP_6035197 | 44019403 | 44020447 | 1045 | 3 |
| 6 | GXP_4414506 | 44023067 | 44024152 | 1085 | 4 |
| 7 | GXP_44546 | 44021160 | 44022199 | 1040 | 1 |
Transcription Factors
The following table presents a selected list of transcription factors that are predicted by the Genomatix MatInspector tool to bind to the GXP_8985856 promoter.[19]

| Transcription Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| TFIIB | Transcription factor II B |
| FOXP1 | Forkhead box protein P1 |
| ZNF384 | Zinc finger protein 384 |
| ZNF300 | KRAB-containing zinc finger protein 300 |
| MZF1 | Myeloid zinc finger protein MZF1 |
| SIX4 | Sine oculis homeobox homolog 4 |
| ETV4 | ETS translocation variant 4 |
| ELK1 | Elk-1 |
| HIC1 | Hypermethylated in cancer 1 |
| ZNF217 | Zinc finger protein 217 |
| LHX6 | LIM homeobox 6 |
Expression

Tissue Specificity
According to RNA-Seq data, TMEM101 is expressed in a wide range of tissues with low tissue specificity.[20] Relatively, it is expressed most highly in breast tissue, the seminal vesicles, the kidneys, and endometrial tissue.[20]
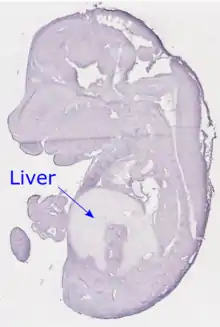
Embryonic Development
A cross section of a mouse embryo that has been stained for TMEM101 mRNA using in situ hybridization techniques shows noticeably lower levels of TMEM101 transcript in the liver than in other tissues.[21]
Differential Expression
TMEM101 has been observed to be expressed at lower levels in ovarian endometriotic cells than in uterine endometrial cells within the same individuals.[22][23]
TMEM101 has also been observed to be expressed at higher levels in estrogen receptor positive ovarian cancer tumors than in estrogen receptor negative ovarian cancer tumors in mouse xenograft models.[24][25]


Interacting Proteins
The IntAct database indicates that the following proteins that have been found to interact with the TMEM101 protein through two-hybrid screening experiments.[26]
| Protein | Description |
|---|---|
| BNIP3 | BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDA protein-interacting protein 3 |
| C4orf3 | Uncharacterized protein C4orf3 |
| GIMAP1 | GTPase IMAP family member 1 |
| NDUFA3 | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 3 |
| NINJ2 | Ninjurin-2 |
| PDZK1IP1 | PDZK1-interacting protein 1 |
| PKMYT1 | Membrane-associated tyrosine- and threonine-specific cdc2-inhibitory kinase |
| STRIT1 | Sarcoplamsic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase regulator DWORF |
| STX10 | Syntaxin-10 |
| SYNJ2BP | Synaptojanin-2-binding protein |
| TMEM65 | Transmembrane protein 65 |
| TMEM243 | Transmembrane protein 243 |
| VAMP1 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 1 |
| VAMP2 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 |
| VAPB | Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B/C |
Homology and Evolution
Orthologs and paralogs
TMEM101 has orthologs in Mammalia, Sauropsida, Amphibia, Osteichthyes, Chondrichthyes, Mollusca, Annelida, Echinodermata, Cnidaria, and Placozoa, among others. A table of selected orthologs is listed below. There are no known paralogs of TMEM101.
| Genus and Species | Common Name | Taxonomic Group | Estimated Date of Divergence (MYA) | Accession Number | Sequence Length (aa) | Sequence Identity | Sequence Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phascolarctos cinereus | Koala | Marsupialia | 159 | XP_020853077.1 | 257 | 89% | 95% |
| Gallus gallus | Chicken | Aves | 312 | XP_003643860.1 | 257 | 80% | 89% |
| Notechis scutatus | Tiger snake | Squamata | 312 | XP_026525463.1 | 257 | 79% | 91% |
| Xenopus Tropicalis | Tropical clawed frog | Anura | 351.8 | NP_988884.1 | 255 | 76% | 88% |
| Danio rerio | Zebrafish | Actinopterygii | 435 | NP_001314814.1 | 255 | 72% | 86% |
| Acanthaster planci | Crown-of-thorns starfish | Echinodermata | 684 | XP_022105916.1 | 252 | 34% | 51% |
| Crassotrea gigas | Pacific oyster | Mollusca | 797 | XP_011422883.2 | 251 | 30% | 51% |
| Pocillopora damicornis | Lace coral | Cnidaria | 824 | XP_027044925.1 | 264 | 32% | 52% |
| Trichoplax adhaerens | Trichoplax | Placozoa | 948 | XP_002108737.1 | 260 | 28% | 51% |
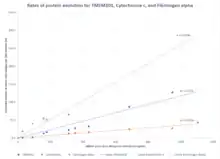
Evolutionary History
The most distantly related species to humans that possesses an ortholog of TMEM101 is Trichoplax adhaerens. Given that Ctenophorans do not possess orthologs of TMEM101, it appears that TMEM101 originated in the basal ParaHoxozoa clade after its divergence from Ctenophora approximately 948 million years ago. Based on a molecular clock analysis, the protein sequence of TMEM101 has on average evolved faster than Cytochrome c but slower than Fibrinogen alpha.
Function
Activation of NF-κB Signaling Pathway
TMEM101 cDNA transcripts have been demonstrated to activate the transcription of NF-κB controlled genes in human embryonic kidney cells.[6]
Clinical Significance
TMEM101 has been noted as a biomarker of breast cancer. High expression of TMEM101 is associated with the Luminal molecular subtype of breast cancer.[7] Additionally, high levels of TMEM101 are associated with an increased risk score for the diagnosis of early stage triple-negative breast cancer.[27]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000091947 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020921 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "TMEM101 transmembrane protein 101 [ Homo sapiens (human) ]". NCBI. Retrieved 22 October 2020.
- Matsuda, A; Suzuki, Y; Honda, G; Muramatsu, S; Matsuzaki, O; Nagano, Y; Doi, T; Shimotohno, K; Harada, T; Nishida, E; Hayashi, H; Sugano, S (22 May 2003). "Large-scale identification and characterization of human genes that activate NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways". Oncogene. 22. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206406. Retrieved 22 October 2020.
- Krijgsman, O; Roepman, P; Zwart, W; Carroll, J; Tian, S; Snoo, F; Bender, R; Bernards, R; Glas, A (4 August 2011). "A diagnostic gene profile for molecular subtyping of breast cancer associated with treatment response". Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 133. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1683-z. Retrieved 22 October 2020.
- "TMEM101 Gene (Protein Coding)". GeneCards. Retrieved 22 October 2020.
- "Compute pI/Mw tool". Expasy. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "SAPS". EMBL-EBI. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "transmembrane protein 101 isoform a [Homo sapiens]". NCBI Protein. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "Ali2D". MPI Bioinformatics Toolkit. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "I-TASSER". Zhang Lab. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "Phyre2". Structural Bioinformatics Group. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "GPS-PAIL". The Cuckoo Workgroup. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- "GPS". The Cuckoo Workgroup. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- "Cell atlas - TMEM101". The Human Protein Atlas. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "Gene2Promoter". Genomatix Software Suite. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- "MatInspector". Genomatix Software Suite. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- "Tissue Expression of TMEM101". The Human Protein Atlas. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- "EB1154 - TMEM101". Genepaint. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- "TMEM101 - Ovarian endometriosis". NCBI GEO. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- Hever, Aniko; Roth, Richard B.; Hevezi, Peter; Marin, Maria E.; Acosta, Jose A.; Acosta, Hector; Rojas, Jose; Herrera, Rosa; Grigoriadis, Dimitri; White, Evan; Conlon, Paul J.; Maki, Richard A.; Zlotnik, Albert (24 July 2007). "Human endometriosis is associated with plasma cells and overexpression of B lymphocyte stimulator". PNAS. 104 (30): 12451–12456. doi:10.1073/pnas.0703451104. PMID 17640886. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- "Ovarian cancer intraperitoneal xenograft model". NCBI GEO. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- Spillman, Monique A.; Manning, Nicole G.; Dye, Wendy W.; Sartorius, Carol A.; Post, Miriam D.; Harrell, Joshua Chuck; Jacobsen, Britta M.; Horwitz, Kathryn B. (November 2010). "Tissue-Specific Pathways for Estrogen Regulation of Ovarian Cancer Growth and Metastasis". Cancer Research. 70 (21). doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1238. PMID 20959477. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- "IntAct Molecular Interaction Database". EMBL-EBI. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- Ren, Y., Jiang, Y., Zuo, W., Xu, X., Jin, X., Ma, D., & Shao, Z. (2019). Abstract P2-08-33: A novel seven-gene signature predicts prognosis in early-stage triple-negative breast cancer. Abstracts: 2018 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium; December 4–8, 2018; San Antonio, Texas, 79(4). https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445.sabcs18-p2-08-33