ETV4
ETS translocation variant 4 (ETV4), also known as polyoma enhancer activator 3 (PEA3), is a member of the PEA3 subfamily of Ets transcription factors.[5][6][7]
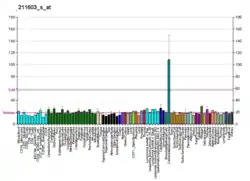
Disease marker
Two variants of a disease associated with ETV4 is Ewing Sarcoma and Extraosseous Ewing's Sarcoma. While both are cancerous tumors, the former grows in the bones most commonly affecting the arms, legs, hips, and spine, while the later affects the soft tissue in the chest, foot, pelvis and spine.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000175832 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000017724 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Isobe M, Yamagishi F, Yoshida K, Higashino F, Fujinaga K (Jul 1995). "Assignment of the ets-related transcription factor E1A-F gene (ETV4) to human chromosome region 17q21". Genomics. 28 (2): 357–9. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1158. PMID 8530053.
- "Entrez Gene: ETV4 Ets variant gene 4 (E1A enhancer binding protein, E1AF)".
- "ETV4 Gene - GeneCards | ETV4 Protein | ETV4 Antibody". www.genecards.org. Retrieved 2019-10-20.
Further reading
- Friedman LS, Ostermeyer EA, Lynch ED, Welcsh P, Szabo CI, Meza JE, Anderson LA, Dowd P, Lee MK, Rowell SE (Jan 1995). "22 genes from chromosome 17q21: cloning, sequencing, and characterization of mutations in breast cancer families and tumors". Genomics. 25 (1): 256–63. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(95)80133-7. PMID 7774926.
- Liu SH, Peng BH, Ma JT, Liu YC, Ng SY (1995). "Serum response element associated transcription factors in mouse embryos: serum response factor, YY1, and PEA3 factor". Developmental Genetics. 16 (3): 229–40. doi:10.1002/dvg.1020160303. PMID 7796532.
- Friedman LS, Ostermeyer EA, Lynch ED, Szabo CI, Anderson LA, Dowd P, Lee MK, Rowell SE, Boyd J, King MC (Dec 1994). "The search for BRCA1". Cancer Research. 54 (24): 6374–82. PMID 7987831.
- Higashino F, Yoshida K, Fujinaga Y, Kamio K, Fujinaga K (Feb 1993). "Isolation of a cDNA encoding the adenovirus E1A enhancer binding protein: a new human member of the ets oncogene family". Nucleic Acids Research. 21 (3): 547–53. doi:10.1093/nar/21.3.547. PMC 309151. PMID 8441666.
- Urano F, Umezawa A, Hong W, Kikuchi H, Hata J (Feb 1996). "A novel chimera gene between EWS and E1A-F, encoding the adenovirus E1A enhancer-binding protein, in extraosseous Ewing's sarcoma". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 219 (2): 608–12. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1996.0281. PMID 8605035.
- Coutte L, Monté D, Baert J, de Launoit Y (Nov 1999). "Genomic organization of the human e1af gene,a member of Ets transcription factors". Gene. 240 (1): 201–7. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00400-X. PMID 10564827.
- Mastrangelo T, Modena P, Tornielli S, Bullrich F, Testi MA, Mezzelani A, Radice P, Azzarelli A, Pilotti S, Croce CM, Pierotti MA, Sozzi G (Aug 2000). "A novel zinc finger gene is fused to EWS in small round cell tumor". Oncogene. 19 (33): 3799–804. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203762. PMID 10949935.
- Davidson B, Goldberg I, Gotlieb WH, Kopolovic J, Ben-Baruch G, Reich R (Apr 2003). "PEA3 is the second Ets family transcription factor involved in tumor progression in ovarian carcinoma". Clinical Cancer Research. 9 (4): 1412–9. PMID 12684413.
- Span PN, Manders P, Heuvel JJ, Beex LV, Sweep CG (May 2003). "E1AF expression levels are not associated with prognosis in human breast cancer". Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 79 (1): 129–31. doi:10.1023/A:1023338424677. PMID 12779089. S2CID 6629346.
- Anderson NL, Polanski M, Pieper R, Gatlin T, Tirumalai RS, Conrads TP, Veenstra TD, Adkins JN, Pounds JG, Fagan R, Lobley A (Apr 2004). "The human plasma proteome: a nonredundant list developed by combination of four separate sources". Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 3 (4): 311–26. doi:10.1074/mcp.M300127-MCP200. PMID 14718574.
- Liu Y, Borchert GL, Phang JM (Apr 2004). "Polyoma enhancer activator 3, an ets transcription factor, mediates the induction of cyclooxygenase-2 by nitric oxide in colorectal cancer cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (18): 18694–700. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308136200. PMID 14976201.
- Suzuki Y, Yamashita R, Shirota M, Sakakibara Y, Chiba J, Mizushima-Sugano J, Nakai K, Sugano S (Sep 2004). "Sequence comparison of human and mouse genes reveals a homologous block structure in the promoter regions". Genome Research. 14 (9): 1711–8. doi:10.1101/gr.2435604. PMC 515316. PMID 15342556.
- Davidson B, Goldberg I, Tell L, Vigdorchik S, Baekelandt M, Berner A, Kristensen GB, Reich R, Kopolovic J (2004). "The clinical role of the PEA3 transcription factor in ovarian and breast carcinoma in effusions". Clinical & Experimental Metastasis. 21 (3): 191–9. doi:10.1023/B:CLIN.0000037703.37275.35. PMID 15387369. S2CID 22579184.
- Fauquette V, Perrais M, Cerulis S, Jonckheere N, Ducourouble MP, Aubert JP, Pigny P, Van Seuningen I (Feb 2005). "The antagonistic regulation of human MUC4 and ErbB-2 genes by the Ets protein PEA3 in pancreatic cancer cells: implications for the proliferation/differentiation balance in the cells". The Biochemical Journal. 386 (Pt 1): 35–45. doi:10.1042/BJ20040706. PMC 1134764. PMID 15461591.
- Zhu X, Jiang J, Shen H, Wang H, Zong H, Li Z, Yang Y, Niu Z, Liu W, Chen X, Hu Y, Gu J (Apr 2005). "Elevated beta1,4-galactosyltransferase I in highly metastatic human lung cancer cells. Identification of E1AF as important transcription activator". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 280 (13): 12503–16. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413631200. PMID 15611127.
- Takahashi A, Higashino F, Aoyagi M, Yoshida K, Itoh M, Kobayashi M, Totsuka Y, Kohgo T, Shindoh M (Feb 2005). "E1AF degradation by a ubiquitin-proteasome pathway". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 327 (2): 575–80. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.12.045. PMID 15629152.
- Nosho K, Yoshida M, Yamamoto H, Taniguchi H, Adachi Y, Mikami M, Hinoda Y, Imai K (May 2005). "Association of Ets-related transcriptional factor E1AF expression with overexpression of matrix metalloproteinases, COX-2 and iNOS in the early stage of colorectal carcinogenesis". Carcinogenesis. 26 (5): 892–9. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.567.1603. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgi029. PMID 15695237.
External links
- ETV4+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P43268 (ETS translocation variant 4) at the PDBe-KB.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.