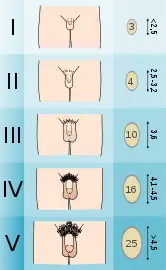
Tanner scale
The Tanner scale (also known as the Tanner stages or Sexual Maturity Rating (SMR)) is a scale of physical development in children, adolescents and adults. The scale defines physical measurements of development based on external primary and secondary sex characteristics, such as the size of the breasts, genitals, testicular volume and development of pubic hair. This scale was first identified in 1969 by James Tanner, a British pediatrician, after a two-decade-long study following the physical changes in girls undergoing puberty.[1][2][3][4]
| Tanner scale | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Tanner stages |
| Purpose | defines physical measurements of development |
Due to natural variation, individuals pass through the Tanner stages at different rates, depending in particular on the timing of puberty. In HIV treatment, the Tanner scale is used to determine which regimen to follow for pediatric or adolescent patients on antiretroviral therapy (adult, adolescent, or pediatric guidelines).[5] The Tanner scale has also been used in forensics to determine aging, but its usage has decreased due to lack of reliability.[6]
Definitions of stages
Adapted from Adolescent Health Care: a practical guide by Lawrence Neinstein, M.D.[7]
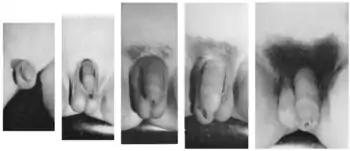
Genitals (male)
- Tanner I
- testicular volume less than 1.5 ml; small penis (prepubertal; typically age nine and younger)
- Tanner II
- testicular volume between 1.6 and 6 ml; skin on scrotum thins, reddens and enlarges; penis length unchanged (9–11)
- Tanner III
- testicular volume between 6 and 12 ml; scrotum enlarges further; penis begins to lengthen (11–12.5)
- Tanner IV
- testicular volume between 12 and 20 ml; scrotum enlarges further and darkens; penis increases in length (12.5–14)
- Tanner V
- testicular volume greater than 20 ml; adult scrotum and penis (14+)
Breasts (female)
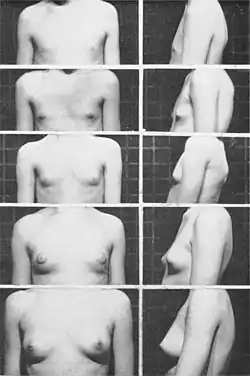

- Tanner I
- no glandular tissue: areola follows the skin contours of the chest (prepubertal) (typically age 10 and younger)
- Tanner II
- breast bud forms, with small area of surrounding glandular tissue; areola begins to widen (10–11.5)
- Tanner III
- breast begins to become more elevated, and extends beyond the borders of the areola, which continues to widen but remains in contour with surrounding breast (11.5–13)
- Tanner IV
- increased breast sizing and elevation; areola and papilla form a secondary mound projecting from the contour of the surrounding breast (13–15)
- Tanner V
- breast reaches final adult size; areola returns to contour of the surrounding breast, with a projecting central papilla. (15+)
Pubic hair (both male and female)
- Tanner I
- no pubic hair at all (prepubertal) (typically age 10 and younger)
- Tanner II
- small amount of long, downy hair with slight pigmentation at the base of the penis and scrotum (males) or on the labia majora (females) (10–11.5)
- Tanner III
- hair becomes more coarse and curly, and begins to extend laterally (11.5–13)
- Tanner IV
- adult-like hair quality, extending across pubis but sparing medial thighs (13–15)
- Tanner V
- hair extends to medial surface of the thighs (15+)
- Height Growth Conclusion
Sometime during Tanner 5, females stop growing and reach their adult height, usually this happens in their mid teens at 15 or 16 years for females. Males also stop growing and reach their adult height sometime during Tanner 5, usually this happens in their late teens at 18-19 years for males.[8][9][10]
Criticism
The scale has been criticized by the pornography industry for its potential to lead to false child pornography convictions, such as in the case when United States federal authorities used it to assert that pornographic actress Lupe Fuentes was underage. Fuentes personally appeared at the trial and provided documentation that showed that the DVDs in question were legally produced.[11][12]
Tanner, the author of the classification system, has argued that age classification using the stages of the scale misrepresents the intended use. Tanner stages do not match with chronological age, but rather maturity stages and thus are not diagnostic for age estimation.[13]
References
- Tanner's stages at Who Named It?
- Marshall WA, Tanner JM (February 1970). "Variations in the pattern of pubertal changes in boys". Arch. Dis. Child. 45 (239): 13–23. doi:10.1136/adc.45.239.13. PMC 2020414. PMID 5440182.
- Marshall WA, Tanner JM (June 1969). "Variations in pattern of pubertal changes in girls". Arch. Dis. Child. 44 (235): 291–303. doi:10.1136/adc.44.235.291. PMC 2020314. PMID 5785179.
- Emmanuel, Mickey; Bokor, Brooke R. (2019), "Tanner Stages", StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing, PMID 29262142, retrieved 2019-08-01
- "Adolescents and Young Adults with HIV Considerations for Antiretroviral Use in Special Patient Populations Adult and Adolescent ARV". AIDSinfo. Retrieved 2019-08-01.
- Encyclopedia of forensic and legal medicine. Payne-James, Jason,, Byard, Roger W. (Second ed.). Amsterdam, Netherlands. 2015-09-29. ISBN 9780128000557. OCLC 924663619.CS1 maint: others (link)
- Adolescent health care : a practical guide. Neinstein, Lawrence S., Neinstein, Lawrence S. (5th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2008. ISBN 9780781792561. OCLC 148727849.CS1 maint: others (link)
- Jarret, Robert R. "Puberty: Tanner Stages – Girls". Pediatric HOUSECALLS. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- Jarret, Robert R. "Puberty: Tanner Stages – Boys". Pediatric HOUSECALLS. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- Goldman, Rena. "The Stages of Puberty: Development in Girls and Boys". Healthline. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- "Lupe Fuentes Saves Man From Bogus 'Child Porn' Charge". AVN. April 16, 2010.
- "Adult Film Star Verifies Her Age, Saves Fan From 20 Years In Prison". Radar Online. April 21, 2010.
- Rosenbloom, AL; Tanner, JM (December 1998). "Misuse of Tanner puberty stages to estimate chronologic age". Pediatrics. 102 (6): 1494. doi:10.1542/peds.102.6.1494. PMID 9882230.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tanner scale. |