Trimethylsulfonium
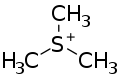
Trimethylsulfonium (systematically named trimethylsulfanium and trimethylsulfur(1+)) is an organic cation with the chemical formula (CH3)3S+ (also written as C
3H
9S+
).
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Trimesium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H9S+ | |
| Molar mass | 77.17 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Compounds
3S%252B_in_the_BPh4-_salt_(code_HEYZAM).png.webp)
Several salts of trimethylsulfonium are known. X-ray crystallography reveals that the sulfur is pyramidal, with C-S-C angles near 102° and C-S bond distance of 177 picometers. Unless the anion is colored, all trimethylsulfonium salts are white or colorless.
| Salt | Formula | Molecular weight (g/mol) | Properties[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trimethylsulfonium chloride | [(CH3)3S]Cl | 112.5 | Colorless crystals, decompose at 100 °C, very soluble in ethanol, very hygroscopic.[3] |
| Trimethylsulfonium bromide | [(CH3)3S]Br | 157 | Colorless crystals from H2O. Decomposes at 172 °C, melts in a sealed tube at 201-201 °C, reacts in neutral aqueous solution.[4] |
| Trimethylsulfonium iodide | [(CH3)3S]I | 204 | Colorless crystals from ethanol, decomposes at 203-207 °C.[4][5] crystal structure monoclinic a=5.94 b=8.00 c=8.92 μm β=126°32′ 2 formulas per unit cell density=1.958[6] |
| Trimethylsulfonium tetrafluoroborate | [(CH3)3S]BF4 | 163.97 | mp 205-210°[7] |
| Trimethylsulfonium methylsulfate | [(CH3)3S]CH3OSO3 | 188.27 | mp 92-94°[8] Crystal structure orthorhombic a=12.6157 b=8.2419 μm c=7.540 cell volume 784.0 2 formulas per unit cell |
Preparation
Sulfonium compounds can be synthesised by treating a suitable alkyl halide with a thioether. For example, the reaction of dimethyl sulfide with iodomethane yields trimethylsulfonium iodide:
- CH3–S–CH3 + CH3–I → (CH3)3SI
Related
An extra oxygen atom can bond to the sulfur atom to yield the trimethylsulfoxonium ion.
Use
Glyphosate herbicide is often supplied as a trimethylsulfonium salt. When mixed with aluminium bromide, or aluminium chloride or even hydrogen bromide, trimethylsulfonium bromide forms an ionic liquid, which melts at temperatures below standard conditions.[9]
References
- Knop, Osvald; Cameron, T. Stanley; Bakshi, Pradip K.; Linden, Antony; Roe, Stephen P. (1994). "Crystal chemistry of tetraradial species. Part 5. Interaction Between Cation Lone Pairs and Phenyl Groups in Tetraphenylborates: Crystal Structures of Me3S+,Et3S+, Me3SO+, Ph2I+, and 1-Azoniapropellane Tetraphenylborates". Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 72 (8): 1870–1881. doi:10.1139/v94-238.
- Heilbron's Dictionary of Organic Compounds, volume 4, revised edition published in 1953. Published in Great Britain
- Blättler, H. (1919). "Über Trimethylsulfoniumverbindungen". Monatshefte für Chemie und verwandte Teile anderer Wissenschaften. 40 (8): 417–429. doi:10.1007/BF01559085. S2CID 197766904.
- Steinkopf, W.; Müller, S. (1923). "Über die Einwirkung von Jodmethyl auf Disulfide". Chem. Ber. 56 (8): 1926–1930. doi:10.1002/cber.19230560834.
- Mussgnug, F. (1941). "Trimethylammoniumjodid und Trimethylsulfoniumjodid". Naturwissenschaften. 29 (17): 256. Bibcode:1941NW.....29..256M. doi:10.1007/BF01479158. S2CID 33842580.
- Zuccaro, D. Ε.; McCullough, J. D. (1 January 1959). "The crystal structure of trimethylsulfonium iodide". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials. 112 (1–6). doi:10.1524/zkri.1959.112.jg.401. S2CID 98338161.
- "Trimethylsulfonium tetrafluoroborate". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved 23 September 2016.
- "Trimethylsulfonium methyl sulfate". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved 23 September 2016.
- Ma, M.; Johnson, K.E. (April 1995). "Some physicochemical characteristics of molten salts derived from trimethylsulfonium bromide". Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 73 (4): 593–598. doi:10.1139/v95-076.