Tympanic plexus
In the tympanic cavity, the tympanic nerve (a branch of CN IX) divides into branches which, along with sympathetic fibres from the carotid plexus, form the tympanic plexus. This plexus is located on the surface of the promontory.
| Tympanic plexus | |
|---|---|
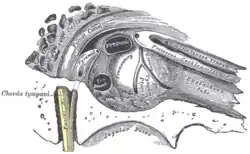 View of the inner wall of the tympanum. (Grooves for tympanic plexus labeled at center.) | |
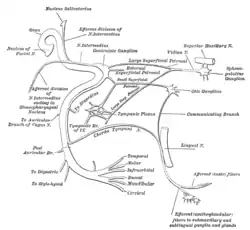 Plan of the facial and intermediate nerves and their communication with other nerves. (Tympanic plexus labeled at center.) | |
| Details | |
| From | caroticotympanic nerves, tympanic nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plexus tympanicus |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.140 |
| TA2 | 6324 |
| FMA | 77533 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
This tympanic plexus branches into:
- the lesser petrosal nerve (preganglionic parasympathetic axons to otic ganglion)
- sensory branches to the tympanic cavity
The branches to the tympanic cavity provide sensory innervation to the mucosa of the tympanic cavity and the internal surface of the tympanic membrane. The cell bodies of these neurons are found in the superior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 909 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (IX)
- lesson3 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
