Typhoon Ida (1945)
Typhoon Ida, known in the Japan as Makurazaki Typhoon (枕崎台風),[1][2] was a weak, but fatal and deadly typhoon which hit Japan in 1945, causing over 2000 deaths.
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Formed | September 10, 1945 |
|---|---|
| Dissipated | September 20, 1945 |
| Highest winds | 1-minute sustained: 130 km/h (80 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 917 hPa (mbar); 27.08 inHg |
| Fatalities | 2,473 death, 1,283 missing |
| Areas affected | Japan |
| Part of the 1945 Pacific typhoon season | |
Overview
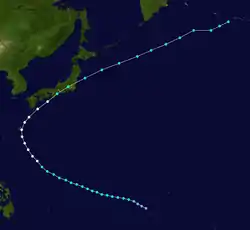
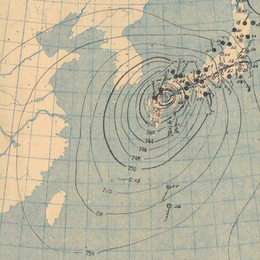
Ida made landfall near Makurazaki in Kagoshima Prefecture on September 17.[1] Ida was the strongest typhoon to hit Kyushu on record, with a minimum sea-level pressure of 916.1 hPa (27.05 inHg) and a maximum wind gust of 62.7 metres per second (140 mph), which was recorded at a weather station in Makurazaki.[3] This reading makes the storm responsible for the second lowest pressure ever recorded in Japan, after the 1934 Muroto typhoon.[2][1][4]
More than 2,000 people were killed in the Hiroshima Prefecture after heavy rains brought by a weakening Ida caused severe landslides.[5][1][6] The storm occurred just days after Japan surrendered after the Pacific War, and the damage caused by Ida worsened the situation.[1][6]
In addition, USS Repose (AH-16) reportedly entered Ida's eye and observed an atmospheric pressure of 25.55 inches of mercury (about 865 hPa).[7][8][9] This is below the Typhoon Tip (870 hPa) in 1979, the official world record for minimum sea level pressure.
References
- "枕崎台風 昭和20年(1945年) 9月17日~9月18日". www.data.jma.go.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 2020-08-08.
- 第三版,日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ), ブリタニカ国際大百科事典 小項目事典,朝日新聞掲載「キーワード」,デジタル大辞泉,百科事典マイペディア,世界大百科事典 第2版,大辞林. "枕崎台風(まくらざきたいふう)とは". コトバンク (in Japanese). Retrieved 2020-08-08.
- Weather Records of Makurazaki Japan Meteorological Agency
- "バイオウェザー・お天気豆知識". www.bioweather.net. Retrieved 2020-08-08.
- Makurazaki typhoon Hiroshima disaster prevention Web Archived 2017-07-14 at the Wayback Machine Hiroshima Prefectural Government
- "Peace Seeds ヒロシマの10代がまく種(第16号) 終戦直後を襲った「枕崎台風」". ヒロシマ平和メディアセンター (in Japanese). Retrieved 2020-08-08.
- 講談社『ギネスブック 世界記録事典 1980』90頁の他、1981年度版、1982年度版等にも記載があるが、865hPaではなく856hPaとなっている。
- "Repose newspaper page 1". web.archive.org. 2001-09-09. Retrieved 2020-08-08.
- "REPOSE (Page 1)". web.archive.org. 1998-12-05. Retrieved 2020-08-08.