USS Fulton (1837)
USS Fulton was a steamer that served the U.S. Navy prior to the American Civil War, and was recommissioned in time to see service in that war. However, her participation was limited to being captured by Confederate forces in the port of Pensacola, Florida, at the outbreak of war.
.jpg.webp) Drawing of Fulton as originally built in 1837 | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Namesake: | Robert Fulton |
| Laid down: | 1835 |
| Launched: | 1837 |
| Commissioned: | 13 December 1837 |
| Decommissioned: | 23 November 1842 |
| In service: | 25 January 1852 |
| Out of service: | 1862 |
| Stricken: | 1862 |
| Captured: |
|
| Fate: | destroyed, 10 May 1862 |
| General characteristics | |
| Displacement: | 720 tons |
| Length: | 180 ft (55 m) |
| Beam: | 34 ft 8 in (10.57 m) |
| Draft: | 13 ft (4.0 m) |
| Propulsion: | steam engine, side wheel |
| Speed: | 10 knots |
| Complement: | 130 |
| Armament: | four 32-pounder guns |
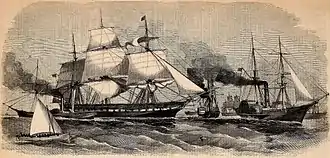
The second ship to be named Fulton by the Navy, a side wheel steamer, her build commenced in 1835, and she was launched 18 May 1837 by Brooklyn Navy Yard;[1] and commissioned 13 December 1837, Captain M. C. Perry in command. She was often called Fulton II. Fulton I was the renamed United States floating battery Demologos.
Service in the North Atlantic
_01.jpg.webp)
Fulton cruised the Atlantic coast, aiding ships in distress, conducting ordnance experiments, and training officers in gunnery. A major event of her early service came on 23 November 1838, when she bested the British steamer SS Great Western in a speed contest off New York. Decommissioned at New York 23 November 1842, Fulton lay in ordinary until 1851, when she was rebuilt and her machinery completely replaced.
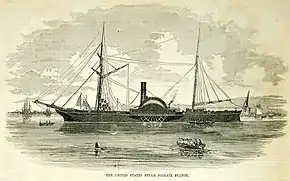
1851 rebuild
_after_1851_reconstruction.jpg.webp)
The third Fulton rebuild commenced in 1850, was launched on 30 August 1851, at the Brooklyn Navy Yard.[1] Fulton was essentially a harbor defense ship and was unsuitable for the cruising missions then emphasized by Navy policy. Accordingly, the New York Navy Yard rebuilt her in 1851 as a much more conventional warship. Fulton was recommissioned 25 January 1852 for duty in the Home Squadron, and sailed from New York 22 February for the West Indies. After the rebuild she was commonly referred to as Fulton III.[2]
During the next six years, aside from necessary repair periods in the yards at Washington, D.C., Norfolk, Virginia, and Boston, Massachusetts, Fulton ranged from the Caribbean to the Gulf of St. Lawrence, transporting Government officials, protecting merchantmen against search on the high seas, and joining in the search for USS Albany (January through May 1855) and the expedition to Nicaragua in 1857 to break up William Walker's filibustering activities. The next year Fulton's commanding officer obtained the release of five American merchant ships held at Tampico, Mexico, by revolutionary forces.
From October 1858 to May 1859 Fulton joined in operations commanded by Commodore W. B. Shubrick during his negotiations to improve relations with Paraguay, sailing the La Plata and the Parana and Paraguay Rivers.
After lying out of commission at Norfolk, Virginia, from 7 May 1859 to 30 July 1859, Fulton cruised off Cuba to suppress the slave trade until laid up at Pensacola, Florida, in mid-October 1859.
The Times reported that she had been wrecked on Santa Rosa Island, off Pensacola, Florida.[3]
Civil War capture
Captured by the Confederates when they took the Pensacola yard on 12 January 1861, Fulton was considered for use in the Confederate States Navy, but was never fitted out. She was destroyed in the evacuation of the yard by the Confederates upon Federal reoccupation 10 May 1862.
References
- "Fleet of Fifty Warships Built in the Brooklyn Navy Yard". The Brooklyn Daily Eagle (Brooklyn, New York). 12 May 1910. pp. 21–22. Retrieved 16 August 2018.
- Stanton, Samuel Ward (1895). "American Steam Vessels". Journal of the American Society for Naval Engineers. 7 (3): 62. doi:10.1111/j.1559-3584.1895.tb01098.x.
- "America". The Times (23428). London. 4 October 1859. col A, p. 7.
- This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.