Urorectal septum
The endodermal cloaca is divided into a dorsal and a ventral part by means of a partition, the urorectal septum, which grows downward from the ridge separating the allantois from the cloacal opening of the intestine and ultimately fuses with the cloacal membrane and divides it into an anal and a urogenital part. The dorsal part of the cloaca forms the rectum, and the anterior part of the urogenital sinus and bladder. The urorectal septum eventually becomes part of the perineal body.
| Urorectal septum | |
|---|---|
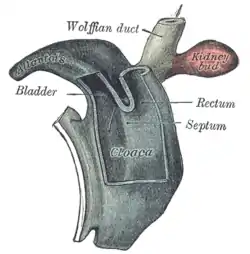 Cloaca of human embryo from twenty-five to twenty-seven days old. | |
| Details | |
| Days | 32 |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | septum urorectale |
| TE | E5.4.9.0.2.0.14 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Clinical significance
Malformation of the urorectal septum can lead to several different types of fistulas.[1]
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1109 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Escobar LF, Heiman M, Zimmer D, Careskey H (2007). "Urorectal septum malformation sequence: Prenatal progression, clinical report, and embryology review". Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 143 (22): 2722–6. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.31925. PMID 17937427. S2CID 19219635.
External links
- http://cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk/cgi-bin/omd?urorectal+septum
- http://www.embryology.ch/anglais/turinary/urinbasse01.html
- http://isc.temple.edu/marino/embryology/parch98/parch_text.htm
- http://www.med.mun.ca/anatomyts/renal/akid5.htm
- http://www.med.umich.edu/lrc/coursepages/M1/embryology/embryo/10digestivesystem.htm
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
