Valley Falls, Oregon
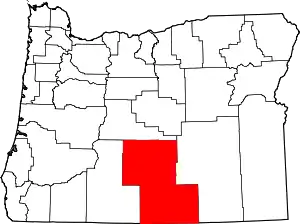
Valley Falls is a small unincorporated community in Lake County, Oregon, United States. The settled area is located at the junction of U.S. Route 395 and Oregon Route 31. The community is named for a small falls on the Chewaucan River just north of the occupied site. East of Valley Falls, the cliff face of Abert Rim overlooks the community.
Valley Falls, Oregon | |
|---|---|
 Valley Falls store and gas station | |
 Valley Falls  Valley Falls | |
| Coordinates: 42.48417°N 120.28194°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Oregon |
| County | Lake |
| Elevation | 4,327 ft (1,319 m) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 (Pacific) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (Pacific) |
History
The area around Valley Falls was occupied by Native Americans for up to 11,000 years prior to the arrival of white settlers. Archaeological evidence shows that the peak period for use by native tribes was between 2,000 and 500 years ago. During that period, the people who lived in the Valley Falls area were probably ancestors of the Klamath and Modoc peoples. Most of these Native Americans lived in pit-houses along the shore of Abert Lake, just north of Valley Falls.[1] There are also a number of ancient petroglyphs near Valley Falls. The Abert Lake Petroglyphs, at the foot of Abert Rim, are thought to be over 10,000 years old.[2]
In 1832, John Work led his Hudson's Bay Company trapping brigade through the Valley Falls area. Work recorded the visit in his journal. In 1843, Captain John C. Fremont explored the area around Valley Falls. Fremont name Abert Rim and nearby Abert Lake after the head of the United States Army's topographical engineers, Colonel John J. Abert.[3][4]
The community was founded and named by C. W. E. Jennings, who opened a store at the site around 1908. It was named for a small falls on the Chewaucan River approximately 1 mile (1.6 km) north of the community. In 1909, a post office was established at Valley Falls. The office was located near the base of Abert Rim. The first postmaster was Ernest L.H. Meyer. However, Jennings later took over from Meyer. At its peak, the community of Valley Falls had a hotel, livery stable, and a dance hall in addition to the Jennings' store and post office. The area was surveyed for a railroad, but it was never built. In 1942, the post office was moved approximately one mile west to the junction of U.S. Route 395 and Oregon Route 31. The Valley Falls post office was closed in 1943.[5][6][7]
Geography
The unincorporated community of Valley Falls is located at the junction of U.S. Route 395 and Oregon Route 31 in the high desert country of Lake County in south-central Oregon. There are only five structures at the site. The main business is a combined gas station and store, located on the west side of the highway, south of the junction. There is also a recreational vehicle park and a guest ranch nearby. Valley Falls is 23 miles (37 km) north of Lakeview, Oregon, on Route 395; 23 miles (37 km) southeast of Paisley, Oregon, on Route 31; and 116 miles (187 km) southwest of Burns, Oregon, on Route 395.[8][9][10][11]
Geology

Abert Rim is approximately one mile east of Valley Falls. The rim is one of the highest escarpments in the United States, rising 2,500 feet (760 m) above the valley floor. The top 800 feet (240 m) is a sheer-cliff. The rim cliff runs over 30 miles (48 km) from north to south, making it the longest exposed block fault scarp in North America. The rim is basalt, formed by large lava flows during the Miocene epoch. After the lava flows stopped, large blocks faults broke and tilted the land. Abert Rim is the result of one of those giant faults.[1][9][12][13]
From Valley Falls, visitors have an unobstructed view of Abert Rim's cliff face.[10] Along the highway just south of the Valley Falls, there is an Outback Scenic Byway kiosk that explains how Abert Rim was formed.[1] There are also two geological information signs north of Valley Falls, one on Route 395 and the other on Route 31.[14]
Climate
The annual average high temperature in Valley Falls is 61.8 °F (17 °C). The warmest month is normally July, which averages over 86 °F (30 °C). The highest temperature ever recorded at the Valley Falls Weather Station was 105 °F (41 °C) in 1961. The annual average low temperature is 31.1 °F (−1 °C). January is normally the coldest month, averaging 22 °F (−6 °C). The lowest temperature ever recorded at the site was −34 °F (−37 °C) in 1962.[15][16]
The area around Valley Falls is relatively dry, with average precipitation of about 13 inches (33 cm) per year. The area around Valley Falls is typical of Oregon's high desert country. The area's highest average precipitation comes between October and June, usually as the result of thunderstorms. From November to March most of the area's precipitation comes in the form of snow.[17][18][19]
| Climate data for Valley Falls, Oregon | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 41.3 (5.2) |
44.9 (7.2) |
51.9 (11.1) |
57.1 (13.9) |
67.3 (19.6) |
77.2 (25.1) |
86.2 (30.1) |
84.7 (29.3) |
75.4 (24.1) |
63.3 (17.4) |
50.1 (10.1) |
41.3 (5.2) |
61.8 (16.6) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 31.7 (−0.2) |
33.9 (1.1) |
38.7 (3.7) |
42.9 (6.1) |
50.8 (10.4) |
58.5 (14.7) |
66.1 (18.9) |
64.2 (17.9) |
55.7 (13.2) |
46.5 (8.1) |
37.6 (3.1) |
30.4 (−0.9) |
46.5 (8.1) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 22.1 (−5.5) |
22.9 (−5.1) |
25.4 (−3.7) |
28.7 (−1.8) |
34.3 (1.3) |
39.9 (4.4) |
46.0 (7.8) |
43.8 (6.6) |
36.1 (2.3) |
29.7 (−1.3) |
25.0 (−3.9) |
19.4 (−7.0) |
31.1 (−0.5) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 1.5 (38) |
1.4 (36) |
1.0 (25) |
1.0 (25) |
1.5 (38) |
1.2 (30) |
0.4 (10) |
0.3 (7.6) |
0.6 (15) |
1.0 (25) |
1.2 (30) |
1.4 (36) |
12.5 (320) |
| Source: National Climatic Data Center (temperature)[15] and Western Regional Climate Center (precipitation)[17] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
The United States Geological Survey identifies Valley Falls as a "populated place". That is "a place or area with clustered or scattered buildings and a permanent human population. A populated place is usually not incorporated and by definition has no legal boundaries."[20] United States Census data are not available for Valley Falls. The Valley Falls area is part of the Summer Lake Census County Division, but specific census data for the community are not presented in 2010 census reports.[21]
Local points of interest
- Abert Rim
- Abert Lake
- Abert Lake Petroglyphs (listed on National Register of Historic Places)[2]
- Chandler State Wayside
- Chewaucan River
- Oregon Outback Byway
References
- "Abert Rim", Oregon History Marker, Oregon Travel Information Council, Outback Scenic Byway, near Valley Falls, Oregon, 12 July 2014.
- "Abert Lake Petroglyph Site", National Register of Historic Places Registration Form, Lakeview District, Bureau of Land Management, United States Department of the Interior, Lakeview, Oregon, 20 November 1974.
- McArthur, Lewis A. and Lewis L. McArthur, "Lake Abert", Oregon Geographic Names (Seventh Edition), Oregon Historical Society Press, Portland, Oregon, 2003 (1928), p. 552.
- Brogan, Phil F., "Fremont Given Western Assignment", East of the Cascades (Third Edition), Binford and Mort, Portland, Oregon, 1965, p. 38.
- McArthur, Lewis A. and Lewis L. McArthur, "Valley Falls", Oregon Geographic Names (Seventh Edition), Oregon Historical Society Press, Portland, Oregon, 2003 (1928), p. 988.
- "Valley Falls", The Oregon Outback National Scenic Byway, Lake County Chamber of Commerce, Lakeview, Oregon, 16 July 2014.
- Juillerat, Lee, "Store Stocks it All", The World, Coos Bay, Oregon, 4 March 1980, p. 19.(subscription required)
- Oregon topographic map, United States Geological Survey, United States Department of Interior, Reston, Virginia; displayed via ACME mapper, www.acme.com, 29 October 2013.
- "Abert Rim" (PDF), The Oregon Outback Scenic Byway, National Scenic Byway Driving Guide, Oregon Department of Transportation, Salem, Oregon, 30 July 2014.
- Lasater, Erika and Paul Denny, "Places to Visit in Oregon's Outback", www.oregonsoutback.com, Pendleton, Oregon, 16 July 2014.
- "Valley Falls, Lake County, 97636", www.smalltownoregon.com, 30 July 2014.
- "Lake Abert and Abert Rim", Lakeview District, Bureau of Land Management, United States Department of Interior, Lakeview, Oregon, 16 July 2014.
- Brogan, Phil F., "Escarpment Reach to Clouds", East of the Cascades (Third Edition), Binford and Mort, Portland, Oregon, 1965, p. 282.
- Longe, Erwin F., "Geology markers Along Oregon Highways" (PDF), Ore Bin (Volume 33, Number 10), Oregon Department of Geology and Mineral Industries, Portland, Oregon, October 1971, p. 188.
- "Valley Falls, OR US", Data Tools: 1981-2010 Normals, National Climatic Data Center, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Asheville, North Carolina, 30 July 2014.
- "Valley Falls, Oregon: Period of Record General Climate Summary – Temperature", period 1948 to 2003, NOAA Weather Station Identification: 358812 (Valley Falls, OR), Valley Falls, Oregon, 30 July 2014.
- "Valley Falls, Oregon: Period of Record General Climate Summary – Precipitation", period 1948 to 2003, NOAA Weather Station Identification: 358812 (Valley Falls, OR), Valley Falls, Oregon, 30 July 2014.
- Van Denburgh, A. S., "Climate" (PDF), Solute Balance at Abert and Summer Lakes, South-Central Oregon, Geological Survey Professional Paper 502-C, United States Geological Survey, United States department of Interior, United States Government Printing Office, Washington, District of Columbia, 1975, p. C4.
- "Oregon Topics: Weather/Climate", Oregon Blue Book, Oregon State Archives, Oregon Secretary of State, Salem, Oregon, January 2013.
- "Feature Detail Report for: Valley Falls", Geographic Names Information System, United States Geological Survey, United States Department of Interior, Reston, Virginia, 30 July 2014.
- "American Indian Areas, Counties, County Subdivisions, and Places - Section 5" (map of Klamath and Lake counties subdivisions) (PDF), Oregon: 2010 Summary Population and Housing Characteristics, United States Census 2010, Economics and Statistics Administration, United States Census Bureau, United States Department of Commerce, p. E-8 Oregon.