Villa Capra "La Rotonda"
Villa La Rotonda is a Renaissance villa just outside Vicenza in northern Italy designed by Italian Renaissance architect Andrea Palladio. The villa’s correct name is Villa Almerico Capra Valmarana, but it is also known as "La Rotonda", "Villa Rotonda", "Villa Capra", and "Villa Almerico Capra". The name Capra derives from the Capra brothers, who completed the building after it was ceded to them in 1592. Along with other works by Palladio, the building is conserved as part of the World Heritage Site "City of Vicenza and the Palladian Villas of the Veneto".
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | Vicenza, Veneto, Italy |
| Part of | City of Vicenza and the Palladian Villas of the Veneto |
| Criteria | Cultural: (i), (ii) |
| Reference | 712bis-004 |
| Inscription | 1994 (18th session) |
| Extensions | 1996 |
| Website | www |
| Coordinates | 45°31′53″N 11°33′37″E |
 Location of Villa Rotonda  Villa Capra "La Rotonda" (Italy) | |
Inspiration
In 1565 a priest, Paolo Almerico, on his retirement from the Vatican (as referendario apostolico of Pope Pius IV and afterwards Pius V), decided to return to his home town of Vicenza in the Venetian countryside and build a country house. This house, later known as 'La Rotonda', was to be one of Palladio's best-known legacies to the architectural world. Villa Capra may have inspired a thousand subsequent buildings, but the villa was itself inspired by the Pantheon in Rome.
Design
The site selected was a hilltop just outside the city of Vicenza. Unlike some other Palladian villas of the Veneto, the building was not designed from the start to accommodate a working farm. This sophisticated building was designed for a site which was, in modern terminology, "suburban". Palladio classed the building as a "palazzo" rather than a villa.
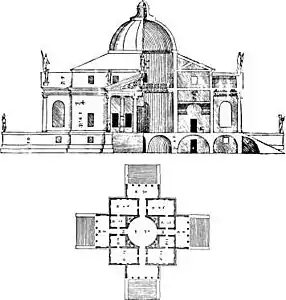
The design is for a completely symmetrical building having a square plan with four facades, each of which has a projecting portico. The whole is contained within an imaginary circle which touches each corner of the building and centres of the porticos. (illustration, left).
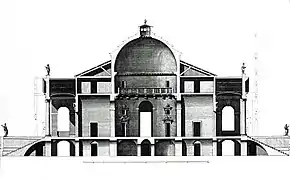
The name La Rotonda refers to the central circular hall with its dome. To describe the villa, as a whole, as a rotunda is technically incorrect, as the building is not circular but rather the intersection of a square with a cross. Each portico has steps leading up to it, and opens via a small cabinet or corridor to the circular domed central hall. This and all other rooms were proportioned with mathematical precision according to Palladio's own rules of architecture which he published in I quattro libri dell'architettura.[1] Works spaces for the villa's servants are hidden in a low level underneath the first floor, which is accessed via staircases hidden inside the walls of the central hall.[2]
The design reflected the humanist values of Renaissance architecture. In order for each room to have some sun, the design was rotated 45 degrees from each cardinal point of the compass. Each of the four porticos has pediments graced by statues of classical deities. The pediments were each supported by six Ionic columns. Each portico was flanked by a single window. All principal rooms were on the second floor or piano nobile.
Building began in 1567. Neither Palladio nor the owner, Paolo Almerico, were to see the completion of the villa. Palladio died in 1580 and a second architect, Vincenzo Scamozzi, was employed by the new owners to oversee the completion. One of the major changes he made to the original plan was to modify the two-storey central hall.

Palladio had intended it to be covered by a high semi-circular dome but Scamozzi designed a lower dome with an oculus (intended to be open to the sky) inspired by the Pantheon in Rome. The dome was ultimately completed with a cupola.
Interior

The interior design of the Villa was to be as wonderful, if not more so, than the exterior.
Alessandro and Giovanni Battista Maganza and Anselmo Canera were commissioned to paint frescoes in the principal salons.
Among the four principal salons on the piano nobile are the West Salon (also called the Holy Room, because of the religious nature of its frescoes and ceiling), and the East Salon, which contains an allegorical life story of the first owner, Paolo Almerico, his many admirable qualities portrayed in fresco.
The highlight of the interior is the central, circular hall, surrounded by a balcony and covered by the domed ceiling; it soars the full height of the main house up to the cupola, with walls decorated in trompe-l'œil.
Abundant frescoes create an atmosphere that is more reminiscent of a cathedral than the principal salon of a country house.
Landscape

From the porticos, views of the surrounding countryside can be seen; this is no coincidence as the Villa was designed to be in perfect harmony with the landscape.
This was in complete contrast to such buildings as Villa Farnese of just 16 years earlier.
Thus, while the house appears to be completely symmetrical, it actually has certain deviations, designed to allow each facade to complement the surrounding landscape and topography. Hence, there are variations in the facades, in the width of steps, retaining walls, etc. In this way, the symmetry of the architecture allows for the asymmetry of the landscape, and creates a seemingly symmetrical whole. The landscape is a panoramic vision of trees and meadows and woods, with Vicenza on the horizon.
The northwest portico is set onto the hill as the termination of a straight carriage drive from the principal gates. This carriageway is an avenue between the service blocks, built by the Capra brothers, who acquired the Villa in 1591; they commissioned Vincenzo Scamozzi to complete the villa and construct the range of staff and agricultural buildings.
Current conditions
In 1994 UNESCO designated the building as part of a World Heritage Site.[3]
The last owner of the villa was Mario di Valmarana († Oct. 13, 2010), a former professor of architecture at the University of Virginia.[4] It was his declared ambition to preserve Villa Rotonda so that it may be appreciated by future generations. The interior is open to the public on Wednesdays and Saturdays, except during the winter months, and the grounds are open every day.
Film
In 1979 the American film director Joseph Losey filmed Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart's opera Don Giovanni in Villa La Rotonda and the Veneto region of Italy. the film was nominated for several César Awards in 1980 including Best Director, and has generally been praised as one of the finer cinematic adaptations of opera.
Photo gallery
 Front
Front Side
Side Shaded view
Shaded view Service corridor leading up to building facade
Service corridor leading up to building facade carved marble fireplace mantel over a fireplace
carved marble fireplace mantel over a fireplace Open pediment over doorway
Open pediment over doorway
 Palladio: I quattro libri
Palladio: I quattro libri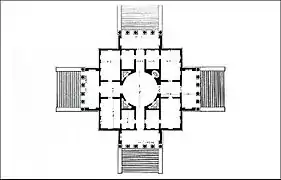 Palladio: I quattro libri
Palladio: I quattro libri
Influences
England
Five houses have been built in England based on Palladio's Villa Rotonda: Henbury Hall, Cheshire, is the most recent; Chiswick House, Greater London, and Mereworth Castle, Kent, are protected as listed buildings; Foots Cray Place, Kent, and Nuthall Temple, Nottinghamshire have been demolished.
Palestinian Territories
The "House of Palestine", built at the top of biblical Mount Gerizim, which towers over the Palestinian city of Nablus, north of Jerusalem, carefully resembles the Villa Rotonda. It is owned by Palestinian millionaire Munib al-Masri.
Poland
Palaces built in Poland based on Palladio's Villa Rotonda include the Królikarnia (Rabbit House) Palace, the Belweder in Warsaw and the Skórzewski Palace in Lubostroń.
Belarus
The interior of the main building of the Gomel Palace in Gomel in the Eastern Belarus is based on Villa Rotonda.
United States
For the competition to design the President's House in Washington, DC, Thomas Jefferson anonymously submitted a design that was a variation on the Villa Rotonda. Though James Hoban's Palladian design for what would become known as the White House was selected, the influence of the Villa Rotonda can also be seen at Jefferson's own iconic home of Monticello.
References
- A. Palladio, I Quattro Libri dell'Architettura, Venezia (Venice) 1570, libro (book) II, p. 18 (in Italian)
- HKW, Communal Villa, Lecture, 2015. 31 minute mark. https://www.hkw.de/en/app/mediathek/video/47405
- In 1996 the World Heritage Site "Vicenza, City of Palladio" was extended and renamed "City of Vicenza and the Palladian Villas of the Veneto".
- UVA Today (Oct 14, 2010). "In Memoriam: Mario di Valmarana". Archived from the original on June 29, 2012. Retrieved May 16, 2011.
Sources
- dal Lago, Adalbert (1969). Villas and Palaces of Europe. Paul Hamlyn, ISBN 978-0-600-01235-1.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Villa Capra "La Rotonda". |
External links
- Description of the building written by the Palladio Museum in Vicenza (in English and Italian)
- "La rotonda"
- "Commentary and Images of Villa Capra" from GreatBuilding.com
- Virtually visit an interpretation of the Villa Capra in Second Life.
- Architectural analysis of Villa Capra
- "Solar Orientation and Historic Buildings". solarhousehistory.com.
