Whyteleafe
Whyteleafe is a village in the district of Tandridge, Surrey, England, with a few streets falling inside the London Borough of Croydon. The village, in a dry valley of the North Downs, has three railway stations (on two parallel lines). Neighbouring villages and towns include Woldingham, Caterham, Coulsdon, Warlingham, and Kenley. To the west are Kenley Aerodrome, Kenley Common (owned by the Corporation), Coxes Wood, and Blize Wood. To the east are Riddlesdown, the Dobbin and Marden Park.
| Whyteleafe | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) Typical landscape of Whyteleafe along the dry valley from the A22 | |
.jpg.webp) Part of the shopping area on Godstone Road near to Whyteleafe and Upper Warlingham railway stations | |
 Whyteleafe Location within Surrey | |
| Area | 2.17 km2 (0.84 sq mi) |
| Population | 3,900 (Civil Parish 2011)[1] |
| • Density | 1,797/km2 (4,650/sq mi) |
| OS grid reference | TQ336583 |
| Civil parish |
|
| District | |
| Shire county | |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | Whyteleafe |
| Postcode district | CR3 |
| Dialling code | 020 01883 |
| Police | Surrey |
| Fire | Surrey |
| Ambulance | South East Coast |
| UK Parliament | |
The churchyard contains graves of airmen who died during WWII, stationed at RAF Kenley nearby. The village forms part of the Greater London Built-up Area.[2]
History
The village name comes from the distinctive white underside of the whitebeam trees growing in the area.[3] In 1855 Nathaniel Glover purchased White Leaf field and George Henry Drew later completed the building that was called "White Leafe House". By 1881 the surrounding area had become known as "Whiteleafe".[4] As with Kenley the history of its land before that was that of other parishes, in this case Caterham and to a lesser extent Warlingham and Coulsdon.
Its first primary school was built in 1892, enlarged in 1900 and again in 1907.
In 1911 the population of Whyteleafe was "now larger than that of Warlingham village...A county council secondary school for girls has been set up in this year (1911)."[5]
Amenities
Whyteleafe has: a large pub, a micropub, a newsagent, general store, two petrol stations (M&S and Waitrose food outlets), a post office, hairdresser, chemist, ladies' outfitter, baker, fish and chip shop, kebab shop, Indian restaurant, Chinese restaurant, launderette, barber, Tesco Express and an e-cigarette store.
To the south of Whyteleafe are the headquarters of Gold Group International, the largest employer in the parish boundaries.[6]
Whyteleafe School, is a primary school which is part of the multi academy trust GLF and is situated at the bottom of Whyteleafe Hill. It makes use of the site of the former Whyteleafe Girls' Grammar School, vacated in the late 1970s. Warlingham School (secondary) is at the top of Tithe Pit Shaw Lane, on the edge of Whyteleafe in the east.
The C of E church of St Luke was built in 1866, founded as a new parish in the Diocese of Southwark.
Transport
There are three railway stations: Whyteleafe South, Whyteleafe and Upper Warlingham. All three stations are served by Southern services. The Godstone road (A22) cuts through north to south. Bus routes 407 and 434 serve the area and run from Coulsdon, Croydon, Sutton, and Caterham. Whyteleafe village grew after the railway came on its way to Caterham in 1856. A second line, the Oxted Line, following a slightly higher contour, opened in 1884. It serves different destinations to the south but also runs to London Bridge or Victoria.
Sport and leisure
Whyteleafe F.C. is the main football club with various teams and has played in grounds in Church Road since 1959, when it moved from the field off New Barn Lane, used by adjacent Kenley School. Its adult men's team play in the Isthmian League. Separate from its ground in the west of town is the large recreation ground below wooded hills in the east of town which has informal sports fields and a playground.[7]
Caterham and Whyteleafe Tennis Club is located in Manor Park near Whyteleafe South Station [8]
Local government
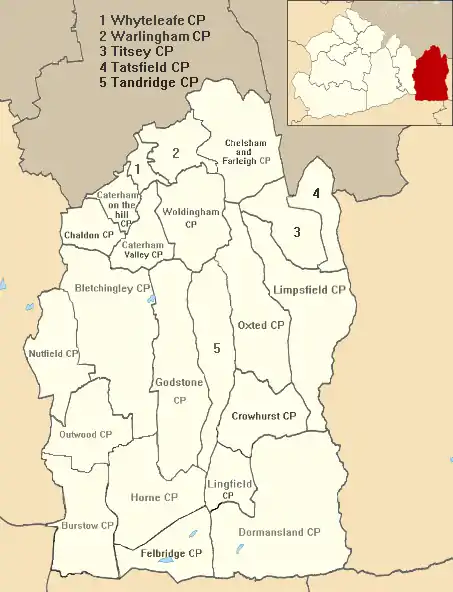
Surrey County Council, headquartered in Kingston, elected every four years, has one councillor representing Caterham Valley, which incorporates the civil parishes of Caterham Valley and Whyteleafe.
| Election | Member[9] |
Ward | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | David Lee | Caterham Valley | |
Whyteleafe has 2 representatives on Tandridge District Council, headquartered in Oxted:
| Election | Member[10] |
Ward | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | David Lee | Valley | |
| 2018 | Jeffrey Gray | Valley | |
Whyteleafe is one of 21 civil parish councils in Tandridge District electing seven parish councillors every four years.[11] The parish council clerk is Simon Bold.
Demography and housing
| Output area | Detached | Semi-detached | Terraced | Flats and apartments | Caravans/temporary/mobile homes | shared between households[1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Civil Parish) | 359 | 278 | 252 | 891 | 3 | 0 |
The average level of accommodation in the region composed of detached houses was 28%, the average that was apartments was 22.6%.
| Output area | Population | Households | % Owned outright | % Owned with a loan | hectares[1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Civil Parish) | 3,900 | 1,783 | 21.8% | 43.6% | 217 |
The proportion of households in the civil parish who owned their home outright compares to the regional average of 35.1%. The proportion who owned their home with a loan compares to the regional average of 32.5%. The remaining % is made up of rented dwellings (plus a negligible % of households living rent-free).
Notable People
• Jelani Allman
• Alexander Hadouka-Taylor
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Whyteleafe. |
References
- Key Statistics; Quick Statistics: Population Density United Kingdom Census 2011 Office for National Statistics Retrieved 21 November 2013
- "2011 Census – Built-up areas". ONS. Retrieved 28 January 2014.
- Packham, editors, Gwyneth Fookes & Roger (2006). A History of Whyteleafe. [Sanderstead, U.K.]: The Bourne Society. p. 153. ISBN 978-0-900992-67-4.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- Packham, editors, Gwyneth Fookes & Roger (2006). A History of Whyteleafe. [Sanderstead, U.K.]: The Bourne Society. p. 36. ISBN 978-0-900992-67-4.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- H.E. Malden (editor) (1912). "Parishes: Caterham". A History of the County of Surrey: Volume 4. Institute of Historical Research. Retrieved 1 December 2013.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- "Principal Employers in Tandridge" (PDF). Surrey County Council. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 March 2013. Retrieved 30 September 2012. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Google map of recreation ground Retrieved 2014-01-01
- http://www.mytennislife.co.uk/venue/caterham-and-whyteleafe-tennis-club/
- "Surrey's County Councillors". Surrey County Council. Retrieved 10 May 2018.
- "Whyteleafe Councillors". Tandridge.gov.uk. Tandridge District Council. Retrieved 10 May 2018.
- "Who we are". Whyteleafe Village Council. Retrieved 10 May 2018.