XZ Tauri
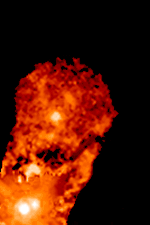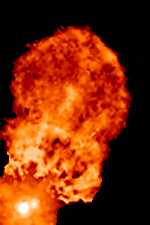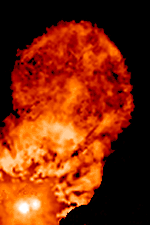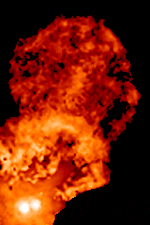
XZ Tauri is a binary system approximately 460 light-years away in the constellation Taurus. The system consists of two T Tauri stars orbiting each other about 6 billion kilometers apart (roughly the same distance as Pluto is from the Sun). The system made news in 2000 when a superflare was observed in the system.
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Taurus |
| Right ascension | 04h 31m 40.08690s[1] |
| Declination | +18° 13′ 56.6424″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.00 |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M2.0 + M3.5[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Distance | 460 ly (140[3] pc) |
| Details[2] | |
| A | |
| Mass | 0.37 M☉ |
| Radius | 1.1 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.17 L☉ |
| B | |
| Mass | 0.29 M☉ |
| Radius | 1.7 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.31 L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,550[3] K |
| Age | 4.6[3] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
References
- Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- Hartigan, Patrick; Kenyon, Scott J. (January 2003). "A Spectroscopic Survey of Subarcsecond Binaries in the Taurus-Auriga Dark Cloud with the Hubble Space Telescope". The Astrophysical Journal. 583 (1): 334–357. arXiv:astro-ph/0209608. Bibcode:2003ApJ...583..334H. doi:10.1086/345293.
- Osorio, Mayra; et al. (July 2016). "A Dwarf Transitional Protoplanetary Disk around XZ Tau B". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 825 (1): 6. arXiv:1606.03118. Bibcode:2016ApJ...825L..10O. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/825/1/L10. L10.
- "XZ Tau". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2020-12-09.
- "Jets, bubbles, and bursts of light in Taurus". www.spacetelescope.org. ESA/Hubble. Retrieved 6 November 2014.
External links
- "Movies from Hubble Show the Changing Faces of Infant Stars". HubbleSite. NASA. 21 September 2000. Retrieved 23 August 2009.
- XZ Tauri at Constellation Guide
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.