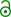1944 Atlantic hurricane season
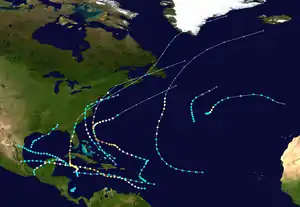
The 1944 Atlantic hurricane season featured the first instance of upper-atmosphere data being incorporated into tropical cyclone track forecasting. The season officially began on June 15, 1944, and ended on November 15, 1944. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The season's first cyclone developed on July 13, while the final system by November 13.The season was fairly active season, with 14 tropical storms, 8 hurricanes, and 3 major hurricanes.[nb 1] In real-time, forecasters at the Weather Bureau tracked eleven tropical storms, but later analysis uncovered evidence of three previously unclassified tropical storms.
| 1944 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
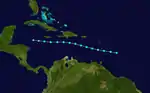
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | July 13, 1944 |
| Last system dissipated | November 3, 1944 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | "Great Atlantic" |
| • Maximum winds | 145 mph (230 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 933 mbar (hPa; 27.55 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 21 |
| Total storms | 14 |
| Hurricanes | 8 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 3 |
| Total fatalities | 1,025-1,125 |
| Total damage | $202 million (1944 USD) |
| Related articles | |
The strongest storm of the season was the Great Atlantic hurricane, which struck Long Island and New England, causing at least 391 deaths and about $100 million (1944 USD) in damage across the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Canada, and at sea. The Jamaica hurricane and Cuba–Florida hurricane were also powerful and left major impacts. The former left "several millions of dollars" in Jamaica, while 116 deaths were recorded throughout its path. The Cuba–Florida hurricane devastated both regions, resulting in at least 318 fatalities and damage exceeding $100 million. A hurricane which struck Mexico in late September caused 200-300 deaths in the Isthmus of Tehuantepec due to flooding.
Seasonal summary
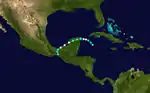
The season began on July 13 with the formation of Hurricane One near the Bahamas. One turned northwestward and did not affect land, though low-end tropical storm-force winds were felt in Bermuda. About a week later, Tropical Storm Two hit Martinique before moving west and dissipating on July 27.[2] Just three days later, east of the Turks and Caicos Islands a tropical storm formed and strengthened into a hurricane on August 1. Hurricane Three made landfall later that day in North Carolina, causing $2 million worth of damage. The next storm of the season came on August 16, and quickly strengthened into a hurricane. Then, on August 19, Four strengthened into the first major hurricane of the season. Four then weakened and made landfall in Jamaica at Category 2 intensity, causing over 30 deaths. Having been weakened into a Category 1, on August 22, Four made landfall in the Yucatán Peninsula, causing unknown damage and a high death toll. After exiting the peninsula, a highly weakened Four hit mainland Mexico on August 24 as a tropical depression, and almost instantly dissipated. While Four was intensifying on August 18, Tropical Depression Five formed off the coast of the Yucatán Peninsula, and scraped the coast early the next day. Five strengthened into a tropical storm late on August 19 and made landfall in Tamaulipas three days later. Causing little impact, Five dissipated the next day. On September 9, an area of low pressure quickly organized into a tropical storm in the Gulf of Mexico. Early on September 11, Tropical Storm Six made landfall, causing the highest daily rainfall total since 1937. Also on September 9, a tropical storm formed in the central Atlantic and moved west-northwest. Seven slowly intensified into a Category 4 hurricane, and then, very early in the morning on September 15, the hurricane made landfall in New England, causing a very high death toll and catastrophic damage. As Seven's remnants dissipated, a tropical wave developed into Tropical Storm Eight. On September 20, after strengthening into a hurricane, Eight made landfall in the Yucatán Peninsula. Later that day, Eight briefly entered the Bay of Campeche before making a second landfall in southern Mexico. Eight dissipated on September 22 due to mountains.
As Eight was dissipating on September 21, a tropical storm formed in the Central Atlantic. Three days later, it intensified into Hurricane Nine. The next day, Nine briefly became a Category 2 hurricane before a cold front came and caused Nine to become extratropical early on September 26. The next two tropical storms of the season, Ten and Eleven, both lasted from September 30 to October 3 and did not affect land, though Ten had numerous ship reports on it. On October 11, a tropical storm formed in the northeast Atlantic. Early the next day, Twelve reached peak intensity as a low-end Category 1 hurricane. However, Twelve soon weakened from hurricane intensity. On October 15, as Twelve started to affect Portugal, Twelve transitioned into an extratropical cyclone. While Twelve was becoming a hurricane, a disturbance northeast of Guatemala became a tropical depression. While moving very slowly northward, the depression quickly became Tropical Storm Thirteen and was soon a hurricane. On October 15, Thirteen strengthened into the third major hurricane of the season. The next day, as Thirteen strengthened into a Category 4, it made landfall in Cuba. Then, moving faster, Thirteen moved north-northeast, making landfall in Florida as a low-end Category 3 on October 18. Quickly weakening, two days later Thirteen made landfall in South Carolina, and proceeded to turn extratropical. The remnants continued for five more days, before entirely dissipating over Greenland. On November 1, a tropical depression formed east of Costa Rica. It quickly organized into Tropical Storm Fourteen. Fourteen reached peak intensity the next day, and then weakened. It dissipated on November 3, thus ending the season.[2]
Systems
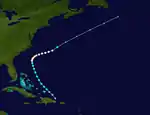
Hurricane One
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 13 – July 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) 995 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave was noted near Grenada on July 11;[3] it organized into the season's first tropical depression two days later around 06:00 UTC while situated near Navidad Bank in the Turks and Caicos Islands. Upon designation, the Weather Bureau planned reconnaissance missions for the first time ever to intercept the newly formed cyclone. It intensified as it moved northwest, attaining tropical storm intensity by 00:00 UTC on July 14 and further strengthening into the season's first hurricane around 06:00 UTC on July 16. After reaching peak winds of 80 mph (130 km/h),[2] the hurricane recurved toward the northeast and began to weaken, though Bermuda reported winds near 40 mph (65 km/h) upon the storm's closest approach. It transitioned into an extratropical cyclone around 00:00 UTC on July 19 and continued into the northern Atlantic, where it was absorbed by a larger extratropical low southeast of Newfoundland the next day.[3][2]
Tropical Storm Two
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | July 24 – July 27 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 mph (100 km/h) (1-min) 999 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave organized into a tropical storm east of Barbados around 06:00 UTC on July 24, although it is possible the system existed farther east in the absence of widespread observations. The system passed just south of Martinique,[2] where Fort-de-France recorded peak winds of 55 mph (89 km/h),[3] before continuing on a west-northwest course through the Caribbean Sea. Though it was initially believed the small storm struck Haiti, where considerable damage was reported along the coastline near Port-au-Prince, and ultimately degenerated, modern reanalysis suggests the cyclone continued south of the island. The system was then intercepted by strong wind shear that led to its demise west-southwest of Jamaica by 18:00 UTC on July 27. Its remnants continued westward and were last noted north of Honduras the following day.[2][4]
Hurricane Three
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
 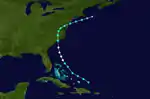 | |
| Duration | July 30 – August 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) 985 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave organized into a tropical storm about 135 mi (215 km) east of Cockburn Town in the Turks and Caicos Islands around 12:00 UTC on July 30.[3] The newly formed system intensified on a west-northwest course parallel to the Bahamas, attaining hurricane strength by 00:00 UTC on August 1. From there, it curved toward the north before making landfall on Oak Island, North Carolina, with peak winds of 80 mph (130 km/h) at 23:00 UTC. The system weakened as it progressed through the Mid-Atlantic and into the northwestern Atlantic, and it was last considered a tropical depression around 06:00 UTC on August 4 about 105 mi (165 km) east of Nantucket.[2]
Despite the storm's small size, it produced wind gusts of 72 mph (116 km/h) in Wilmington, North Carolina, where many houses were unroofed, communication lines were toppled, glass windows were shattered, and hundreds of trees were uprooted. Throughout Carolina Beach and Wrightsville Beach, an unusually high tide—combined with waves perhaps as large as 30 ft (9 m)—demolished several cottages and homes, or otherwise swept the structures off their foundations. The former city was particularly hard hit as its famed boardwalk was smashed to pieces, while in Wrightsville Beach, local police estimated that the water reached 18 ft (5 m) by its city hall. Two fishing piers were destroyed in each city.[4] Crops sustained catastrophic loss throughout coastal beach counties. Rainfall was generally moderate, reaching 3–5 in (76–127 mm) across eastern North Carolina, with a maximum storm-total amount of 7.7 in (195.6 mm) in Cheltenham, Maryland.[5] Damage reached $2 million. As the cyclone exited into the Atlantic, it produced a gust of 38 mph (61 km/h) in Atlantic City, New Jersey. Though no fatalities occurred along the storm's path in the wake of mass evacuations,[3] there were several casualties, including a few with serious injuries.[4]
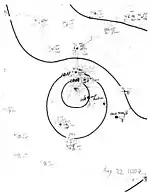
Hurricane Four
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
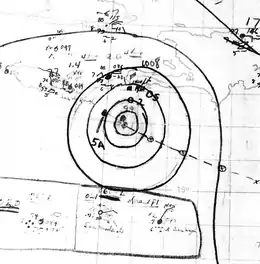  | |
| Duration | August 16 – August 24 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 973 mbar (hPa) |
The fourth cyclone of the season was first noted as strong tropical storm east of Barbados around 18:00 UTC on August 16.[3] The small storm passed over Grenada and into the eastern Caribbean Sea, where it quickly intensified into a hurricane. On a west-northwest course, the system organized into the season's first major hurricane around 12:00 UTC on August 19, attaining peak winds of 120 mph (195 km/h) six hours later. The potent hurricane grazed the northern coastline of Jamaica and continued westward in a slightly weakened state before making a second landfall south of Playa del Carmen on the Yucatán Peninsula with winds of 90 mph (150 km/h) early on August 22. The cyclone entered the Bay of Campeche as a strong tropical storm but fell to an intensity of 40 mph (65 km/h) before moving ashore just north of Tecolutla, Veracruz. Once inland, it quickly dissipated by 12:00 UTC on August 24.[2]
As the cyclone entered the Caribbean, it intercepted a British vessel which then went missing, with all 74 passengers aboard presumed dead. Across Jamaica, numerous buildings were heavily damaged, including faulty dwellings that were blown down or crushed under fallen trees. Significant crop loss was observed, with 41% of coconut trees and 90% of banana trees destroyed; in some cases, every tree was toppled in coconut plantations. Two railway vans, each weighing 14.5 t (29,000 lbs), were overturned; as such, it was estimated that gusts reached 100–120 mph (160–195 km/h) along the northeastern coastline. At least 30 people were killed across the island. In the nearby Cayman Islands, wind gusts topped 80 mph (130 km/h), though no damage was reported. [4] Overall, the storm killed 116 people.[3]
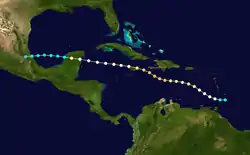
Tropical Storm Five
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
 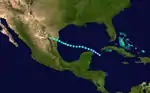 | |
| Duration | August 18 – August 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) 1007 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave was first noted passing through the Windward Islands on August 13.[4] Trekking through the Caribbean Sea, coalescing into a tropical depression about 115 mi (185 km) east of the Isla de Cozumel by 12:00 UTC on August 18. Narrowly missing the Yucatán Peninsula, the system continued west-northwest into the central Gulf of Mexico, where it attained tropical storm intensity by 18:00 UTC on August 19 and reached peak winds of 60 mph (95 km/h) by early on August 21. The system moved ashore northeast of San Fernando, Tamaulipas with slightly weaker winds of 50 mph (85 km/h) before progressing inland and dissipating by 06:00 UTC on August 23.[2] Little impact was noted from the cyclone, with an observation station in northeastern Nuevo León recording a wind gust of only 17 mph (27 km/h). However, the storm did produce a maximum gust of 45 mph (72 km/h) in Brownsville, Texas.[4] Rainfall in the Rio Grande Valley was mostly beneficial due to drought conditions.[6]
Tropical Storm Six
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
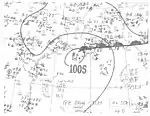 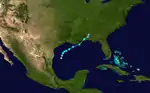 | |
| Duration | September 9 – September 11 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 mph (100 km/h) (1-min) 992 mbar (hPa) |
On September 8, a weak area of low pressure developed along the tail-end of a stationary front across the northern Gulf of Mexico.[4] It quickly organized into a tropical depression by 00:00 UTC the next day, positioned about 170 mi (275 km) southeast of Matamoros, Tamaulipas, and further attained tropical storm intensity twelve hours later. The fledgling system moved north and then northeast, making its first landfall along the Mississippi River Delta with peak winds of 65 mph (100 km/h) around 19:00 UTC on September 10. The system made its second landfall along Dauphin Island, Alabama, at 23:00 UTC at a slightly reduced intensity. It lost character by 12:00 UTC on September 11 and was last documented about 40 mi (65 km) southwest of Montgomery, Alabama.[2]
As the cyclone moved ashore, Mobile, Alabama, recorded its highest 24-hour rainfall total – 7.04 in (179 mm) – since 1937. The streets of the city were inundated by flood waters, sustaining considerable damage alongside bridges. The Mobile River reached a height of 3.8 ft (1.2 m) above sea level, its highest crest since 1932. Pensacola, Florida, recorded peak winds of 54 mph (87 km/h) that resulted in about $500 worth of damage from damaged dwelling roofs. Tides peaked around 1 ft (0.3 m).[4]
Hurricane Seven
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
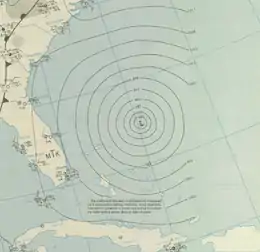  | |
| Duration | September 9 – September 15 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 145 mph (230 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 933 mbar (hPa) |
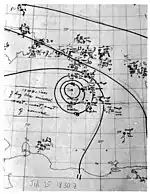
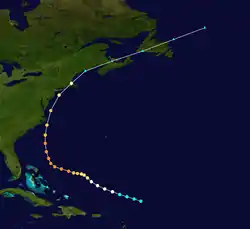
Observations from a reconnaissance aircraft flight indicated that a tropical wave had developed into a tropical cyclone by early on September 9 about 300 mi (485 km) northeast of the Lesser Antilles.[4] Already at tropical storm intensity, the system strengthened into a Category 1 hurricane about 24 hours later as it tracked west-northwestward. The storm intensified, reaching major hurricane intensity early on September 12. Several hours later, the storm strengthened into a Category 4 hurricane. The hurricane then curved north-northwestward on September 13.[2] At 17:00 UTC that day, a ship observed a barometric pressure of 933 mbar (27.6 inHg), the lowest in relation to the storm. Based on the pressure-wind relationship, sustained wind speeds likely peaked at 145 mph (230 km/h).[4] Early on September 14, the hurricane fell to Category 3 intensity, several hours before passing just offshore North Carolina. The cyclone weakened further to a Category 2 prior to making landfall near East Hampton, New York, around 02:00 UTC on September 15 and near Charlestown, Rhode Island, about two hours later. The storm emerged into the Gulf of Maine and then transitioned into an extratropical cyclone near Mount Desert Island, Maine. The extratropical remnants continued east-northeastward across Atlantic Canada before dissipating over the far north Atlantic on September 16.[2]
The cyclone produced hurricane-force winds along the East Coast of the United States from North Carolina to Massachusetts. Sustained winds in North Carolina peaked at 110 mph (180 km/h) at Hatteras. Across the state, the hurricane damaged 316 homes and destroyed 28 others, while 351 buildings were damaged and 80 others were destroyed. In Virginia, Cape Henry recorded a sustained wind of 134 mph (216 km/h).[7] However, Landsea; et al. disputed this and calculated that the sustain wind speed was at about a 30-second duration, rather than 1-minute, while the anemometer height was about 52 ft (16 m) above ground. Instead, the state likely experienced sustained winds up to Category 2 intensity.[4] Throughout Virginia, 1,350 homes suffered some degree of damage, while 782 buildings were damaged and 31 others were demolished. In Maryland, the storm damaged 650 homes, while the cyclone also damaged 300 buildings and destroyed 15 others. The storm damaged about 1,800 homes and 850 buildings in Delaware. New Jersey experienced some of the worst impacts from the hurricane, especially along the coast, due to storm surge and sustained winds up to 91 mph (146 km/h) in Atlantic City. Throughout the state, the cyclone demolished 463 homes and 217 buildings, while damaging 3,066 other homes and 635 other buildings. The storm produced hurricane-force winds in coastal New York, including in New York City, as well as waves up to 6.4 ft (2.0 m) above mean low tide. A total 117 homes and 272 buildings were destroyed and 2,427 homes and 852 suffered some degree of structural impact. In Connecticut, the hurricane demolished 60 residences and 500 buildings, while causing damage to 5,136 dwellings and 4,550 other structures. Rhode Island observed hurricane-force winds and tides up to 12 ft (3.7 m) above mean low tide at Providence. Within the state, the cyclone wrecked 23 homes and 368 buildings and damaged 5,525 homes and 7,597 buildings. Massachusetts reported similar conditions, especially near the coast. The hurricane destroyed 230 homes and 158 buildings and inflicted some degree of damage to 3,898 homes and 915 buildings. Overall, the hurricane caused about $100 million in damage and 46 deaths on land in the United States. Additionally, at least 344 people were killed at sea due to maritime incidents relating to the storm. The largest loss of life occurred when the USS Warrington sunk about 450 mi (725 km) east of Vero Beach, Florida, leading to the deaths of 248 sailors.[7] In Canada, the Atlantic provinces reported some wind damage to buildings, homes, and trees, as well as power outages. One person died in Nova Scotia due to electrocution.[8]
Hurricane Eight
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | September 19 – September 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) 996 mbar (hPa) |
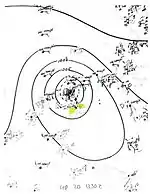
A tropical wave led to the formation of another tropical storm over the northwestern Caribbean Sea around 06:00 UTC on September 19.[3] It moved northwest after formation while steadily intensifying, attaining hurricane strength by 00:00 UTC the next day. The storm moved ashore near Cancún, Quintana Roo, with winds of 80 mph (130 km/h). After moving inland, the cyclone weakened to a tropical storm and curved southwestward. After emerging into the Bay of Campeche early on September 21, it re-attained peak winds of 80 mph (130 km/h) and made a second landfall near Paraíso, Tabasco. The cyclone turned south over the mountainous terrain of Mexico,[4] dissipating after 12:00 UTC on September 22.[2]
At least two people drowned offshore Campeche when a 100 ton (91,000 kg)-schooner sank. The hurricane produced torrential rainfall in the Isthmus of Tehuantepec region of Mexico, causing severe flooding. Between 200 and 300 people drowned,[3] while survivors sought refuge in trees and atop roofs and boxcars. Aircraft and boats conducted search and rescue operations throughout the region.[9] Floods also wrought extensive damage to the communication and transportation systems.[3]
Hurricane Nine
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
 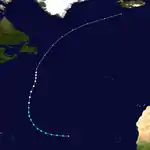 | |
| Duration | September 21 – September 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) |
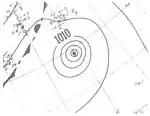
The ninth storm of the season formed early on September 21 via a tropical wave that departed the western coast of Africa several days prior.[2][4] The cyclone only slowly organized as it tracked west-northwest and then north, attaining hurricane strength early on September 24. After reaching its peak as a Category 2 hurricane with winds of 100 mph (160 km/h) around 12:00 UTC the next day, an approaching cold front prompted the beginning of extratropical transition, a process it completed early on September 26 well south of Newfoundland. The post-tropical cyclone curved northeast over the far northern Atlantic and was last noted south of Iceland two days later.[2]
Tropical Storm Ten
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | September 30 – October 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) 1003 mbar (hPa) |
On September 28, a broad area of low pressure developed adjacent to a dissipating warm front over the north-central Atlantic.[4] The cyclone congealed over the next two days and attained tropical storm status by 00:00 UTC on September 30,[2] corroborated by a nearby ship report.[4] It slowly intensified on a north and then northeast course, peaking with winds of 50 mph (85 km/h) early on October 1. The system weakened to a tropical depression the following day and was soon absorbed by an approaching extratropical cyclone by 00:00 UTC on October 3.[2]
Tropical Storm Eleven
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | September 30 – October 3 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) |
The eleventh tropical storm of the season began about 80 mi (130 km) north of Barbados around 06:00 UTC on September 30 as indicated by numerous ship and island observations. The short-lived cyclone moved northwest and then north ahead of an approaching trough, acquiring peak winds of 45 mph (75 km/h) shortly after formation before presumably dissipating on October 3. Alternatively, in the absence of widespread observations, the system may have continued into the central Atlantic unnoticed.[2][4]
Hurricane Twelve
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | October 11 – October 15 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) 998 mbar (hPa) |
A week into October, a broad area of low pressure began to take shape along a frontal boundary across the northeastern Atlantic. The system steadily acquired tropical characteristics, and it is first recognized as a tropical storm by 00:00 UTC on October 11 while located about 570 mi (915 km) west-southwest of the Azores. It drifted east and then northeast, attaining hurricane intensity and peaking with winds of 80 mph (130 km/h) by early on October 12. The cyclone resumed its eastward motion shortly thereafter and weakened below hurricane strength, passing north of the Azores before transitioning into an extratropical cyclone early on October 15. The post-tropical storm tracked east-southeast into Portugal and Spain, where sustained winds of 46 mph (74 km/h) were recorded in Seville.[2][4]
Hurricane Thirteen
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | October 12 – October 20 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 145 mph (230 km/h) (1-min) 937 mbar (hPa) |
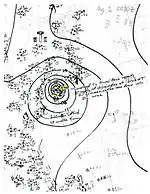
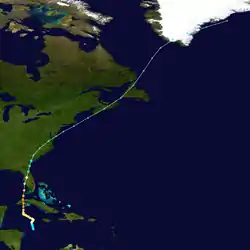
On October 12, a disturbance in the western Caribbean Sea organized into a tropical depression near the Swan Islands.[4][10] The system quickly strengthened as it drifted towards the north, becoming a hurricane the following day.[2] After turning towards the west, it passed south of Grand Cayman and then resumed an accelerated northward heading near the 83rd meridian west between October 16–17.[4][2] The hurricane intensified significantly during this period, quickly attaining Category 4 intensity before reaching its peak strength with winds of 145 mph (230 km/h) on October 18.[2] The storm made landfalls over Isla de la Juventud and the Cuban mainland with this intensity later that day,[2] passing 10–15 mi (16–24 km) west of Havana.[10] The storm weakened after crossing Cuba, but was unusually large given its location.[4] Its center passed over the Dry Tortugas as a major hurricane late on October 18 before striking Sarasota, Florida, the following morning with winds of 105 mph (170 km/h).[4] The storm's winds diminished gradually over the Florida peninsula, and eventually the system transitioned into an extratropical cyclone over South Carolina on October 20. This phase of the storm continued for four days before merging with the Icelandic Low near Greenland.[4][10]
The hurricane proved to be an important test of the American rawinsonde network, whose upper-atmosphere data were successfully incorporated into tropical cyclone track forecasting for the first time in history.[11] Squally conditions battered the Cayman Islands for three days, destroying all crops;[12] the 31.29 in (795 mm) of rain recorded on Grand Cayman was the highest in the island's history.[13][14] At least 300 people were killed in Cuba, though the full extent of casualties remains unknown as reports from rural areas of the island were never realized.[10] In Havana, numerous buildings were damaged.[15] A station in the city documented 163 mph (262 km/h) wind gust, which stood as the strongest gust measured in the country until 2008.[16] Florida's citrus crop suffered extensively, exacerbated by the hurricane's timing near optimal harvest time.[17] Total damage in the state amounted to $63 million,[10] with about $50 million attributed to crop damage.[17] Eighteen deaths were reported in the state and 24 others were hospitalized.[10] Heavy rains and gusty winds were felt throughout the Eastern Seaboard from the hurricane and its extratropical remnants,[5][18] causing widespread power outages. Overall, the hurricane caused more than $100 million in damage and at least 318 fatalities.[10]
Tropical Storm Fourteen
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | November 1 – November 3 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min) 1002 mbar (hPa) |
The final tropical cyclone of the 1944 season began as a tropical depression about 35 mi (55 km) southeast of San Andrés around 00:00 UTC on November 1. Executing a short counter-clockwise motion, the depression attained tropical storm intensity six hours later and further intensified to attain peak winds of 70 mph (110 km/h) early the next day. In the presence of minimal ship and land observations, however, it is possible the storm alternatively became a hurricane, with historical precedence in Hurricane Martha. It then weakened and dissipated on November 3 without moving ashore.[2][4]
Notes
- A major hurricane is a storm that ranks as Category 3 or higher on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale.[1]
References
- Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. National Hurricane Center (Report). Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. May 23, 2013. Retrieved September 21, 2020.
- "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)" (Database). United States National Hurricane Center. May 25, 2020.
- Edgar W. Woolard (December 1944). Monthly Weather Review: North Atlantic Hurricanes and Tropical Disturbances of 1944 (PDF) (Report). Washington, D.C.: Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory. Retrieved May 15, 2017.
- Christopher W. Landsea; et al. "Documentation of Atlantic Tropical Cyclones Changes in HURDAT". Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory. Retrieved May 15, 2017.
- Rainfall Associated With Hurricanes (PDF) (Report). Weather Prediction Center. July 1956. Retrieved May 12, 2017.
- "Hurricane Veers Into Campeche, Perils Mexico". The Brownsville Herald (44). Brownsville, Texas. August 23, 1944. p. 1. Retrieved February 4, 2021 – via Newspapers.com.
- Sumner, H. C. (September 1944). Woolward, Edgar W. (ed.). "The North Atlantic Hurricane Of September 8–14, 1944" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. Washington, D.C.: American Meteorological Society. 72 (9): 187–189. Bibcode:1944MWRv...72..187S. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1944)072<0187:TNAHOS>2.0.CO;2. Retrieved June 19, 2015.

- 1944-7 (Report). Environment Canada. November 7, 2009. Archived from the original on November 18, 2018. Retrieved February 4, 2021.
- "All Types of Craft Rushed to Rescue of Mexico Flood Victims". Iowa City Press-Citizen. Iowa City, Iowa. Associated Press. October 2, 1944. p. 8. Retrieved February 4, 2021 – via Newspapers.com.
- Sumner, H. C. (November 1944). "The North Atlantic Hurricane of October 13–21, 1944" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. Washington, D.C.: American Meteorological Society. 72 (11): 221–223. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1944)072<0221:TNAHOO>2.0.CO;2. Retrieved May 11, 2019.
- Rappaport, Edward N.; Simpson, Robert H. (January 1, 2003). "Impact of Technologies from Two World Wars". In Simpson, Robert H.; Anthes, Richard; Garstang, Michael; Simpson, Joanne (eds.). Hurricane! Coping with disaster: Progress and Challenges Since Galveston, 1900. Washington, D.C.: American Geophysical Union. pp. 49–50. doi:10.1029/SP055. ISBN 9780875902975. (subscription required)
- "Cayman Crops Destroyed". The Gazette (155). Montreal, Quebec. The Canadian Press. October 18, 1944. p. 1. Retrieved May 11, 2019 – via Newspapers.com.
- Barnes, Jay (May 2007). "Hurricanes in the Sunshine State, 1900–1949". Florida's hurricane history (2nd ed.). Chapel Hill, North Carolina: The University of North Carolina Press. pp. 163–166. ISBN 9780807858097.
- Roth, David M. (May 26, 2009). "Tropical Cyclone Rainfall" (PowerPoint Presentation). Camp Springs, Maryland: Weather Prediction Center. Archived from the original on May 31, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- "Six Killed, Damage Heavy as Hurricane Rips Havana". St. Petersburg Times (87). St. Petersburg, Florida. Associated Press. October 19, 1944. p. 11. Retrieved June 23, 2019 – via Newspapers.com.
- Rubiera, José (October 8, 2014). "Crónica del Tiempo: Los huracanes y octubre". CubaDebate (in Spanish). Havana, Cuba: Universidad de las Ciencias Informáticas. Archived from the original on June 7, 2019. Retrieved June 27, 2019.
- Bennett, W. J. (October 1944). "Florida Section". Climatological Data. Jacksonville, Florida: National Climatic Data Center. 48 (10): 55.
- "Hurricane Lashes South Carolina, Moves On". St. Petersburg Times (88). St. Petersburg, Florida. Associated Press. October 20, 1944. pp. 1, 2. Retrieved June 24, 2019 – via Newspapers.com.