2019 Greek legislative election
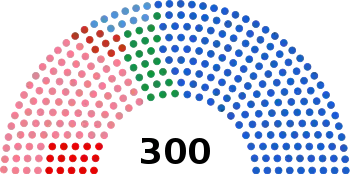
The 2019 Greek legislative election was held on 7 July 2019.[1][2] All 300 seats in the Hellenic Parliament were contested.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 300 seats in the Hellenic Parliament 151 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Registered | 9,962,261 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 57.91% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
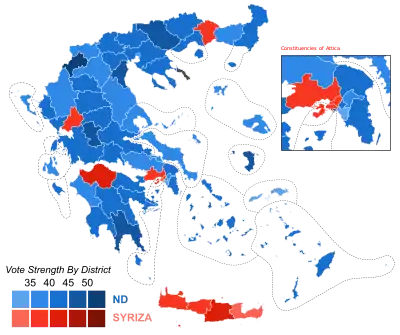 Map of electoral districts, showing the largest party by share of votes. Blue indicates New Democracy was the largest, and Pink indicates SYRIZA was the largest. Darker shades indicate stronger vote share. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Preliminary results showed that the centre-right liberal conservative New Democracy party, led by Kyriakos Mitsotakis, won 158 seats, an outright majority that is more than double the party's previous representation. The party took nearly 40% of the popular vote.
This was the first national election in Greece and third election overall since the voting age was lowered to 17, and the number of parliamentary constituencies was increased from 56 to 59. Athens B, the largest constituency with 44 seats before the 2018 reform, was broken up into smaller constituencies, the largest of which has 18 seats.
On 26 May 2019, following his defeat in the 2019 European Parliament election in Greece and the concurrent local elections, Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras announced that a snap election would be held as soon as possible following the second round of the 2019 municipal elections.[3]
Electoral system
.svg.png.webp)

Compulsory voting was in force for the elections, with voter registration being automatic.[4] However, none of the legally existing penalties or sanctions have ever been enforced.[5]
A number of changes to the electoral system were introduced following the September 2015 elections. The voting age was reduced from 18 to 17 in July 2016,[6] with the same law also abolishing the majority bonus system, which gave a 50-seat bonus to the largest party. Instead, all 300 seats would be awarded proportionally.[6] However, this law did not come into effect for the 2019 elections, as it was not approved with the required supermajority despite the Syriza-led government expressing support for its introduction for the 2019 elections.[7] As a result, the previous system remained in force, with 250 seats elected in multi-member constituencies using a 3% electoral threshold, plus 50 bonus seats for the largest party.
The number of parliamentary constituencies was also modified in December 2018, with Athens B split into Athens B1 (North), Athens B2 (West), and Athens B3 (South), while Attica was split into East Attica and West Attica.[8]
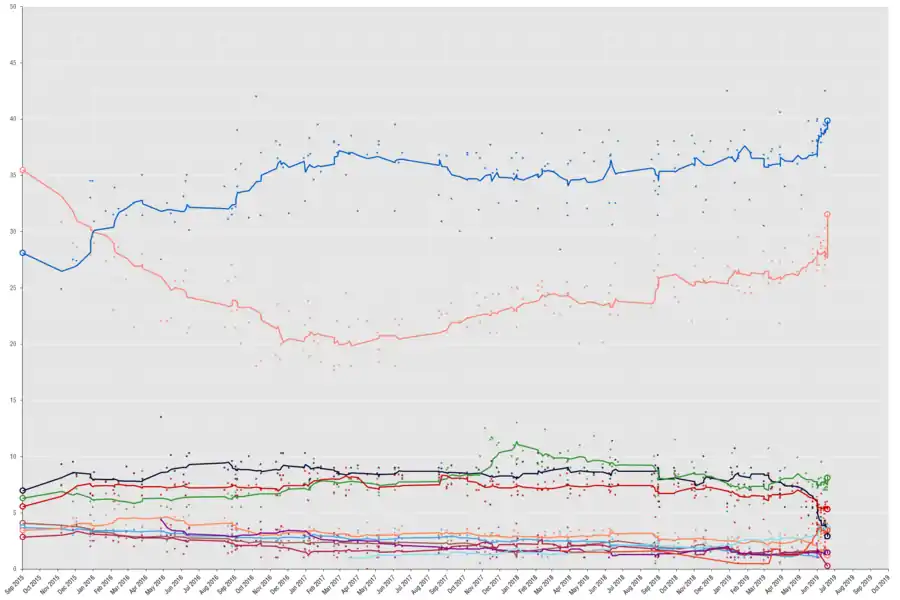
Opinion polls
Conduct
A few minutes before the polls closed, a group of young protesters stormed the 33-d polling station in the distinct of Exarcheia in Athens and stole the ballot box. Subsequently, a previously unknown anarchist group called 'Ballot-seeking Arsonists' claimed responsibility. The group claimed that they burned the stolen ballot box. As a result, a repeat election at the same polling station was held a week later, on Sunday, 14 July.[9][10] The results did not change the final allocation of seats due to the small volume of votes.
Results
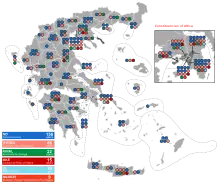
 | ||||||
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Democracy | 2,251,426 | 39.85 | 158 | +83 | ||
| Syriza | 1,781,180 | 31.53 | 86 | –59 | ||
| Movement for Change | 457,527 | 8.10 | 22 | +5 | ||
| Communist Party of Greece | 299,595 | 5.30 | 15 | 0 | ||
| Greek Solution | 208,806 | 3.70 | 10 | New | ||
| MeRA25 | 194,233 | 3.44 | 9 | New | ||
| Golden Dawn | 165,711 | 2.93 | 0 | –18 | ||
| Course of Freedom | 82,673 | 1.46 | 0 | New | ||
| Union of Centrists | 70,161 | 1.24 | 0 | –9 | ||
| Recreate Greece | 41,647 | 0.74 | 0 | 0 | ||
| EPAM–AKKEL | 28,269 | 0.50 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Antarsya | 23,191 | 0.41 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Popular Unity | 15,930 | 0.28 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Greek Assembly | 14,173 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Communist Party of Greece (Marxist–Leninist) | 7,778 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Marxist–Leninist Communist Party of Greece | 2,791 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Workers Revolutionary Party | 1,993 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Organisation of Internationalist Communists of Greece | 1,675 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Syn...Fonia Politikon Kommaton | 96 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Independents | 472 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 120,172 | – | – | – | ||
| Total | 5,769,542 | 100 | 300 | 0 | ||
| Registered voters/turnout | 9,962,261 | 57.91 | – | – | ||
| Source: Ministry of the Interior | ||||||
References
- "Greek elections: New Democracy on course for majority". BBC News. 7 July 2019. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- Mylonas, Harris (2020). "Greece: Political Developments and Data in 2019". European Journal of Political Research Political Data Yearbook. doi:10.1111/2047-8852.12299. ISSN 2047-8852.
- "After defeat, Greek PM calls for snap elections | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
- "Constitution of Greece" (PDF). Hellenic Parliament. Retrieved 5 November 2011.
Article 51, Clause 5: The exercise of the right to vote is compulsory.
- Υποχρεωτική η ψήφος αλλά "παγωμένες" οι κυρώσεις [Voting is mandatory, but penalties "frozen"]. Eleftherotypia (in Greek). Archived from the original on 17 February 2013. Retrieved 7 November 2011.
- Εφημερίδα της Κυβερνήσεως τη Ελληνικής Δημοκρατίας [Government Gazette of the Hellenic Republic] (in Greek), A, Athens: National Publishing House, 27 July 2016, retrieved 12 February 2019
- "Σκουρλέτης: Μακάρι η απλή αναλογική να εφαρμοστεί στις επόμενες εκλογές" [Skourletis: I hope the simple proportional representation system will be enforced in the next elections]. www.kathimerini.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 12 March 2019.
- Εφημερίδα της Κυβερνήσεως τη Ελληνικής Δημοκρατίας [Government Gazette of the Hellenic Republic] (in Greek), A, Athens: National Publishing House, 31 December 2018, retrieved 12 February 2019
- "Anarchist group claims responsibility for stolen ballot box". Kathimerini. 8 July 2019. Retrieved 8 July 2019.
- "Anarchists Storm Polling Station and Burn Ballot Box in Athens". Greek Reporter. 7 July 2019. Retrieved 8 July 2019.
_(cropped)_(2).jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)


