50th Armored Division (United States)
The 50th Armored Division was a division of the Army National Guard from July 1946 until 1993.
| 50th Armored Division | |
|---|---|
 50th Armored Division shoulder sleeve insignia | |
| Active | 1946–93 |
| Country | |
| Branch | |
| Type | Armored warfare |
| Size | Division |
| Part of | New Jersey Army National Guard |
| Nickname(s) | "Jersey Blues" |
| Commanders | |
| Notable commanders | Donald W. McGowan |
| Insignia | |
| Distinctive unit insignia |  |
| U.S. Armored Divisions | |
|---|---|
| Previous | Next |
| 49th Armored Division (Inactive) | N/A |
History

On 13 October 1945 the War Department published a postwar policy statement for the entire Army, calling for a 27-division Army National Guard structure with 25 infantry divisions and two armored divisions. Once the process of negotiation was complete, among the new formations formed were the 49th and 50th Armored Divisions, the first armored divisions in the Army National Guard. The 50th Armored Division replaced the 44th Infantry Division within the New Jersey Army National Guard, with the 50th Armored assuming the 44th Infantry's "Jersey Blues" nickname. Most 50th Armored Division units were legacy units of the 44th Infantry and inherited the lineage and history of those units.
In a 1968 reorganization, the 50th Armored was joined by the 27th Armored Brigade from New York, the legacy units left after the inactivation of the 27th Armored Division. Since the 50th Armored Division was no longer completely within New Jersey, it retired the "Jersey Blues" nickname. In 1968, the 50th Armored Division was reorganized to draw its units from New Jersey and the Vermont Army National Guard. Armor battalions in New Jersey and Vermont were upgraded to M48A1 and M48A3 Patton medium tanks.
Between 1975-76 Vermont and New Jersey armor battalions started turning in their M48A3 tanks and began receiving the M48A5 which had the same 105mm gun and fire control system as the M60A1 in use by the active Army. During this time, many Vermont tank crews competed in gunnery exercises held in West Germany and consistently brought back awards. The division's training was rigorous during the Soviet threat peak years of the late 1970s to mid 1980s. Germany was the primary area of operations for the division if it was to have been activated.
The bi-state organization comprised:[1]
- Headquarters, 50th Armored Division (Somerset, New Jersey)
- 104th Engineer Battalion HQ & HQ, Co.A, Co.B, Co.C, Co.E (bridge) Teaneck, New Jersey. Co.D, Vermont
- 5th Squadron, 117th Cavalry
- 150th Aviation Battalion (UH-1 & AH-1 Hueys) (later 1st Battalion, 150th Aviation)
- 1st Brigade (Woodbridge, New Jersey)
- 2nd Brigade (Cherry Hill, New Jersey)
- 86th Brigade (Montpelier, Vermont)
- Division Artillery (Trenton, New Jersey)
- Division Support Command
The Center of Military History notes that reorganizing the Army National Guard to meet the new 'Division 86' structures in the mid-1980s was a challenging process, and most Guard divisions expanded their recruiting areas. The 50th Armored Division did not, and instead had the allotment for one of its brigades moved to the Texas Army National Guard, making the future of the division within the force structure 'uncertain'. During this time, both battalions of Vermont's 172nd Armor 86th Brigade began doing their annual training at Fort Hood, Texas, a change from their former armor deployment base of Fort Drum, New York. By October 1986, Vermont's 86th Brigade left the 50th Armor Division and became part of the 26th Infantry Division. A few years later the 86th went to the 42nd ID and got M60A3 medium tanks.
Inactivation
On 1 September 1993, the 50th Armored Division was inactivated and its remaining brigades joined other divisions.[2] New Jersey's 50th Infantry Brigade, which took the Division's lineage, was made part of the 42nd Infantry Division. The 36th Infantry Brigade from Texas was reabsorbed into the 49th Armored Division. In the early 1990s further consolidation followed the fall of the Soviet Union, and the 26th Infantry Division disbanded, causing Vermont's 86th Brigade to join the 42nd Infantry Division and soon receive M1A2 Abrams main battle tanks. While under the 50th Armor Division, Vermont's 1-172nd and 2-172nd Armored Battalions of the 86th Brigade excelled at tank gunnery and field exercises, making the 86th Brigade the only Army National Guard unit to ever consistently accomplish Tank Table XIII, an honor it continued to earn even after the 50th AD disbanded. Due to further military consolidations, the 86th Brigade turned in its Abrams tanks in 2006 and ended its Armor designation just short of 40 years.
Organization 1989
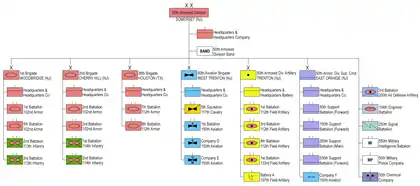
1-150 Aviation
At the end of the Cold War the division was a unit of the New Jersey Army National Guard, with a round-out brigade from the Texas Army National Guard. The division was organized according to the Army of Excellence table of organization and equipment:
- 50th Armored Division, Somerset, New Jersey
- Headquarters & Headquarters Company
- 1st Brigade, Woodbridge[3]
- Headquarters & Headquarters Company
- 1st Battalion, 102nd Armor, Phillipsburg[4][5][3]
- 2nd Battalion, 113th Infantry Newark[6][3]
- 3rd Battalion, 113th Infantry, Riverdale[6][3]
- 2nd Brigade, Cherry Hill[3]
- Headquarters & Headquarters Company
- 2nd Battalion, 102nd Armor, West Orange[7][5][3]
- 3rd Battalion, 102nd Armor Vineland[5][3]
- 1st Battalion, 114th Infantry, Woodbury[8][9][3]
- 2nd Battalion, 114th Infantry Long Branch[9][3]
- 36th Brigade, Houston, Texas (Texas Army National Guard)[10][11][12]
- 50th Aviation Brigade, West Trenton[3]
- Headquarters & Headquarters Company
- 5th Squadron, 117th Cavalry (Reconnaissance), Westfield Army Airfield[14][3]
- 1st Battalion, 150th Aviation (Attack), West Trenton[3]
- Company D, 150th Aviation (Command Support), Burlington Army Airfield (Vermont Army National Guard)
- Company E, 150th Aviation (Assault), New Castle Army Airfield (Delaware Army National Guard)
- 50th Armored Division Artillery, Trenton[15][16][17]
- Headquarters & Headquarters Battery
- 1st Battalion, 112th Field Artillery Cherry Hill[3] (18 × M109A3 155mm self-propelled howitzers)[18][15][16][17][19]
- 3rd Battalion, 112th Field Artillery, Morristown[3] (18 × M109A3 155mm self-propelled howitzers)[18][15][16][17][19]
- 4th Battalion, 112th Field Artillery Lawrenceville (12 × M110A2 203mm self-propelled howitzers)[18][15][16][17][19]
- 1st Battalion, 133rd Field Artillery Beaumont (Texas Army National Guard) (18 × M109A3 155mm self-propelled howitzers)[15][16][17][19][11]
- Battery A, 197th Field Artillery (Target Acquisition) (New Hampshire Army National Guard)[20][15][16][17][19]
- 50th Armored Division Support Command, East Orange[21][3]
- Headquarters & Headquarters Company
- 50th Support Battalion (Forward), Teaneck[3]
- 150th Support Battalion (Forward), Jersey City[3]
- 250th Support Battalion (Main), Sea Girt[22][3]
- 536th Support Battalion (Forward) (Texas Army National Guard)
- Company F, 150th Aviation (Aviation Intermediate Maintenance), Dover[3]
- 3rd Battalion, 200th Air Defense Artillery (New Mexico Army National Guard)[23] (MIM-72 Chaparral, M163 Vulcan & FIM-92 Stinger)
- 104th Engineer Battalion, Teaneck[24][3]
- 250th Signal Battalion, Plainfield[25]
- 550th Military Intelligence Battalion, Pedricktown[26][27]
- 50th Military Police Company, Somerset[3][28]
- 50th Chemical Company, Sea Girt[3]
- 50th Armored Division Band, Jersey City[3]
The brigade's armor battalions were equipped with M60A3 TTS main battle tanks. M48A5 Patton tanks had been replaced by M60A3 TTS tanks by May 1987 and by the end of 1989 the National Guard fielded 3,072 M60A3 TTS.[29][30][31] The 410 M1 Abrams[29] tanks of the National Guard were issued to round-out units of army divisions.[32] The division's infantry battalions were equipped with M113 armored personnel carriers, of which the National Guard had 6,870 at the end of Fiscal Year 1987, with a further 1,411 due to be taken in service in 1988.[29] The standard helicopters of National Guard units were the AH-1S Cobra, of which the National Guard had approximately 350 by 1989,[33] the OH-58C Kiowa and the UH-1H Iroquois helicopters.[34] Cavalry Reconnaissance units fielded 19 × M60A3 TTS, 8 × AH-1S Cobra, 12 × OH-58C Kiowa and 1 × UH-1H Iroquois helicopters; attack battalions fielded 21 × AH-1S Cobra, 13 × OH-58C Kiowa and 3 × UH-1H Iroquois helicopters,[35] while the assault aviation company fielded 15 × UH-1H Iroquois helicopters and the command support aviation company UH-1 helicopters in various configurations.
References
- Notes
- David C Isby and Charles Kamps Jr, Armies of NATO's Central Front, Jane's Publishing Company Ltd, London, 1985, p. 384
- New Jersey Military and Veterans Affairs – Militia Museum of New Jersey
- Annual Report 1988. The New Jersey Department of Military and Veterans' Affairs. 1988.
- "Brigadier General Kenneth F. Wondrack". National Guard Bureau. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "102nd Cavalry Regiment Lineage". US Army Center of Military History. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "113th Infantry Regiment". National Guard Militia Museum of New Jersey. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Brigadier General Frank W. Dulfer". National Guard Bureau. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Brigadier General Frank R. Carlini". National Guard Bureau. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "114th Infantry Regiment Lineage". US Army Center of Military History. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "A Brief History of the Texas National Guard after World War II". Texas Military Forces Museum. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "133rd U.S. Field Artillery Regiment". Texas Military Forces Museum. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Department of the Army Historical Summary". Center of Military History. 1988. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Major General Darren G. Owens". National Guard Bureau. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "117th Cavalry Regiment". National Guard Militia Museum of New Jersey. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Field Artillery - February 1987". US Army Field Artillery School. 1987. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- "Field Artillery - December 1989". US Army Field Artillery School. 1988. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- "Field Artillery - February 1990". US Army Field Artillery School. 1990. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- "112th Field Artillery Regiment Lineage". US Army Center of Military History. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- McKenney, Janice E. "Field Artillery - Army Lineage Series - Part 2" (PDF). US Army Center of Military History. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- "197th Fires Brigade Lineage - Annex 3". US Army Center of Military History. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "42nd Support Group Lineage". US Army Center of Military History. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Change of Command" (PDF). The Westfield (NJ) Leader, Thursday December 15, 1988. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- "Air Defense Artillery" (PDF). US Army Center of Military History. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "104th Engineer Battalion". National Guard Militia Museum of New Jersey. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- Raines, Rebecca Robbins. "Signal Corps" (PDF). US Army Center of Military History. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- "Military Intelligence, Volume 15, Issue 4". Military Intelligence Magazine October - December 1989. 1989. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- John Patrick Finnegan; Romana Danysh. "Military Intelligence" (PDF). US Army Center of Military History. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- "Justification of the budget estimates, Army - 1988". US Congress. 1987. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Hearings on National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Years 1988/1989". United States Congress - House Committee on Armed Services. 1988. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- "Historical Summary: FY 1984 - 5 Research, Development, and Acquisition". Department of the Army. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- "M60A3 (TTS) Basis of Issue Plan". US Army. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- "Three Guard units to get M1 tanks". Armor July-August 1982. 1982. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- "Hearings on National Defense Authorization Act for fiscal years 1988/1989". United States Congress - House Committee on Armed Services. 1988. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- "Hearings on National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Years 1988/1989". United States Congress - House Committee on Armed Services. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- Lussier, Frances M. "An Analysis of U.S. Army Helicopter Programs". Congress of the United States - Congressional Budget Office. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- Bibliography
- "Chapter XIII The Total Army". Manoeuvre and Firepower: The Evolution of Divisions and Separate Brigades. United States Army Center of Military History. 1998. CMH Pub 60-14. Archived from the original on 26 December 2012.
- http://www.geocities.com/armored50th/50th_Armored.html (Archived 2009-10-23)