Trenton, New Jersey
Trenton is the capital city of the U.S. state of New Jersey and the county seat of Mercer County.[22] It briefly served as the capital of the United States in 1784.[23] The city's metropolitan area, consisting of Mercer County, is grouped with the New York Combined Statistical Area by the United States Census Bureau,[24] but it directly borders the Philadelphia metropolitan area and was from 1990 until 2000 part of the Philadelphia Combined Statistical Area.[25] As of the 2010 United States Census, Trenton had a population of 84,913,[10][11][12] making it the state's 10th-largest municipality after having been the state's ninth-largest municipality in 2000.[26] The population declined by 490 (-0.6%) from the 85,403 counted in the 2000 Census, which had in turn declined by 3,272 (-3.7%) from the 88,675 counted in the 1990 Census.[27] The Census Bureau's Population Estimates Program calculated that the city's population was 83,203 in 2019,[13] ranking the city the 413th-most-populous in the country.[14]
Trenton, New Jersey | |
|---|---|
| City of Trenton | |
 Downtown on the Delaware River | |
 Flag | |
| Nickname(s): Capital City Turning Point of the Revolution. | |
| Motto(s): "Trenton Makes, The World Takes"[1] | |
 Location within Mercer County
| |
 Census Bureau map of Trenton, New Jersey | |
 Trenton Location in Mercer County  Trenton Location in New Jersey  Trenton Location in the United States | |
| Coordinates: 40.223841°N 74.763624°W[2][3] | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | |
| Founded | June 3, 1719 |
| Incorporated | November 13, 1792 |
| Named for | William Trent |
| Government | |
| • Type | Faulkner Act |
| • Body | City Council |
| • Mayor | Reed Gusciora (term ends June 30, 2022)[5][6] |
| • Administrator | Adam E. Cruz[7] |
| • Municipal clerk | Dwayne M. Harris[8] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 8.21 sq mi (21.25 km2) |
| • Land | 7.58 sq mi (19.63 km2) |
| • Water | 0.63 sq mi (1.62 km2) 7.62% |
| Area rank | 229th of 565 in state 9th of 12 in county[2] |
| Elevation | 49 ft (15 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 84,913 |
| • Estimate (2019)[13] | 83,203 |
| • Rank | 413th in country (as of 2019)[14] 10th of 565 in state 2nd of 12 in county[15] |
| • Density | 11,101.9/sq mi (4,286.5/km2) |
| • Density rank | 26th of 565 in state 1st of 12 in county[15] |
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (Eastern (EDT)) |
| ZIP Codes | |
| Area code | 609[18] |
| FIPS code | 3402174000[2][19][20] |
| GNIS feature ID | 0885421[2][21] |
| Website | trentonnj |
Trenton dates back at least to June 3, 1719, when mention was made of a constable being appointed for Trenton while the area was still part of Hunterdon County. Boundaries were recorded for Trenton Township as of March 2, 1720.[28] A courthouse and jail were constructed in Trenton around 1720, and the Freeholders of Hunterdon County met annually in Trenton.[29] Trenton became New Jersey's capital as of November 25, 1790, and the City of Trenton was formed within Trenton Township on November 13, 1792. Trenton Township was incorporated as one of New Jersey's initial group of 104 townships by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on February 21, 1798. On February 22, 1834, portions of Trenton Township were taken to form Ewing Township. The remaining portion of Trenton Township was absorbed by the City of Trenton on April 10, 1837. A series of annexations took place over a 50-year period, with the city absorbing South Trenton borough (April 14, 1851), portions of Nottingham Township (April 14, 1856), both the Borough of Chambersburg Township, and Millham Township (both on March 30, 1888), as well as Wilbur Borough (February 28, 1898). Portions of Ewing Township and Hamilton Township were annexed to Trenton on March 23, 1900.[28][30]
History
.jpg.webp)
The earliest known inhabitants of the area that is today Trenton were the Lenape Native Americans.[31] The first European settlement in what would become Trenton was established by Quakers in 1679, in the region then called the Falls of the Delaware, led by Mahlon Stacy from Handsworth, Sheffield, England. Quakers were being persecuted in England at this time and North America provided an opportunity to exercise their religious freedom.[32]
By 1719, the town adopted the name "Trent-towne", after William Trent, one of its leading landholders who purchased much of the surrounding land from Stacy's family. This name later was shortened to "Trenton".[33][34][35]
During the American Revolutionary War, the city was the site of the Battle of Trenton, George Washington's first military victory. On December 25–26, 1776, Washington and his army, after crossing the icy Delaware River to Trenton, defeated the Hessian troops garrisoned there.[36] The second battle of Trenton, Battle of the Assunpink Creek, was fought here on January 2, 1777.[37] After the war, the Congress of the Confederation met for two months at the French Arms Tavern from November 1, 1784, to December 24, 1784.[23] While the city was preferred by New England and other northern states as a permanent capital for the new country, the southern states ultimately prevailed in their choice of a location south of the Mason–Dixon line.[38] On April 21, 1789, the city hosted a reception for George Washington on his journey to New York City for his first inauguration.[39]
Trenton became the state capital in 1790, but prior to that year the New Jersey Legislature often met in the city.[40] The city was incorporated in 1792.[28]
During the War of 1812, the United States Army's primary hospital was at a site on Broad Street.[41]
Throughout the 19th century, Trenton grew steadily, as European immigrants came to work in its pottery and wire rope mills. In 1837, with the population now too large for government by council, a new mayoral government was adopted, with by-laws that remain in operation to this day.[42]
The Trenton Six were a group of black men arrested for the alleged murder of an elderly white shopkeeper in January 1948 with a soda bottle. They were arrested without warrants, denied lawyers and sentenced to death based on what were described as coerced confessions. With the involvement of the Communist Party and the NAACP, there were several appeals, resulting in a total of four trials. Eventually the accused men (with the exception of one who died in prison) were released. The incident was the subject of the book Jersey Justice: The Story of the Trenton Six, written by Cathy Knepper.[43][44]
Riots of 1968
The Trenton Riots of 1968 were a major civil disturbance that took place during the week following the assassination of civil rights leader Martin Luther King Jr. in Memphis on April 4. Race riots broke out nationwide following the murder of the civil rights activist. More than 200 Trenton businesses, mostly in Downtown, were ransacked and burned. More than 300 people, most of them young black men, were arrested on charges ranging from assault and arson to looting and violating the mayor's emergency curfew. In addition to 16 injured policemen, 15 firefighters were treated at city hospitals for smoke inhalation, burns, sprains and cuts suffered while fighting raging blazes or for injuries inflicted by rioters. Citizens of Trenton's urban core often pulled false alarms and would then throw bricks at firefighters responding to the alarm boxes. This experience, along with similar experiences in other major cities, effectively ended the use of open-cab fire engines. As an interim measure, the Trenton Fire Department fabricated temporary cab enclosures from steel deck plating until new equipment could be obtained. The losses incurred by downtown businesses were initially estimated by the city to be $7 million, but the total of insurance claims and settlements came to $2.5 million.[45]
Trenton's Battle Monument neighborhood was hardest hit. Since the 1950s, North Trenton had witnessed a steady exodus of middle-class residents, and the riots spelled the end for North Trenton. By the 1970s, the region had become one of the most blighted and crime-ridden in the city.[46]
Geography

According to the United States Census Bureau, the city had a total area of 8.21 square miles (21.25 km2), including 7.58 square miles (19.63 km2) of land and 0.63 square miles (1.62 km2) of water (7.62%).[2][3]
Several bridges across the Delaware River connect Trenton to Morrisville, Pennsylvania, all of which are operated by the Delaware River Joint Toll Bridge Commission.[47] The Trenton–Morrisville Toll Bridge, originally constructed in 1952, stretches 1,324 feet (404 m), carrying U.S. Route 1.[48] The Lower Trenton Bridge, bearing the legend "Trenton Makes The World Takes Bridge", is a 1,022-foot (312 m) span that was constructed in 1928 on the site of a bridge that dates back to 1804.[49] The Calhoun Street Bridge, dating back to 1884, is 1,274 feet (388 m) long.[50]
Trenton is located near the geographic center of the state, which is located 5 miles (8.0 km) southeast of the city.[51][52] The city is sometimes included as part of North Jersey and as the southernmost city of the Tri-State Region, while others consider it a part of South Jersey and thus, the northernmost city of the Delaware Valley.[53]
However, Mercer County constitutes its own metropolitan statistical area, formally known as the Trenton-Princeton MSA.[54] Locals consider Trenton to be a part of an ambiguous area known as Central Jersey, and thus part of neither region. They are generally split as to whether they are within New York or Philadelphia's sphere of influence. While it is geographically closer to Philadelphia, many people who have recently moved to the area commute to New York City, and have moved there to escape the New York region's high housing costs.
Trenton is one of two state capitals that border another state – the other being Carson City, Nevada.[55] It is also one of the seven state capitals located within the Piedmont Plateau.
Trenton borders Ewing Township, Hamilton Township and Lawrence Township in Mercer County; and Falls Township, Lower Makefield Township and Morrisville in Bucks County, Pennsylvania across the Delaware River in Pennsylvania.[56][57][58]
The Northeast Corridor goes through Trenton. A straight line drawn between Center City, Philadelphia and Downtown Manhattan would pass within 2000 feet of the New Jersey State House.
Panoramic views

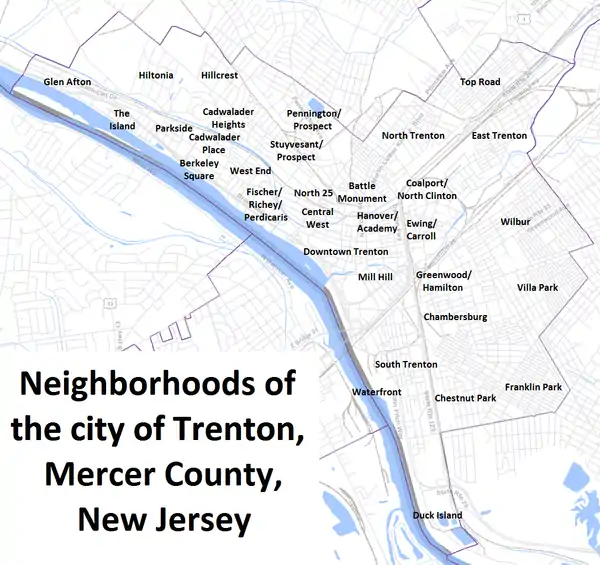
Neighborhoods
The city of Trenton is home to numerous neighborhoods and sub-neighborhoods. The main neighborhoods are taken from the four cardinal directions (North, South, East, and West). Trenton was once home to large Italian, Hungarian, and Jewish communities, but, since the 1950s, demographic shifts have changed the city into a relatively segregated urban enclave of middle and lower income African Americans. Italians are scattered throughout the city, but a distinct Italian community is centered in the Chambersburg neighborhood, in South Trenton.[59] This community has been in decline since the 1970s, largely due to economic and social shifts to the suburbs surrounding the city. Today Chambersburg has a large Latino community. Many of the Latino immigrants are from Mexico, Guatemala and Nicaragua. There is also a significant and growing Asian community in the Chambersburg neighborhood primarily made up of Burmese and Bhutanese/Nepali refugees.
The North Ward, once a mecca for the city's middle class, is now one of the most economically distressed, torn apart by race riots following the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. in 1968. Nonetheless, the area still retains many important architectural and historic sites. North Trenton still has a large Polish-American neighborhood that borders Lawrence Township, many of whom attend St. Hedwig's Roman Catholic Church on Brunswick Avenue. St. Hedwig's church was built in 1904 by Polish immigrants, many of whose families still attend the church. North Trenton is also home to the historic Shiloh Baptist Church—one of the largest houses of worship in Trenton and the oldest African American church in the city, founded in 1888.[60] The church is currently pastored by Rev. Darrell L. Armstrong, who carried the Olympic torch in 2002 for the Winter Olympics in Salt Lake City. Also located just at the southern tip of North Trenton is the city's Battle Monument, also known as "Five Points". It is a 150 ft (46 m) structure that marks the spot where George Washington's Continental Army launched the Battle of Trenton during the American Revolutionary War. It faces downtown Trenton and is a symbol of the city's historic past.[61]
South Ward is a diverse neighborhood, home to many Latin American, Italian-American, and African American residents.[62]
East Ward is the smallest neighborhood in Trenton and is home to the Trenton Transit Center and Trenton Central High School. The Chambersburg neighborhood is within the East Ward and was once noted in the region as a destination for its many Italian restaurants and pizzerias. With changing demographics, many of these businesses have either closed or relocated to suburban locations.
West Ward is the home of Trenton's more suburban neighborhoods.
Neighborhoods in the city include:[63]
- Downtown Trenton
- East Trenton
- Western Trenton (not the same as West Trenton, which is outside the city limits in Ewing)
- Berkeley Square
- Cadwalader Heights
- Central West
- Fisher/Richey/Perdicaris
- Glen Afton
- Hillcrest
- Hiltonia
- Parkside
- Pennington/Prospect
- Stuyvesant/Prospect
- The Island
- West End
- South Trenton
- Chambersburg
- Chestnut Park
- Duck Island
- Franklin Park
- Lamberton/Waterfront
- North Trenton
- Battle Monument (Five Points)
- North 25
- Top Road
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification, Trenton lies in the transition from a humid subtropical (Cfa) to a cooler humid continental climate (Dfa), favoring the former, with four seasons of approximately equal length and precipitation fairly evenly distributed through the year. The Cfa climate is the result of adiabatic warming of the Appalachians, low altitude and proximity to the coast without being on the immediate edge for moderate temperatures.[64]
Winters are cold and damp: the daily average temperature in January is 32.0 °F (0.0 °C),[65] and temperatures at or below 10 °F (−12 °C) occur on 3.9 nights annually, while there are 16–17 days where the temperature fails to rise above freezing. Episodes of extreme cold and wind can occur with wind chill values below 0 °F (−18 °C). The plant hardiness zone at the Trenton Municipal Court is 7a with an average annual extreme minimum air temperature of 1.2 °F (−17.1 °C).[66]
Summers are hot and humid, with a July daily average of 76.0 °F (24.4 °C); temperatures reaching or exceeding 90 °F (32 °C) occur on 15–16 days. episodes of extreme heat and humidity can occur with heat index values reaching 100 °F (38 °C). Extremes in air temperature have ranged from −14 °F (−26 °C) on February 9, 1934, up to 106 °F (41 °C) as recently as July 22, 2011.[67] However, air temperatures reaching 0 °F (−18 °C) or 100 °F (38 °C) are uncommon.
The average precipitation is 48.34 inches (123 cm) per year, which is fairly evenly distributed through the year. The driest month on average is February, with 2.81 in (71 mm) of precipitation on average, while the wettest month is July with 5.32 in (14 cm) of rainfall on average which corresponds with the annual peak in thunderstorm activity. The all-time single-day rainfall record is 7.25 in (18.4 cm) on September 16, 1999, during the passage of Hurricane Floyd. The all-time monthly rainfall record is 14.55 in (37.0 cm) in August 1955, due to the passage of Hurricane Connie and Hurricane Diane. The wettest year on record was 1996, when 67.90 in (172 cm) of precipitation fell. On the flip side, the driest month on record was October 1963, when only 0.05 in (0.1 cm) of rain was recorded. The 28.79 in (73 cm) of precipitation recorded in 1957 were the lowest ever for the city.[68]
Snowfall can vary even more year to year. The average seasonal (November–April) snowfall total is 24 to 30 inches (61 to 76 cm), but has ranged from as low as 2 in (5.1 cm) in the winter of 1918–19 to as high as 76.5 in (194.3 cm) in 1995–96, which included the greatest single-storm snowfall, the Blizzard of January 7–8, 1996, when 24.2 inches (61.5 cm) of snow fell.[69] The average snowiest month is February which corresponds with the annual peak in nor'easter activity.
Ecology
According to the A. W. Kuchler U.S. potential natural vegetation types, Trenton, New Jersey would have an Appalachian Oak (104) vegetation type with an Eastern Hardwood Forest (25) vegetation form.[70]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 1,946 | — | |
| 1810 | 3,000 | — | |
| 1820 | 3,942 | 31.4% | |
| 1830 | 3,925 | −0.4% | |
| 1840 | 4,035 | * | 2.8% |
| 1850 | 6,461 | 60.1% | |
| 1860 | 17,228 | * | 166.6% |
| 1870 | 22,874 | 32.8% | |
| 1880 | 29,910 | 30.8% | |
| 1890 | 57,458 | * | 92.1% |
| 1900 | 73,307 | 27.6% | |
| 1910 | 96,815 | 32.1% | |
| 1920 | 119,289 | 23.2% | |
| 1930 | 123,356 | 3.4% | |
| 1940 | 124,697 | 1.1% | |
| 1950 | 128,009 | 2.7% | |
| 1960 | 114,167 | −10.8% | |
| 1970 | 104,638 | −8.3% | |
| 1980 | 92,124 | −12.0% | |
| 1990 | 88,675 | −3.7% | |
| 2000 | 85,403 | −3.7% | |
| 2010 | 84,913 | −0.6% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 83,203 | [13][71][72] | −2.0% |
| Population sources: 1790–1920[73] 1840[74] 1850–1870[75] 1850[76] 1870[77] 1880–1890[78] 1910–1930[79] 1930–1990[80] 2000[81][82] 2010[10][11][12][83] * = Territory change in previous decade.[28] | |||
2010 Census
The 2010 United States Census counted 84,913 people, 28,578 households, and 17,747 families in the city. The population density was 11,101.9 per square mile (4,286.5/km2). There were 33,035 housing units at an average density of 4,319.2 per square mile (1,667.7/km2). The racial makeup was 26.56% (22,549) White, 52.01% (44,160) Black or African American, 0.70% (598) Native American, 1.19% (1,013) Asian, 0.13% (110) Pacific Islander, 15.31% (13,003) from other races, and 4.10% (3,480) from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 33.71% (28,621) of the population.[10]
Of the 28,578 households, 32.0% had children under the age of 18; 25.1% were married couples living together; 28.1% had a female householder with no husband present and 37.9% were non-families. Of all households, 30.8% were made up of individuals and 9.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.79 and the average family size was 3.40.[10]
25.1% of the population were under the age of 18, 11.0% from 18 to 24, 32.5% from 25 to 44, 22.6% from 45 to 64, and 8.8% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 32.6 years. For every 100 females, the population had 106.5 males. For every 100 females ages 18 and older there were 107.2 males.[10]
2006-2010 survey
The Census Bureau's 2006–2010 American Community Survey showed that (in 2010 inflation-adjusted dollars) median household income was $36,601 (with a margin of error of +/- $1,485) and the median family income was $41,491 (+/- $2,778). Males had a median income of $29,884 (+/- $1,715) versus $31,319 (+/- $2,398) for females. The per capita income for the city was $17,400 (+/- $571). About 22.4% of families and 24.5% of the population were below the poverty line, including 36.3% of those under age 18 and 17.5% of those age 65 or over.[84]
2000 Census
As of the 2000 United States Census[19] there were 85,403, people, 29,437 households, and 18,692 families residing in the city. The population density was 11,153.6 inhabitants per square mile (4,306.4/km2). There were 33,843 housing units at an average density of 4,419.9/sq mi (1,706.5/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 52.06% Black, 32.55% White, 0.35% Native American, 0.84% Asian, 0.23% Pacific Islander, 10.76% from other races, and 3.20% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 21.53% of the population.[81][82] There were 29,437 households, 32.4% of which had children under the age of 18 living with them. 29.0% were married couples living together, 27.1% had a female householder with no husband present, and 36.5% were non-families. 29.7% of all households were made up of individuals, and 12.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.75 and the average family size was 3.38.[81][82]
In the city the age distribution of the population shows 27.7% under the age of 18, 10.1% from 18 to 24, 31.9% from 25 to 44, 18.9% from 45 to 64, and 11.4% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 32 years. For every 100 females, there were 97.6 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.0 males.[81][82]
The median income for a household in the city was $31,074, and the median income for a family was $36,681. Males had a median income of $29,721 versus $26,943 for females. The per capita income for the city was $14,621. About 17.6% of families and 21.1% of the population were below the poverty line, including 26.8% of those under age 18 and 19.5% of those age 65 or over.[81][82]
Top 10 ethnicities reported during the 2000 Census by percentage were:[81][82]
Economy

Trenton was a major manufacturing center in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. One relic of that era is the slogan "Trenton Makes, The World Takes", which is displayed on the Lower Free Bridge (just north of the Trenton–Morrisville Toll Bridge).[85] The city adopted the slogan in 1917 to represent Trenton's then-leading role as a major manufacturing center for rubber, wire rope, ceramics and cigars. It was home to American Standards largest fixture factory.[86]
Along with many other United States cities in the 1970s, Trenton fell on hard times when manufacturing and industrial jobs declined. Concurrently, state government agencies began leasing office space in the surrounding suburbs. State government leaders (particularly governors William Cahill and Brendan Byrne) attempted to revitalize the downtown area by making it the center of state government. Between 1982 and 1992, more than a dozen office buildings were constructed primarily by the state to house state offices.[87] Today, Trenton's biggest employer is still the state of New Jersey. Each weekday, 20,000 state workers flood into the city from the surrounding suburbs.[88]
Notable businesses of the thousands based in Trenton include Italian Peoples Bakery, a wholesale and retail bakery established in 1936.[89] De Lorenzo's Tomato Pies and Papa's Tomato Pies were also fixtures of the city for many years, though both recently relocated to the suburbs.
Urban Enterprise Zone
Portions of Trenton are part of an Urban Enterprise Zone. The city was selected in 1983 as one of the initial group of 10 zones chosen to participate in the program.[90] In addition to other benefits to encourage employment within the Zone, shoppers can take advantage of a reduced 3.3125% sales tax rate (half of the 6 5⁄8% rate charged statewide) at eligible merchants.[91] Established in January 1986, the city's Urban Enterprise Zone status expires in December 2023.[92]
The UEZ program in Trenton and four other original UEZ cities had been allowed to lapse as of January 1, 2017, after Governor Chris Christie, who called the program an "abject failure", vetoed a compromise bill that would have extended the status for two years.[93] In May 2018, Governor Phil Murphy signed a law that reinstated the program in these five cities and extended the expiration date in other zones.[94]
In 2018, the city had an average property tax bill of $3,274, the lowest in the county, compared to an average bill of $8,292 in Mercer County and $8,767 statewide.[95][96]
Television market
Trenton has long been part of the Philadelphia television market. However, following the 2000 United States Census, Trenton was shifted from the Philadelphia metropolitan statistical area to the New York metropolitan statistical area. With a similar shift by the New Haven, Connecticut, area to the New York area, they were the first two cases where metropolitan statistical areas differed from their defined Nielsen television markets.[97] Also, Trenton was the site of the studios of the former public television station New Jersey Network (aka NJN).
Landmarks
- New Jersey State Museum – Combines a collection of archaeology and ethnography, fine art, cultural history and natural history.[98]
- New Jersey State House was originally constructed by Jonathan Doane in 1792, with major additions made in 1845, 1865 and 1871.[99]
- New Jersey State Library serves as a central resource for libraries across the state as well as serving the state legislature and government.[100]
- Trenton City Museum – Housed in the Italianate-style 1848 Ellarslie Mansion since 1978, the museum features artworks and other materials related to the city's history.[101]
- Trenton War Memorial – Completed in 1932 as a memorial to the war dead from Mercer County during World War I and owned and operated by the State of New Jersey, the building is home to a theater with 1,800 seats that reopened in 1999 after an extensive, five-year-long renovation project.[102]
- Old Barracks – Dating back to 1758 and the French and Indian War, the Barracks were constructed as a place to house British troops in lieu of housing the soldiers in the homes of area residents. The site was used by both the Continental Army and British forces during the Revolutionary War and stands as the last remaining colonial barracks in the state.[103]
- Trenton Battle Monument – Located in the heart of the Five Points neighborhood, the monument was built to commemorate the Continental Army's victory in the December 26, 1776, Battle of Trenton.[61] The monument was designed by John H. Duncan and features a statue of George Washington atop a pedestal that stands on a granite column 148 feet (45 m) in height.[104]
- Trenton City Hall – The building was constructed based on a 1907 design by architect Spencer Roberts and opened to the public in 1910. The council chambers stand two stories high and features a mural by Everett Shinn that highlights Trenton's industrial history.[105]
- William Trent House – Constructed in 1719 by William Trent, who the following year laid out what would become the city of Trenton, the house was owned by Governor Lewis Morris, who used the house as his official residence in the 1740s. Governor Philemon Dickerson used the home as his official residence in the 1830s, as did Rodman M. Price in the 1850s.[106]
Sports
| Club | League | Venue | MLB affiliate | Established | Championships |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trenton Thunder | MLB Draft League | Arm & Hammer Park | None | 1994 | 3 |

Because of Trenton's near-equal distance to both New York City and Philadelphia, and because most homes in Mercer County receive network broadcasts from both cities, locals are sharply divided in fan loyalty between both cities. It is common to find Philadelphia's Phillies, Eagles, 76ers, Union and Flyers fans cheering (and arguing) right alongside fans of New York's Yankees, Mets, Nets, Knicks, Rangers, Islanders, Jets, Red Bulls and Giants or the New Jersey Devils.[107]
Between 1948 and 1979, Trenton Speedway, located in adjacent Hamilton Township, hosted world class auto racing. Drivers such as Jim Clark, A. J. Foyt, Mario Andretti, Al Unser, Bobby Unser, Richard Petty and Bobby Allison raced on the one-mile (1.6 km) asphalt oval and then re-configured 1 1⁄2-mile race track.[108] The speedway, which closed in 1980, was part of the larger New Jersey State Fairgrounds complex, which also closed in 1983. The former site of the speedway and fairgrounds is now the Grounds for Sculpture.[109]
The Trenton Thunder, minor league team owned by Joe Plumeri, plays at 6,341-seat Arm & Hammer Park, the stadium which Plumeri had previously named after his father in 1999.[110][111][112] The team was previously affiliated with the New York Yankees, Boston Red Sox, Detroit Tigers, and Chicago White Sox, but became an unaffiliated collegiate summer baseball team of the MLB Draft League beginning in 2021.[113]
The Trenton Freedom of the Professional Indoor Football League were founded in 2013 and played their games at the Sun National Bank Center. The Freedom ended operations in 2015, joining the short-lived Trenton Steel (in 2011) and Trenton Lightning (in 2001) as indoor football teams that had brief operating lives at the arena.[114]
Parks and recreation
- Cadwalader Park – Trenton's largest city park covering 109.5 acres (44.3 ha), it was designed by landscape architect Frederick Law Olmsted, who is most famous for designing New York City's Central Park.[115]
Historic sites
- Adams and Sickles Building (added January 31, 1980 as #80002498) is a focal point for West End neighborhood, and is remembered for its soda fountain and corner druggist.[116]
- Friends Burying Ground, adjacent to the Trenton Friends Meeting House, is the burial site of several national and state political figures prominent in the city's early history.[117]
- Trenton Friends Meeting House (added April 30, 2008 as #08000362), dating back to 1739, it was occupied by the British Dragoons in 1776 and by the Continental Army later in the Revolutionary War.[118]
Government

Local government
The City of Trenton is governed within the Faulkner Act, formally known as the Optional Municipal Charter Law, under the Mayor-Council system of municipal government, one of 71 municipalities (of the 565) statewide that use this form of government.[119] The governing body is comprised of a mayor and a seven-member city council. Three city council members are elected at-large, and four come from each of four wards. The mayor and council members are elected concurrently on a non-partisan basis to four-year terms of office as part of the May municipal election.[4][120]
As of 2020, the mayor of Trenton is Reed Gusciora, who had previously served in the New Jersey General Assembly before taking office as mayor.[121] Members of the city council are Council President Kathy McBride (At-Large), Jerell A. Blakeley (At-Large), Marge Caldwell-Wilson (North Ward), Joseph A. Harrison (East Ward), George P. Muschal (South Ward), Santiago Rodriquez (At-Large) and Robin M. Vaughn (West Ward), all serving terms of office ending June 30, 2022.[5][122][123][124][125]
Interim mayor 2014
From February 7 to July 1, 2014, the acting mayor was George Muschal who retroactively assumed the office on that date due to the felony conviction of Tony F. Mack, who had taken office on July 1, 2010.[126] Muschal, who was council president, was selected by the city council to serve as the interim mayor to finish the term.[127]
Mayor's conviction and removal from office
On February 7, 2014, Mack and his brother, Raphiel Mack, were convicted by a federal jury of bribery, fraud and extortion, based on the details of their participation in a scheme to take money in exchange for helping get approvals to develop a downtown parking garage as part of a sting operation by law enforcement.[128] Days after the conviction, the office of the New Jersey Attorney General filed motions to have Mack removed from office, as state law requires the removal of elected officials after convictions for corruption.[129] Initially, Mack fought the removal of him from the office but on February 26, a superior court judge ordered his removal and any actions taken by Mack between February 7 and the 26th could have been reversed by Muschal.[127] Previously, Mack's housing director quit after it was learned he had a theft conviction. His chief of staff was arrested trying to buy heroin. His half-brother, whose authority he elevated at the city water plant, was arrested on charges of stealing. His law director resigned after arguing with Mack over complying with open-records laws and potential violations of laws prohibiting city contracts to big campaign donors.[130]
Federal, state and county representation

Trenton is located in the 12th Congressional District[131] and is part of New Jersey's 15th state legislative district.[11][132][133] Prior to the 2010 Census, Trenton had been split between the 4th Congressional District and the 12th Congressional District, a change made by the New Jersey Redistricting Commission that took effect in January 2013, based on the results of the November 2012 general elections.[134]
For the 116th United States Congress, New Jersey's Twelfth Congressional District is represented by Bonnie Watson Coleman (D, Ewing Township).[135][136] New Jersey is represented in the United States Senate by Democrats Cory Booker (Newark, term ends 2021)[137] and Bob Menendez (Paramus, term ends 2025).[138][139]
For the 2020–2021 session (Senate, General Assembly), the 15th Legislative District of the New Jersey Legislature is represented in the State Senate by Shirley Turner (D, Lawrence Township, Mercer County) and in the General Assembly by Verlina Reynolds-Jackson (D, Trenton) and Anthony Verrelli (D, Hopewell Township, Mercer County, New Jersey).[140][141]
Mercer County is governed by a County Executive who oversees the day-to-day operations of the county and by a seven-member Board of Chosen Freeholders that acts in a legislative capacity, setting policy. All officials are chosen at-large in partisan elections, with the executive serving a four-year term of office while the freeholders serve three-year terms of office on a staggered basis, with either two or three seats up for election each year.[142] As of 2014, the County Executive is Brian M. Hughes (D, term ends December 31, 2015; Princeton).[143] Mercer County's Freeholders are Freeholder Chair Andrew Koontz (D, 2016; Princeton),[144] Freeholder Vice Chair Samuel T. Frisby, Sr. (2015; Trenton),[145] Ann M. Cannon (2015; East Windsor Township),[146] Anthony P. Carabelli (2016; Trenton),[147] John A. Cimino (2014, Hamilton Township),[148] Pasquale "Pat" Colavita, Jr. (2015; Lawrence Township)[149] and Lucylle R. S. Walter (2014; Ewing Township)[150][151][152] Mercer County's constitutional officers are County Clerk Paula Sollami-Covello (D, 2015),[153] Sheriff John A. Kemler (D, 2014)[154] and Surrogate Diane Gerofsky (D, 2016).[155][156]
Politics
As of March 23, 2011, there were a total of 37,407 registered voters in Trenton, of which 16,819 (45.0%) were registered as Democrats, 1,328 (3.6%) were registered as Republicans and 19,248 (51.5%) were registered as Unaffiliated. There were 12 voters registered to other parties.[157]
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016[158] | 7.7% 1,715 | 90.6% 20,131 | 1.7% 379 |
| 2012[159] | 6.2% 1,528 | 93.4% 23,125 | 0.4% 97 |
| 2008[160] | 8.2% 2,157 | 89.9% 23,577 | 0.5% 141 |
| 2004[161] | 16.3% 3,791 | 79.8% 18,539 | 0.4% 146 |
In the 2012 presidential election, Democrat Barack Obama received 93.4% of the vote (23,125 cast), ahead of Republican Mitt Romney with 6.2% (1,528 votes), and other candidates with 0.4% (97 votes), among the 27,831 ballots cast by the city's 40,362 registered voters (3,081 ballots were spoiled), for a turnout of 69.0%.[159][162] In the 2008 presidential election, Democrat Barack Obama received 89.9% of the vote here (23,577 cast), ahead of Republican John McCain with 8.2% (2,157 votes) and other candidates with 0.5% (141 votes), among the 26,229 ballots cast by the city's 41,005 registered voters, for a turnout of 64.0%.[160] In the 2004 presidential election, Democrat John Kerry received 79.8% of the vote here (18,539 ballots cast), outpolling Republican George W. Bush with 16.3% (3,791 votes) and other candidates with 0.4% (146 votes), among the 23,228 ballots cast by the city's 39,139 registered voters, for a turnout percentage of 59.3.[161]
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017[163] | 8.6% 872 | 89.8% 9,128 | 1.7% 169 |
| 2013[164] | 24.7% 3,035 | 74.7% 9,179 | 0.7% 77 |
| 2009[165] | 12.4% 1,560 | 81.6% 10,235 | 3.5% 440 |
| 2005[166] | 15.3% 1,982 | 81.0% 10,484 | 3.6% 471 |
In the 2013 gubernatorial election, Democrat Barbara Buono received 74.7% of the vote (9,179 cast), ahead of Republican Chris Christie with 24.7% (3,035 votes), and other candidates with 0.6% (77 votes), among the 11,884 ballots cast by the city's 38,452 registered voters (407 ballots were spoiled), for a turnout of 30.9%.[164][167] In the 2009 gubernatorial election, Democrat Jon Corzine received 81.6% of the vote here (10,235 ballots cast), ahead of Republican Chris Christie with 12.4% (1,560 votes), Independent Chris Daggett with 2.4% (305 votes) and other candidates with 1.1% (135 votes), among the 12,537 ballots cast by the city's 38,345 registered voters, yielding a 32.7% turnout.[165]
Fire department
The city of Trenton is protected on a full-time basis by the city of Trenton Fire and Emergency Services Department (TFD), which has been a paid department since 1892 after having been originally established in 1747 as a volunteer fire department.[168] The TFD operates out of seven fire stations and operates a fire apparatus fleet of 7 engine companies, 3 ladder companies and one rescue company, along with one HAZMAT unit, an air cascade unit, a mobile command unit, a foam unit, one fireboat, and numerous special, support and reserve units, under the command of a Battalion Chief each shift.[169][170]
- Fire station locations and apparatus
| Engine company | Ladder company | Special unit | Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine 1 | Ladder 1 (tiller) | Marine 1 (fire boat) | 460 Calhoun Street |
| Engine 3 (squirt) | Ladder 2 (tiller) | 720 S. Broad Street | |
| Engine 6 | 561 N. Clinton Avenue | ||
| Engine 7 | 502 Hamilton Avenue | ||
| Engine 8 | Battalion Chief 1 | 698 Stuyvesant Avenue | |
| Engine 9 | Foam Unit 1 | 1464 W. State Street | |
| Engine 10 | Tower Ladder 4 | Rescue 1, Haz-Mat 1, Mobile Command Unit, Air Cascade Unit | 244 Perry Street |
Education
Colleges and universities
Trenton is the home of two post-secondary institutions: Thomas Edison State University, serving adult students around the nation and worldwide[171] and Mercer County Community College's James Kerney Campus.[172]
The College of New Jersey, formerly named Trenton State College, was founded in Trenton in 1855 and is now located in nearby Ewing Township. Rider University was founded in Trenton in 1865 as The Trenton Business College. In 1959, Rider moved to its current location in nearby Lawrence Township.[173]
Public schools
The Trenton Public Schools serve students in pre-kindergarten through twelfth grade.[174] The district is one of 31 former Abbott districts statewide,[175] which are now referred to as "SDA Districts" based on the requirement for the state to cover all costs for school building and renovation projects in these districts under the supervision of the New Jersey Schools Development Authority.[176][177] The district's board of education, with seven members, sets policy and oversees the fiscal and educational operation of the district through its superintendent administration. As a Type I school district, the board's trustees are appointed by the mayor to serve three-year terms of office on a staggered basis, with either two or three seats up for re-appointment each year.[178][179] The school district has undergone a 'construction' renaissance throughout the district.
As of the 2018–19 school year, the district, comprised of 20 schools, had an enrollment of 14,500 students and 884.4 classroom teachers (on an FTE basis), for a student–teacher ratio of 16.4:1.[180] Schools in the district (with 2018–19 enrollment data from the National Center for Education Statistics[181]) are Columbus Elementary School[182] (371 students; in grades K-5), Franklin Elementary School[183] (405; K-5), Grant Elementary School[184] (571; PreK-5), Gregory Elementary School[185] (567; K-5), Harrison Elementary School[186] (221; PreK-5), P.J. Hill Elementary School[187] (800; PreK-5), Jefferson Elementary School[188] (434; K-5), Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. Elementary School[189] (775; K-5), Mott Elementary School[190] (426; K-5), Parker Elementary School[191] (531; K-5), Robbins Elementary School[192] (541; K-5), Washington Elementary School[193] (409; K-5), Wilson Elementary School[194] (498; PreK-5), Grace A. Dunn Middle School[195] (893; 6–8), Hedgepeth-Williams Middle School[196] (674; 6–8), Joyce Kilmer Middle School[197] (370; 6–8), Luis Munoz Rivera Middle School[198] (483; 6–8), Trenton Ninth Grade Academy[199] (707; 9), Daylight/Twilight Alternative High School[200] (443; 9–12) and Trenton Central High School[201] (1,818; 9–12).[202][203][204]
Eighth grade students from all of Mercer County are eligible to apply to attend the high school programs offered by the Mercer County Technical Schools, a county-wide vocational school district that offers full-time career and technical education at its Health Sciences Academy, STEM Academy and Academy of Culinary Arts, with no tuition charged to students for attendance.[205][206]
Charter schools
Trenton is home to several charter schools, including Capital Preparatory Charter High School, Emily Fisher Charter School, Foundation Academy Charter School, International Charter School, Paul Robeson Charter School and Village Charter School.[207]
The International Academy of Trenton, owned and monitored by the SABIS school network, became a charter school in 2014. On February 22, 2017, Trenton's mayor, Eric Jackson, visited the school when it opened its doors in the former Trenton Times building on 500 Perry Street, after completion of a $17 million renovation project. After receiving notice from the New Jersey Department of Education that the school's charter would not be renewed due to issues with academic performance and school management, the school closed its doors on June 30, 2018.[208]
Private schools
Trenton Catholic Academy high school serves students in grades 9–12, while Trenton Catholic Academy grammar school serves students in Pre-K through 8th grade; both schools operate under the auspices of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Trenton.[209]
Trenton is home to Al-Bayaan Academy, which opened for preschool students in September 2001 and added grades in subsequent years.[210]
Trenton Community Music School is a not-for-profit community school of the arts. The school was founded by executive director Marcia Wood in 1997. The school operates at Blessed Sacrament Catholic Church (on Tuesdays) and the Copeland Center for the Performing Arts (on Saturdays).
Crime
In 2005, there were 31 homicides in Trenton, which at that time was the largest number in a single year in the city's history.[211] The city was named the 4th "Most Dangerous" in 2005 out of 129 cities with a population of 75,000 to 99,999 ranked nationwide in the 12th annual Morgan Quitno survey.[212] In the 2006 survey, Trenton was ranked as the 14th most dangerous city overall out of 371 cities included nationwide in the Morgan Quitno survey, and was again named as the fourth most dangerous municipality of 126 cities in the 75,000–99,999 population range.[213] Homicides went down in 2006 to 20, but back up to 25 in 2007.[214] In 2018 the city had 21 murders,[215] the same as in 2017, when the city accounted for 21 of the 25 homicides in all of Mercer County.[216]
In September 2011, the city laid off 108 police officers due to budget cuts; this constituted almost one-third of the Trenton Police Department and required 30 senior officers to be sent out on patrols in lieu of supervisory duties.[217]
In 2013, the city set a new record with 37 homicides.[218] In 2014, there were 23 murders through the end of July and the city's homicide rate was on track to break the record set the previous year until an 81-day period when there were no murders in Trenton; the city ended the year with 34 murders.[219][220] The number of homicides declined to 17 in 2015.[221]
New Jersey State Prison
The New Jersey State Prison (formerly Trenton State Prison) has two maximum security units. It houses some of the state's most dangerous individuals, which included New Jersey's death row population until the state banned capital punishment in 2007.[222]
The following is inscribed over the original entrance to the prison:
Labor, Silence, Penitence.
The Penitentiary House,
Erected By Legislative
Authority.
Richard Howell, Governor.
In The XXII Year Of
American Independence
MDCCXCVII
That Those Who Are Feared
For Their Crimes
May Learn To Fear The Laws
And Be Useful
Hic Labor, Hic Opus.[223]
Transportation
Roads and highways
_from_the_overpass_for_East_State_Street_in_Trenton_City%252C_Mercer_County%252C_New_Jersey.jpg.webp)
As of May 2010, the city had a total of 168.80 miles (271.66 km) of roadways, of which 145.57 miles (234.27 km) were maintained by the municipality, 11.33 miles (18.23 km) by Mercer County, 10.92 miles (17.57 km) by the New Jersey Department of Transportation and 0.99 miles (1.59 km) by the Delaware River Joint Toll Bridge Commission.[224]
City highways include the Trenton Freeway (part of U.S. Route 1)[225] and the John Fitch Parkway, which is part of Route 29.[226] Canal Boulevard, more commonly known as Route 129, connects US 1 and Route 29 in South Trenton.[227] U.S. Route 206,[228] Route 31[229] and Route 33[230] also pass through the city via regular city streets (Broad Street/Brunswick Avenue/Princeton Avenue, Pennington Avenue, and Greenwood Avenue, respectively).
Route 29 connects the city to Interstate 295 and Interstate 195, the latter providing a connection to the New Jersey Turnpike (Interstate 95) at Exit 7A in Robbinsville Township.
Public transportation

Public transportation within the city and to/from its nearby suburbs is provided in the form of local bus routes run by NJ Transit. SEPTA also provides bus service to adjacent Bucks County, Pennsylvania.
The Trenton Transit Center, located on the heavily traveled Northeast Corridor, serves as the northbound terminus for SEPTA's Trenton Line (local train service to Philadelphia) and southbound terminus for NJ Transit Rail's Northeast Corridor Line (local train service to New York Penn Station). The train station also serves as the northbound terminus for the River Line, a diesel light rail line that runs to Camden.[231] Two additional River Line stops, Cass Street and Hamilton Avenue, are located within the city.[232]
Long-distance transportation is provided by Amtrak train service along the Northeast Corridor.[233]
The closest commercial airport is Trenton–Mercer Airport in Ewing Township, about 8 miles (13 km) from the center of Trenton, which has been served by Frontier Airlines offering service to and from 13 points nationwide.[234]
Other nearby major airports are Newark Liberty International Airport and Philadelphia International Airport, located 55.2 miles (88.8 km) and 43.4 miles (69.8 km) away, respectively, and reachable by direct New Jersey Transit or Amtrak rail link (to Newark) and by SEPTA Regional Rail (to Philadelphia).
NJ Transit Bus Operations provides bus service between Trenton and Philadelphia on the 409 route, with service to surrounding communities on the 600, 601, 602, 603, 604, 606, 607, 608, 609 and 611 routes.[235][236]
The Greater Mercer Transportation Management Association offers service on the Route 130 Connection between the Trenton Transit Center and the South Brunswick warehouse district with stops along the route including Hamilton train station, Hamilton Marketplace, Hightstown and East Windsor Town Center Plaza.[237]
Media
Trenton is served by two daily newspapers: The Times and The Trentonian, as well as a monthly advertising magazine: "The City" Trenton N.E.W.S.. Radio station WKXW is also licensed to Trenton. Defunct periodicals include the Trenton True American. A local television station, WPHY-CD TV-25, serves the Trenton area.[238]
Trenton is officially part of the Philadelphia television market but some local pay TV operators also carry stations serving the New York market. While it is its own radio market, many Philadelphia and New York stations are easily receivable.
Notable people
People who were born in, residents of, or otherwise closely associated with Trenton include:
Academics
- Charles Conrad Abbott (1843–1919), archaeologist and naturalist.[239]
- Mary Joyce Doyle (1923–2016), nun and librarian who founded the library consortium that revolutionized the borrowing of books in Bergen County, New Jersey through the creation of the Bergen County Cooperative Library System.[240]
- Robert B. Duffield (1917-2000), radiochemist who headed the Argonne National Laboratory.[241]
- N. Gregory Mankiw (born 1958), macroeconomist.[242]
- George T. Reynolds (1917–2005), physicist best known for his accomplishments in particle physics, biophysics and environmental science.[243]
- Joshua M. Zeitz (born 1974), historian.[244]
Actors and actresses
- Jean Acker (1893–1978), film actress who was the estranged wife of silent film star Rudolph Valentino.[245]
- Betty Bronson (1907–1971), actress.[246]
- Roxanne Hart (born 1952), actress who appeared in the film Highlander and on television in Chicago Hope.[247]
- Richard Kind (born 1956), actor and voice actor, known for his roles in the sitcoms Mad About You (as Dr. Mark Devanow) and Spin City (as Paul Lassiter).[248]
- Ernie Kovacs (1919–1962), television comedian and film actor.[249]
- Judith Light (born 1949), actress.[250]
- Amy Locane (born 1971), actress.[251]
- Amy Robinson (born 1948), actress and film producer.[252]
- Sommore Rambough (born 1967), comedian.[253]
- Ty Treadway (born 1967), host of Merv Griffin's Crosswords.[254]
- Sammy Williams (1948–2018), actor best known for his role as Paul in the musical A Chorus Line, for which he won the 1976 Tony Award for Best Featured Actor in a Musical.[255]
Artists
- Edward Marshall Boehm (1913–1969), sculptor and his wife Helen Boehm (1920–2010), who promoted his works.[256]
- Ruth Donnelly (1896–1982), stage and film actress.[257]
- Peter Hujar (1934–1987), photographer best known for his black-and-white portraits.[258]
Authors, writers, journalists, poets
- Edward Bloor (born 1950), novelist.[259]
- Edward Y. Breese (1912–1979), popular fiction writer.[260]
- John Brooks (1920–1993), writer and longtime contributor to The New Yorker magazine.[261]
- Russell Gordon Carter (1892–1957), writer.[262]
- Janis Hirsch (born c. 1950) is a comedy writer best known for producing and writing for television series.[263]
- Pam Houston (born 1962), author of short stories, novels and essays who is best known for her first book, Cowboys Are My Weakness.[264]
- William Mastrosimone (born 1947), playwright.[265]
- Mark Osborne (born 1970) film director, writer, producer and animator, whose work includes Kung Fu Panda.[266]
- Bob Ryan (born 1946), sportswriter, regular contributor on the ESPN show Around the Horn.[267]
- Ntozake Shange (1948–2018), playwright and poet best known for the Obie Award-winning play For Colored Girls Who Have Considered Suicide / When the Rainbow Is Enuf.[268]
- Nancy Wood (1936–2013), author, poet and photographer.[269]
Colonial figures
- James Francis Armstrong (1750–1816), chaplain in the American Revolutionary War and a Presbyterian minister for 30 years in Trenton.[270]
- Samuel John Atlee (1739–1786), soldier and statesman who was a delegate to the Continental Congress for Pennsylvania.[271]
- John Cadwalader (1742–1786), commander of Pennsylvania troops during the American Revolutionary War.[272]
- Lambert Cadwalader (1742–1823), merchant who fought in the Revolutionary War, then represented New Jersey in the Continental Congress and the United States House of Representatives.[273]
- Thomas Cadwalader (1707–1779), physician and namesake of Cadwalader Park.[274]
- Philemon Dickinson (1739–1809), lawyer and politician who served as a brigadier general of the New Jersey militia, as a Continental Congressman from Delaware and a United States Senator from New Jersey.[275]
- Mary Hays (1744–1832), woman who fought during the Revolutionary War at the Battle of Monmouth, and is generally believed to have been the inspiration of the story of Molly Pitcher.[276]
Government, education and politics
- Samuel Alito (born 1950), Associate Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court.[277]
- Henry W. Antheil Jr. (1912–1940), American diplomat killed in the shootdown of the Kaleva airplane by Soviet aircraft in the wake of the Soviet occupation of the Baltic States.[278][279]
- John T. Bird (1829–1911), represented New Jersey's 3rd congressional district (1869–1873).[280]
- James Bishop (1816–1895), represented New Jersey's 3rd congressional district in the U.S. House of Representatives (1855–1857).[281]
- Peggy Blackford (born 1942), American Ambassador to Guinea-Bissau from 1995 until relations were suspended in June 1998.[282]
- J. Hart Brewer (1844–1900), represented New Jersey's 2nd congressional district (1881–1885).[283]
- Frank O. Briggs (1851–1913), politician who was the mayor of Trenton from 1899 to 1902, and United States Senator from New Jersey from 1907 to 1913.[284]
- Michele Brown, CEO of the New Jersey Economic Development Authority.[285]
- James Buchanan (1839–1900), represented New Jersey's 2nd congressional district from 1885 to 1893.[286]
- Newton A.K. Bugbee (1876–1965), businessman and politician who served as New Jersey State Comptroller and chairman of the New Jersey Republican State Committee, and was the Republican candidate for Governor of New Jersey in 1919.[287]
- Robert J. Burkhardt (1916–1999), politician who served as Secretary of State of New Jersey and chairman of the New Jersey Democratic State Committee.[288]
- Aneesh Chopra (born 1972), served as the first Chief Technology Officer of the United States.[289]
- James L. Conger (1805–1876), politician who represented Michigan's 3rd congressional district.[290]
- Martin Connor (born 1945), former member of the New York State Senate.[291]
- Willard S. Curtin (1905–1996), member of the United States House of Representatives from Pennsylvania.[292]
- William Lewis Dayton Jr. (1839–1897), United States Ambassador to the Netherlands.[293]
- Wayne DeAngelo (born 1965), politician who has served in the New Jersey General Assembly since 2008, where he represents the 14th Legislative District.[294]
- David Dinkins (1927-2020), first black mayor of New York City.[295]
- George Washington Doane (1799–1859), churchman, educator (founder of Doane Academy) and bishop in the Episcopal Church for the Diocese of New Jersey.[296]
- Frederick W. Donnelly (1866–1935), politician who served as Mayor of Trenton from 1911 until 1932.[297]
- Richard Grant Augustus Donnelly (1841–1905), politician who served as Mayor of Trenton from 1884 to 1886.[297]
- Thomas A. Ferguson (born 1950), Director of the Bureau of Engraving and Printing from 1998 to 2005.[298]
- Richard Funkhouser (1917–2008), geologist and diplomat who served as United States Ambassador to Gabon.[299]
- Harry Heher (1889–1972), Justice on the New Jersey Supreme Court.[300]
- Charles R. Howell (1904–1973), represented New Jersey's 4th congressional district in the U.S. House of Representatives (1949–55).[301]
- Elijah C. Hutchinson (1855–1932), represented New Jersey's 4th congressional district (1915–1923).[302]
- Marie Hilson Katzenbach (1882-1970), educator who was the first woman to serve as president of the New Jersey State Board of Education.[303]
- Nicholas Katzenbach (born 1922), U.S. Attorney General during the Johnson Administration.[304]
- Dick LaRossa (born 1946), politician and former television presenter who served two terms in the New Jersey Senate, where he represented the 15th Legislative District.[305]
- A. Leo Levin (1919–2015), law professor at the University of Pennsylvania Law School.[306]
- Sol Linowitz (1913–2005), diplomat, lawyer, and businessman.[307]
- Francis J. McManimon (1926–2020), politician who served in the New Jersey General Assembly from 1972 to 1982 and in the New Jersey Senate from 1982 to 1992.[308]
- Joseph P. Merlino (1922–1998), politician who served as President of the New Jersey Senate from 1978 to 1981.[309]
- A. Dayton Oliphant (1887–1963), associate justice of the New Jersey Supreme Court from 1945 to 1946, and again from 1948 to 1957.[310]
- Anne M. Patterson (born 1959), associate justice of the New Jersey Supreme Court.[311]
- D. Lane Powers (1896–1968), represented New Jersey's 4th congressional district in the U.S. House of Representatives (1933–1945).[312]
- Verlina Reynolds-Jackson, politician who represents the 15th Legislative District in the New Jersey General Assembly.[313]
- Daniel Bailey Ryall (1798–1864), U.S. Representative from New Jersey (1839–1841).[314]
- Antonin Scalia (1936–2016), Associate Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court[315]
- Sido L. Ridolfi (1913–2004), politician who served in the New Jersey Senate from 1954 to 1972.[316]
- Charles Skelton (1806–1879), represented New Jersey's 2nd congressional district (1851–1855).[317]
- Robin L. Titus (born 1954), physician and politician who serves as a Republican member of the Nevada Assembly.[318]
- Bennet Van Syckel (1830–1921), associate justice of the New Jersey Supreme Court from 1869 to 1904.[319]
- Albert C. Wagner (1911–1987), director of the New Jersey Department of Corrections from 1966 to 1973.[320]
- Allan B. Walsh (1874–1953), represented the 4th congressional district (1913–1915).[321]
- Karl Weidel (1923–1997), who served in the New Jersey General Assembly from 1970 to 1986.[322]
- Ira W. Wood (1856–1931), represented New Jersey's 4th congressional district (1904–1913).[323]
Military
- Stephen Hart Barlow (1895–?), served as Quartermaster General of New Jersey from 1934 to 1942.[324]
- Clifford Bluemel (1885–1973), United States Army brigadier general who commanded the 31st Division during the Battle of Bataan before being captured by Japanese forces and held as a prisoner of war.[325]
- Thomas McCall Cadwalader (1795–1873), United States Army Major general.[326]
- Frank William Crilley (1883–1947), United States Navy diver and a recipient of the Medal of Honor.[327]
- Samuel Gibbs French (1818–1910), Major General in the Confederate States Army.[328]
- William J. Johnston (1918–1990), Medal of Honor recipient for gallantry during World War II.[329]
- Needham Roberts (1901–1949), soldier in the Harlem Hellfighters and recipient of the Purple Heart and the Croix de Guerre for his valor during World War I.[330]
- Norman Schwarzkopf Jr. (1934–2012), Commander-in-Chief of the U.S. Central Command in the Gulf War.[331]
Music
- George Antheil (1900–1959), pianist, composer, writer and inventor.[332]
- Hodgy Beats (born 1990 as Gerard Damien Long), member of the Los Angeles hip-hop collective Odd Future.[333]
- Carman (born 1956), contemporary Christian music singer.[334]
- Shawn Corey Carter (born 1969, a.k.a. Jay-Z), rap mogul, CEO.[335]
- Charles Chapman (1950–2011), jazz guitarist.[336]
- Richie Cole (born 1948), jazz alto saxophonist.[337][338]
- Johnny Coles (1926–1997), jazz trumpeter.[339]
- Richard Crooks (1900–1972), tenor at the New York Metropolitan Opera.[340]
- Sarah Dash (born 1944), singer, formerly of glam rock group, Labelle.[341]
- Nona Hendryx (born 1944), singer formerly of glam rock group Labelle.[342]
- Maury Muehleisen (born 1949), guitarist and songwriting partner for Jim Croce.[343]
- Wise Intelligent, and other members of the hip-hop group Poor Righteous Teachers.[344][345]
- Marion Zarzeczna, concert pianist.[346]
Sports
- Terrance Bailey (born 1965), former basketball player who led NCAA Division I in scoring playing for Wagner College in 1985–86.[347]
- Bo Belinsky (1936–2001), professional baseball player.[348]
- Elvin Bethea (born 1946), Pro Football Hall of Fame defensive end who played his entire NFL career with the Houston Oilers.[349]
- Mike Bloom (1915–1993), professional basketball player for the Baltimore Bullets, Boston Celtics, Minneapolis Lakers and Chicago Stags.[350]
- Steve Braun (born 1948), professional baseball player.[351]
- Tal Brody (born 1943), Euroleague basketball shooting guard, drafted # 12 in the NBA draft.[352]
- Antron Brown (born c. 1976), drag racer who became the sport's first African American champion when he won the 2012 Top Fuel National Hot Rod Association championship.[353]
- Wally Campbell (1926–1954), stock car, midget, and sprint car racer who was the 1951 NASCAR Modified champion.[354]
- George Case (1915–1989), outfielder who played for the Washington Senators.[355]
- Terrance Cauthen (born 1976), lightweight boxer who won a bronze medal at the 1996 Summer Olympics.[356]
- Donald Cogsville (born 1965), former soccer player who earned six caps with the U.S. national team and is CEO of a real estate investment firm.[357]
- Gwynneth Coogan (born 1965), former Olympic athlete, educator and mathematician.[358]
- Hollis Copeland (born 1955), former professional basketball player who played for the New York Knicks.[359]
- Harry Deane (1846–1925), early professional baseball player.[360]
- J.J. Dillon (born 1945), former professional wrestler.[361]
- Dan Donigan (born 1967), former professional soccer player.[362]
- Al Downing (born 1941), professional baseball player.[363]
- John Easton (1933–2001), baseball player who played briefly for the Philadelphia Phillies.[364]
- Nick Frascella (1914–2000), basketball player who played in the National Basketball League for the Akron Goodyear Wingfoots.[365]
- Dave Gallagher (born 1960), professional baseball player.[366]
- Samuel Goss (born 1947), boxerwho competed in the men's bantamweight event at the 1968 Summer Olympics.[367]
- Greg Grant (born 1966), NBA basketball player.[368]
- Mel Groomes (1927–1997), football player and baseball coach who played for the Detroit Lions.[369]
- Thomas Hardiman (born 1947), former handball player who competed in the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich.[370]
- Jacke Healey (born 1988), college baseball coach and former shortstop who is co-head coach of the Oakland Golden Grizzlies baseball team.[371]
- Roy Hinson (born 1961), professional basketball player.[372]
- Dahntay Jones (born 1980), professional basketball player.[373]
- Patrick Kerney (born 1976), defensive end who played in the NFL for the Atlanta Falcons and Seattle Seahawks.[374]
- Tad Kornegay (born 1982) defensive back for the Saskatchewan Roughriders and BC Lions of the Canadian Football League.[375]
- Brandel Littlejohn, professional wrestler who competes for Ring of Honor, where he performs under the ring name "Cheeseburger".[376]
- Kareem McKenzie (born 1979), offensive tackle for the New York Giants of the National Football League.[377]
- Bob Milacki (born 1964), former MLB pitcher who played mostly with the Baltimore Orioles.[378]
- Karin Miller (born 1977), former professional tennis player.[379]
- Keith Newell (born 1988), football offensive lineman for the Philadelphia Soul of the Arena Football League.[380]
- Myles Powell (born 1997), basketball player for the Seton Hall Pirates men's basketball team.[381]
- Duane Robinson (born 1968), retired professional soccer forward who played in the American Professional Soccer League and the United States Interregional Soccer League.[382]
- Dennis Rodman (born 1961), professional basketball player.[383]
- Bobby Sanguinetti (born 1988), professional ice hockey defenseman who plays for HC Lugano in the National League[384]
- Carlijn Schoutens (born 1994), Dutch-American speed skater who qualified for the U.S. team at the 2018 Winter Olympics in the women's 3,000-meter event.[385]
- Gary Stills (born 1974), professional American football player.[386]
- La'Keisha Sutton (born 1990), professional basketball player for the Harlem Globetrotters.[387]
- Alphonso Taylor (born 1969), defensive tackle who played in the NFL for the Denver Broncos.[388]
- Vince Thompson (born 1957), former professional football running back who played in the NFL for the Detroit Lions.[389]
- Mike Tiernan (1867–1918), major league baseball player.[390]
- Dantouma Toure (born 2004), soccer player who plays as a winger for New York Red Bulls II in the USL Championship via the New York Red Bulls Academy.[391]
- Troy Vincent (born 1971), former professional football player, president of the NFL Players Association.[392]
- Charlie Weis (born 1956), head coach of the Notre Dame Fighting Irish football team from 2005 to 2009.[393]
- Nick Werkman (born c. 1941), basketball player for the Seton Hall Pirates, who led the NCAA in scoring in 1962–63 and was in the top three nationally on his two other collegiate seasons.[394]
Others
- Orfeo Angelucci (1912–1993), contactee who claimed to be in ongoing contact with extraterrestrial beings.[395]
- Anthony Balaam (born 1965), serial killer known as The Trenton Strangler.[396]
- Geoffrey Berman (born 1959), lawyer currently serving as the Interim United States Attorney for the Southern District of New York.[397]
- Jude Burkhauser (1947–1998), artist, museum curator and researcher.[398]
- Emily Roebling Cadwalader (1879–1941), Philadelphia socialite and yacht owner.[399]
- John Lambert Cadwalader (1836–1914), lawyer who was a name partner of Cadwalader, Wickersham & Taft.[400]
- Jon Caldara, libertarian activist who serves as the president of the Independence Institute.[401]
- Bernard Cywinski (1940–2011), architect who designed the Liberty Bell Center at Independence National Historical Park.[402]
- Mathias J. DeVito (c. 1930–2019), businessperson and lawyer who served as the president and chief executive officer of The Rouse Company.[403]
- Matthew Edward Duke (1915–1960), pilot who turned to making a living off flying anti-Castro Cubans to exile in the United States for $1,000 a job.[404]
- Brian Duperreault (born 1947), CEO of AIG[405]
- Harrington Emerson (1853–1931), efficiency engineer and business theorist.[406]
- Al Herpin (1862–1947), known as the "Man Who Never Slept".[407]
- Edward Kmiec (born 1936), retired Roman Catholic Bishop of Buffalo.[408]
- Jonathan LeVine (born 1968), owner of Jonathan LeVine Gallery.[409][410]
- Thomas Maddock (1818–1899), inventor and potter who started the American indoor toilet industry.[411]
- J. Lee Nicholson (1863–1924), accountant, consultant and lecturer, considered to be the father of cost accounting in the United States.[412]
- Zebulon Pike (1779–1813), explorer and namesake of Pikes Peak.[413]
- Joe Plumeri (born 1944), chairman and CEO of Willis Group and owner of the Trenton Thunder.[414][415]
- Bruce Ritter (1927–1999), Catholic priest and one-time Franciscan friar who founded the charity Covenant House in 1972 for homeless teenagers and led it until he was forced to resign in 1990.[416]
- Frank D. Schroth (1884–1974), owner of the Brooklyn Eagle, had earlier worked as a reporter at The Times.[417]
- Thomas N. Schroth (1921–2009), editor of Congressional Quarterly and founder of The National Journal.[418]
- Victor W. Sidel (1931–2018), physician who was one of the co-founders of Physicians for Social Responsibility in 1961.[419]
- Robert Stempel (born 1933), chairman and CEO of General Motors.[420]
- Margaret E. Thompson (1911–1992), numismatist specializing in Greek coins.[421]
- Irvin Ungar (born 1948), former pulpit rabbi and antiquarian bookseller, considered the foremost expert on the artist Arthur Szyk.[422]
- Albert W. Van Duzer (1917–1999), bishop of the Episcopal Diocese of New Jersey, serving from 1973 to 1982.[423]
- Ken Wolski (born 1948), registered nurse, marijuana legalization advocate and 2012 Green Party nominee for U.S. Senate.[424]
References
- Kuperinsky, Amy. "'The Jewel of the Meadowlands'?: N.J.'s best, worst and weirdest town slogans", NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, January 22, 2015. Accessed July 12, 2016. "Trenton. There are scant few unfamiliar with the huge neon sign installed in 1935 that sits on the Lower Trenton Bridge, declaring 'Trenton Makes, The World Takes.' Lumber company owner S. Roy Heath came up with the slogan, originally 'The World Takes, Trenton Makes,' for a chamber of commerce contest in 1910."
- 2019 Census Gazetteer Files: New Jersey Places, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 1, 2020.
- US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990, United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- 2012 New Jersey Legislative District Data Book, Rutgers University Edward J. Bloustein School of Planning and Public Policy, March 2013, p. 73.
- Trenton City Council Chambers, Trenton, New Jersey. Accessed March 15, 2020.
- 2020 New Jersey Mayors Directory, New Jersey Department of Community Affairs. Accessed February 1, 2020.
- Administration & Finance Department, City of Trenton. Accessed March 15, 2020.
- City Clerk, City of Trenton. Accessed March 15, 2020.
- "City of Trenton". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved March 14, 2013.
- DP-1 – Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 for Trenton city, Mercer County, New Jersey Archived February 12, 2020, at Archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed January 10, 2012.
- Municipalities Sorted by 2011-2020 Legislative District, New Jersey Department of State. Accessed February 1, 2020.
- Table DP-1. Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2010 for Trenton city Archived May 6, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed January 10, 2012.
- QuickFacts for Trenton city, New Jersey; Mercer County, New Jersey; New Jersey from Population estimates, July 1, 2019, (V2019), United States Census Bureau. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places of 50,000 or More, Ranked by July 1, 2019 Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2019, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 1, 2020. Note that townships (including Edison, Lakewood and Woodbridge, all of which have larger populations) are excluded from these rankings.
- GCT-PH1 Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 – State – County Subdivision from the 2010 Census Summary File 1 for New Jersey Archived February 12, 2020, at Archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed August 11, 2013.
- Look Up a ZIP Code for Trenton, NJ, United States Postal Service. Accessed January 10, 2012.
- Zip Codes, State of New Jersey. Accessed September 7, 2013.
- Area Code Lookup – NPA NXX for Trenton, NJ, Area-Codes.com. Accessed September 7, 2013.
- U.S. Census website, United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- Geographic codes for New Jersey, Missouri Census Data Center. Accessed September 1, 2019.
- US Board on Geographic Names, United States Geological Survey. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- New Jersey County Map, New Jersey Department of State. Accessed July 10, 2017.
- Parker, L.A. "City celebrating role as U.S. capital in 1784", The Trentonian, November 6, 2009. Accessed January 10, 2012. "City and state leaders kicked off a two-month celebration yesterday with a news conference highlighting Trenton's brief role as the capital of the United States in 1784."
- New York-Newark, NY-NJ-CT-PA Combined Statistical Area, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 28, 2014.
- "Revised Delineations of Metropolitan Statistical Areas, Micropolitan Statistical Areas, and Combined Statistical Areas, and Guidance on Uses of the Delineations of These Areas.", Office of Management and Budget Bulletin 13-01, February 28, 2013. Accessed April 22, 2019.
- The Counties and Most Populous Cities and Townships in 2010 in New Jersey: 2000 and 2010 Archived October 20, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, United States Census Bureau. Accessed January 10, 2012.
- Table 7. Population for the Counties and Municipalities in New Jersey: 1990, 2000 and 2010 Archived August 7, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development, February 2011. Accessed July 12, 2012.
- The Story of New Jersey's Civil Boundaries: 1606–1968, John P. Snyder, Bureau of Geology and Topography; Trenton, New Jersey; 1969. pp. 164–165. Accessed August 21, 2012,
- County History, Hunterdon County, New Jersey. Accessed April 18, 2011.
- Honeyman, Abraham Van Doren. Index-analysis of the Statutes of New Jersey, 1896–1909: Together with References to All Acts, and Parts of Acts, in the 'General Statutes' and Pamphlet Laws Expressly Repealed: and the Statutory Crimes of New Jersey During the Same Period, p. 302. New Jersey Law Journal Publishing Company, 1910. Accessed October 12, 2015.
- "Before There Was Trenton: A 350th Anniversary Look at the 17th Century Display of Early New Netherland Colonial Artifacts June 22 – October 19, 2014", Trenton City Museum, October 12, 2014. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- Hunter, Richard. "Chapter 4: Land Use History", from Abbott Farm National Historic Landmark Interpretive Plan, Mercer County, New Jersey. Accessed May 5, 2016.
- Krystal, Becky. "Trenton, N.J.: One for the history buffs", The Washington Post, February 10, 2011. Accessed January 10, 2012. "Back in the early 18th century, at least, the area was remote enough for Trent, a wealthy Philadelphia merchant, to build his summer home there near the banks of the Delaware River. And though it's dwarfed by its modern-day neighbors, at the time the home reflected its owner's 'ostentatious nature,' Nedoresow said. Further stroking his ego, he named the settlement he laid out 'Trent-towne,' which eventually evolved into the current moniker."
- Hutchinson, Viola L. The Origin of New Jersey Place Names, New Jersey Public Library Commission, May 1945. Accessed October 12, 2015.
- Gannett, Henry. The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States, p. 304. United States Government Printing Office, 1905. Accessed October 12, 2015.
- "This Day in History – Dec 26, 1776: Washington wins first major U.S. victory at Trenton", History (U.S. TV channel), November 13, 2009, updated July 27, 2019. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- Fischer, David Hackett (2006). "The Bridge. Assunpink, The Most Awful Moment". Washington's Crossing. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 290–307. ISBN 0-19-518159-X.
- Messler, Mary J. "Chapter IV: Some Notable Events of Post-Revolutionary Times" from A History of Trenton: 1679–1929, Trenton Historical Society. Accessed May 5, 2016. "The question now resolved itself into a quarrel between the North and the South. New England favored Trenton, whereas the Southern States felt that in the selection of any site north of Mason and Dixon's line their claims for recognition were being slighted, and their interests sacrificed to New England's commercialism."
- Stryker, William S. (1882). Washington's reception by the people of New Jersey in 1789. Trenton, New Jersey. p. 4.
- A Short History of New Jersey, New Jersey. Accessed January 10, 2012.
- Some of Trenton's History, City of Trenton. Accessed October 12, 2015. "During the 1812 War, the primary hospital facility for the U.S. Army was at a temporary location on Broad Street."
- Richman, Steven M. Reconsidering Trenton: The Small City in the Post-Industrial Age, p. 49. McFarland & Company, 2010. ISBN 9780786462230. Accessed November 15, 2015.
- Blackwell, John|. "1948: A cry for justice", The Trentonian. Accessed June 4, 2018.
- Schlegel, Sharon. "Harrowing case of the 'Trenton Six'", The Times (Trenton), January 28, 2012. Accessed June 4, 2018. "The recently published story of the 'Trenton Six,' dramatically told in Cathy Knepper's newest book, Jersey Justice: The Story of the Trenton Six, is so filled with proven instances of injustice that it is almost hard to believe.... Reading how the men were arrested randomly and haphazardly (despite a partial witness claiming they were not the perpetrators) is horrifying. Equally upsetting is that they were held incommunicado for days without warrants, abused and drugged into confessing."
- Cumbler, John T. A Social History of Economic Decline: Business, Politics and Work in Trenton, p. 283. Rutgers University Press, 1989. ISBN 9780813513744. Accessed February 12, 2014.
- Listokin, David; and Listokin, Barbara. Barriers to the Rehabilitation of Afordable Housing Volume II Case Studies, United States Department of Housing and Urban Development, May 2001. Accessed December 1, 2019. "Socioeconomic and housing challenges are especially severe in some of Trenton’s oldest neighborhoods. In the Old Trenton area, abandonment went unchecked for decades, and when abandoned houses were demolished by the city, the empty lots remaining would fill with garbage and vermin. Another hard-hit location was the 'Battle Monument' area: 'Time has not been kind to the Battle Monument section of this city. The five-block area, the hub of the Battle of Trenton in 1775 and of transportation in the 1950s, has in the last four decades suffered from abandonment and neglect.'"
- Discover Our Bridges, Delaware River Joint Toll Bridge Commission. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- Trenton-Morrisville (Rt. 1) Toll Bridge, Delaware River Joint Toll Bridge Commission. Accessed December 1, 2019. "The Trenton-Morrisville Toll Bridge carries U.S. Route 1 over the Delaware River between Trenton, New Jersey and Morrisville, Pennsylvania.... The bridge is a twelve-span, simply supported composite steel girder and concrete deck structure with an overall length of 1,324 feet."
- Lower Trenton Toll-Supported Bridge, Delaware River Joint Toll Bridge Commission. Accessed December 1, 2019. "The Lower Trenton Toll-Supported Bridge, also known as the 'Trenton Makes The World Takes Bridge,' connects Warren Street in Trenton, N.J. with East Bridge Street in Morrisville, Pa. -- one of three bridges connecting the two communities.... The current 1,022-foot bridge is a five-span Warren Truss built in 1928."
- Calhoun Street Toll-Supported Bridge, Delaware River Joint Toll Bridge Commission. Accessed December 1, 2019. "The Calhoun Street Toll-Supported Bridge is the oldest bridge structure owned and operated by the Delaware River Joint Toll Bridge Commission. It turned 125 years old on October 20, 2009.... Of the 20 bridges in the DRJTBC system, the Calhoun Street Toll-Supported Bridge is the only one made of wrought iron. A Phoenix Pratt truss with a total length of 1,274 feet, it also holds the distinction as the Commission’s longest through-truss bridge and the Commission’s only seven-span truss bridge."
- Science In Your Backyard: New Jersey Archived August 21, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, United States Geological Survey. Accessed October 28, 2014.
- Stirling, Stephen. "U.S. Census shows East Brunswick as statistical center of N.J.", NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, March 31, 2011. Accessed May 21, 2017. "The state's geographic center remains Hamilton Township in Mercer County, just southeast of Trenton."
- Weiss, Daniel. "North/South Skirmishes; A film tries to draw the line between North and South Jersey.", New Jersey Monthly, April 30, 2008. Accessed June 12, 2018.
- Metropolitan Statistical Areas And Components, December 2003, With Codes, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 7, 2011.
- Howe, Randy. Nifty 50 States Brainiac, p. 1159. Kaplan Publishing, 2008. ISBN 9781427797117. Accessed February 12, 2014. "Carson City is one of just two capital cities in the United States that borders another state; the other is Trenton, New Jersey."
- Areas touching Trenton, MapIt. Accessed March 15, 2020.
- Municipalities within Mercer County, NJ, Delaware Valley Regional Planning Commission. Accessed November 15, 2019.
- New Jersey Municipal Boundaries, New Jersey Department of Transportation. Accessed November 15, 2019.
- Di Ionno, Mark. "Chambersburg", The Star-Ledger, July 17, 2007. Accessed March 16, 2012. "The difference between Chambersburg, the traditional Italian section of Trenton, and other city neighborhoods that have undergone 'natural progression' is that Chambersburg hung on so long."
- Richard Grubb & Associates. Three Centuries of African-American History in Trenton: A Preliminary Inventory of Historic Sites, Trenton Historic Society, September 2011. Accessed December 1, 2019. "Shiloh Baptist Church is the city’s oldest African-American Baptist congregation. The first groups of Black Baptists were formed in the city around 1880, with Shiloh formally organized in 1896."
- Trenton Battle Monument, New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Division of Parks and Forestry. Accessed September 7, 2013.
- "In their own words, South Ward candidates explain why they should win City Council seat", The Trentonian, October 18, 2009. Accessed June 12, 2018.
- Locality Search, State of New Jersey. Accessed May 21, 2015.
- "Interactive United States Koppen-Geiger Climate Classification Map". plantmaps.com. Retrieved October 12, 2018.
- Station Name: NJ TRENTON MERCER CO AP, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Accessed February 28, 2013.
- USDA Interactive Plant Hardiness Map, United States Department of Agriculture. Accessed November 26, 2019.
- Staff. "Heat sets new record high in Trenton at 106 degrees", The Trentonian, July 22, 2011. Accessed February 12, 2014. "The thermometer reached a record-setting 106 degrees here in the City of Trenton, easily smashing July 22nd's previous high mark from 1926, when the temp reached 101 degrees."
- "City of Trenton, New Jersey Natural Hazard Mitigation Plan", City of Trenton. Accessed February 12, 2014.
- City of Trenton, New Jersey Natural Hazard Mitigation Plan, City of Trenton, adopted June 19, 2008. Accessed June 12, 2018. "The average snowfall is 24.9 inches, but has ranged from as low as 2 inches (in the winter of 1918–19) to as high as 76.5 inches (in 1995–96). The heaviest snowstorm on record was the Blizzard of 1996 on January 7–8, 1996, when 24.2 inches buried the city."
- U.S. Potential Natural Vegetation, Original Kuchler Types, v2.0 (Spatially Adjusted to Correct Geometric Distortions), Data Basin. Accessed November 26, 2019.
- Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Minor Civil Divisions in New Jersey: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2019, United States Census Bureau. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- Census Estimates for New Jersey April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2019, United States Census Bureau. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- Compendium of censuses 1726–1905: together with the tabulated returns of 1905, New Jersey Department of State, 1906. Accessed July 15, 2013.
- Bowen, Francis. American Almanac and Repository of Useful Knowledge for the Year 1843, p. 231, David H. Williams, 1842. Accessed July 15, 2013. Population of 4,021 is listed for 1840, 14 less than shown in table.
- Raum, John O. The History of New Jersey: From Its Earliest Settlement to the Present Time, Volume 1, pp. 276–7. J. E. Potter and company, 1877. Accessed July 15, 2013. "Trenton the capitol of the State, as well as the seat of justice of the county of Mercer, is beautifully located on the east bank of the Delaware, at the head of tide navigation. Here is located the State Capitol, built in 1793, enlarged in 1845 and 1865, and again in 1871. The State Prison, State Arsenal, State Normal and Model schools are also located here. The city has 7 wards. Its population in 1850, was 6,461; in 1860, 17,228; and in 1870, 22,874"
- Debow, James Dunwoody Brownson. The Seventh Census of the United States: 1850, p. 139. R. Armstrong, 1853. Accessed July 15, 2013.
- Staff. A compendium of the ninth census, 1870, p. 260. United States Census Bureau, 1872. Accessed November 20, 2012.
- Porter, Robert Percival. Preliminary Results as Contained in the Eleventh Census Bulletins: Volume III – 51 to 75, p. 98. United States Census Bureau, 1890. Accessed November 20, 2012.
- Fifteenth Census of the United States : 1930 – Population Volume I, United States Census Bureau, p. 712. Accessed January 10, 2012.
- Table 6. New Jersey Resident Population by Municipality: 1930 – 1990 Archived May 10, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed June 28, 2015.
- Census 2000 Profiles of Demographic / Social / Economic / Housing Characteristics for Trenton city Archived January 31, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, United States Census Bureau. Accessed January 10, 2012.
- DP-1: Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2000 – Census 2000 Summary File 1 (SF 1) 100-Percent Data for Trenton city, New Jersey Archived February 12, 2020, at Archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 12, 2012.
- The Counties and Most Populous Cities and Townships in 2010 in New Jersey: 2000 and 2010 Archived January 13, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed May 21, 2017.
- DP03: Selected Economic Characteristics from the 2006–2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates for Trenton city, Mercer County, New Jersey Archived February 12, 2020, at Archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed January 10, 2012.
- Bruder, Jessica. "Jerseyana; Trenton's Fighting Words", The New York Times, May 2, 2004. Accessed March 16, 2012. "Trenton Makes, the World Takes, reads the famous red neon sign that spans a bridge between the state Capitol and Morrisville, Pa., affectionately known by locals as the Trenton Makes bridge.... In its heyday, Trenton was a world-class producer of rubber, steel, wire rope, and pottery. The cables for three famous suspension bridges – the Brooklyn, George Washington and Golden Gate – were produced here at John A. Roebling's factory."
- Blackwell, Jon. "1911: 'Trenton Makes' history", The Trentonian. Accessed October 28, 2014.
- Mickle, Paul. "1984: A whole new skyline", The Trentonian. Accessed October 28, 2014.
- Raboteau, Albert. "Diversifying city's economy a major goal for Trenton", The Times (Trenton), January 30, 2003. Accessed October 28, 2014. "Another large goal is to lure private companies whose employees, officials say, are likely to work later in the evening and have more money to spend than the 20,000 or so state workers who swell downtown during business hours, then commute home to other municipalities."
- History, Italian Peoples Bakery. Accessed May 13, 2016. "The origin of Italian Peoples Bakery goes back to 1936 when Pasquale Gervasio, the patriarch of the family, opened a bakery on Hamilton Avenue in Trenton, New Jersey."
- Urban Enterprise Zone Tax Questions and Answers, New Jersey Department of Community Affairs, May 2009. Accessed October 28, 2019. "The Urban Enterprise Zone Program (UEZ) was enacted in 1983. It authorized the designation of ten zones by the New Jersey Urban Enterprise Zone Authority: Camden, Newark, Bridgeton, Trenton, Plainfield, Elizabeth, Jersey City, Kearny, Orange and Millville/Vineland (joint zone)."
- Urban Enterprise Zone Program, New Jersey Department of Community Affairs. Accessed October 27, 2019. "Businesses participating in the UEZ Program can charge half the standard sales tax rate on certain purchases, currently 3.3125% effective 1/1/2018"
- Urban Enterprise Zone Effective and Expiration Dates, New Jersey Department of Community Affairs. Accessed January 8, 2018.
- Racioppi, Dustin. "Christie vetoes urban enterprise zone extension", The Record (North Jersey), February 10, 2017. Accessed November 19, 2019. "Gov. Chris Christie on Friday conditionally vetoed the Legislature's attempt to extend the Urban Enterprise Zone status for its five charter communities, calling the economic revitalization program an 'abject failure' with a 'devastating impact' on state revenue.... The Legislature returned with what it called a compromise bill, A-4189, to extend the designation for two years instead of 10 for the first five UEZs -- Bridgeton, Camden, Newark, Plainfield and Trenton -- which expired on Jan. 1."
- "Notice: Law Reinstates Five Urban Enterprise Zones And Also Extends The Expiration Date Of 12 Other UEZs", New Jersey Department of the Treasury Division of Taxation, May 30, 2018. Accessed November 19, 2019. "On May 30, 2018, Governor Murphy signed Senate Bill 846 (A3549). The law reinstated five expired Urban Enterprise Zones (UEZs). If your business is located in one of these zones, you may file an application to establish qualified business status. (Past certifications are no longer valid in these five zones). The five UEZs are in: *Bridgeton *Camden *Newark *Plainfield *Trenton. The UEZs in the five locations listed above expire on December 31, 2023."
- 2018 Property Tax Information, New Jersey Department of Community Affairs, updated January 16, 2019. Accessed November 7, 2019.
- Marcus, Samantha. "These are the towns with the lowest property taxes in each of N.J.’s 21 counties", NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, April 30, 2019. Accessed November 7, 2019. "New Jersey’s average property tax bill may have hit $8,767 last year — a new record — but taxpayers in some parts of the state pay just a fraction of that.... The average property tax bill in Trenton was $3,274 in 2018, the lowest in Mercer County."
- "New Statistical Area Information based on Census 2000" Archived August 2, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development, December 14, 2004. Accessed January 10, 2012.
- 4 Museums in One, New Jersey State Museum. Accessed January 5, 2015.
- State House History, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 5, 2015.
- About the NJ State Library, New Jersey State Library. Accessed January 5, 2015.
- Welcome to the Trenton City Museum, Trenton City Museum. Accessed December 1, 2019. "The museum is located in Ellarslie Mansion, an Italianate villa built in 1848. The mansion is the centerpiece of Cadwalader Park, which was designed by the famed landscape architect Frederick Law Olmsted, whose most famous work is New York City’s Central Park."
- Frequently Asked Questions about the War Memorial, New Jersey Department of State. Accessed September 7, 2013.
- About the Building, Old Barracks Museum. Accessed December 1, 2019. "In 1758, during the French and Indian War, the building now referred to as the Old Barracks was constructed by the colony of New Jersey in direct response to petitions from residents who were protesting compulsory quartering of soldiers in their own homes. It was one of five such buildings throughout New Jersey constructed for the purpose of housing British soldiers during the winter months of the war, and it is the only one still standing."
- Designing the Monument, New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Division of Parks and Forestry. Accessed September 7, 2013.
- Trenton City Hall, Library of Congress. Accessed September 7, 2013.
- About the 1719 Trent House, William Trent House. Accessed December 1, 2019. "William Trent built his country estate north of Philadelphia, in New Jersey, at the Falls of the Delaware River about 1719.... In 1720 Trent laid out a settlement, which he incorporated and named 'Trenton.'"
- Fitzpatrick, Frank. "Jersey's split sports personality Great Divide: Eagles and Giants fans", The Philadelphia Inquirer, January 11, 2009. Accessed October 12, 2015.
- Huneke, Bill. "Trenton Speedway lives on at Pocono", The Times (Trenton), July 6, 2013. Accessed October 12, 2015. "As Indy Car racing returns to Pocono this weekend after a 24-year absence, only a few of the drivers competing were even alive when Trenton's last event was run in 1979."
- History of State Fairgrounds Archived February 10, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Grounds for Sculpture. Accessed March 16, 2012. As horses were replaced by automobiles for transportation, cars became the main attraction on the fairground's racetrack. 'Lucky' Teter and his Hell Drivers made the headlines in the 1930s; in the sixties it was midget car races and a 200-mile race for Indianapolis cars and drivers."
- McGeehan, Patrick. "Private Sector; A Wall St. Son at Nasdaq's Table ", The New York Times, December 17, 2000. Accessed January 5, 2015. "Mr. Plumeri, who owns a minor league team affiliated with the Red Sox, the Trenton Thunder, has even drawn Mr. Simmons to the team's stadium, Samuel J. Plumeri Field, to watch his beloved team play exhibition games."
- Arm & Hammer Park Trenton, New Jersey, Ball Parks of the Minor Leagues. Accessed January 5, 2015. "The playing field was named in 1999 in honor of Samuel Plumeri Sr., one of the driving forces in bring baseball back to New Jersey's state capital."
- Pahigian, Josh. The Ultimate Minor League Baseball Road Trip: A Fan's Guide to AAA, AA, A, and Independent League Stadiums, p. 45. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 9781599216270. Accessed January 5, 2015.
- "Trenton Thunder Continue Affiliation with Major League Baseball in New MLB Draft League". Trenton Thunder. Minor League Baseball. November 30, 2020. Retrieved November 30, 2020.
- Foster, David. "Sacked: Trenton Freedom indoor football team folds", The Trentonian, August 26, 2015. Accessed October 12, 2015. "The Trenton Freedom is the latest professional sports team to shutter operations in the capital city, following the same doomed path of several other organizations at the Sun National Bank Center.... The Trenton Freedom, a member of the Professional Indoor Football League (PIFL), became the third indoor football team to fail at the Sun National Bank Center, lasting one year longer than the previous two. The Trenton Steel called the 8,000-seat arena home for six games in 2011. A decade earlier, the Trenton Lightning lasted just one season."
- Cadwalader Park Archived October 20, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Trenton City Museum. Accessed December 1, 2019. "Cadwalader Park is the largest urban park in the City of Trenton (109.5 acres). It is crossed by the Delaware & Raritan (D&R) Canal State Park.... Discussions among Hill and other Trenton civic leaders led to the engagement of Frederick Law Olmsted’s firm to design a park in 1890."
- Lamar, Martha L.; Powell, L. Matthew; Davies, David S. "Adams and Sickles Building" (PDF), National Register of Historic Places National Park Service, June 5, 1979. Accessed May 13, 2016.
- Trenton Society of Friends Meeting House, Destination Trenton. Accessed May 13, 2016. "In the burying-ground adjoining the Meeting House are buried many citizens who played prominent parts in the early history of the city."
- Trenton Friends Meeting House (PDF), National Register of Historic Places National Park Service. Accessed May 13, 2016.
- Inventory of Municipal Forms of Government in New Jersey, Rutgers University Center for Government Studies, July 1, 2011. Accessed November 18, 2019.
- City Council Overview, Trenton, New Jersey. Accessed December 1, 2019. "The City of Trenton is governed within the Faulkner Act, formerly known as the Optional Municipal Charter Law. Under this act, the Mayor-Council system was developed in 1792."
- Office of the Mayor, Trenton, New Jersey. Accessed March 15, 2020. "Reed Gusciora (born March 27, 1960) was sworn in as the 48th mayor of the City of Trenton on July 1st, 2018. Prior to becoming Mayor, he served in the New Jersey General Assembly since 1996, representing the 15th Legislative District, which includes portions of Mercer and Hunterdon Counties."
- 2019 Municipal User Friendly Budget, Trenton, New Jersey. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- Mercer County Elected Officials, Mercer County, New Jersey, as of November 12, 2019. Accessed November 15, 2019.
- May 8, 2018 Trenton Municipal Election Official Results, Mercer County, New Jersey, last updated May 14, 2018. Accessed July 5, 2018.
- June 12, 2018 Trenton Municipal Runoff Election Results, Mercer County, New Jersey, last updated June 15, 2018. Accessed July 5, 2018.
- Zdan, Alex; and Pizzi, Jenna. "Acting Mayor George Muschal assumes office and vows to put Trenton 'on the right track'", The Times (Trenton), February 26, 2014. Accessed May 21, 2017.
- Pizzi, Jenna. "Trenton council to vote to install George Muschal as interim mayor", The Star-Ledger, March 4, 2014. Accessed October 12, 2015. "Council members decided to amend the agenda for their regularly scheduled meeting to include the action of appointing Muschal to the interim post. He will serve until a new mayor – elected in May – takes over July 1."
- via Associated Press."Mayor Tony Mack of Trenton Is Found Guilty of Taking Bribes", The New York Times, February 7, 2014. Accessed February 12, 2014.
- "NJ calls for convicted Trenton mayor Tony Mack to be removed" Archived February 23, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, WPVI-TV, February 10, 2014. Accessed February 12, 2014. "The state Attorney General's Office filed a request Monday with a state Superior Court judge, asking that Tony Mack be kicked out of office, stripped of his pension and be barred from holding elected office again.... Under state law, people convicted of corruption cannot continue to hold public office. But since Mack has not resigned, the state is asking a judge to enforce the law."
- via Associated Press. "A year of turmoil, stumbles for Trenton's mayor", The Star-Ledger, July 9, 2011. Accessed January 10, 2012.
- Plan Components Report, New Jersey Redistricting Commission, December 23, 2011. Accessed February 1, 2020.
- 2019 New Jersey Citizen's Guide to Government, New Jersey League of Women Voters. Accessed October 30, 2019.
- Districts by Number for 2011–2020, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 6, 2013.
- 2011 New Jersey Citizen's Guide to Government Archived June 4, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, p. 65, New Jersey League of Women Voters. Accessed May 22, 2015.
- Directory of Representatives: New Jersey, United States House of Representatives. Accessed January 3, 2019.
- Biography, Congresswoman Bonnie Watson Coleman. Accessed January 3, 2019. "Watson Coleman and her husband William reside in Ewing Township and are blessed to have three sons; William, Troy, and Jared and three grandchildren; William, Kamryn and Ashanee."
- About Cory Booker, United States Senate. Accessed January 26, 2015. "He now owns a home and lives in Newark's Central Ward community."
- Biography of Bob Menendez, United States Senate, January 26, 2015. "He currently lives in Paramus and has two children, Alicia and Robert."
- Senators of the 116th Congress from New Jersey. United States Senate. Accessed April 17, 2019. "Booker, Cory A. - (D - NJ) Class II; Menendez, Robert - (D - NJ) Class I"
- Legislative Roster 2020-2021 Session, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed August 27, 2020.
- District 15 Legislators, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed August 27, 2020.
- Elected Officials, Mercer County, New Jersey. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- Brian M. Hughes, County Executive, Mercer County, New Jersey. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- Andrew Koontz, Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- Samuel T. Frisby, Sr., Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- Ann M. Cannon, Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- Anthony P. Carabelli, Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- John A. Cimono, Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- Pasquale "Pat" Colavita, Jr., Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- Lucylle R. S. Walter, Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- Meet the Freeholders, Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- 2014 County Data Sheet, Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- County Clerk, Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- Sheriff, Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- County Surrogate, Mercer County. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- Elected Officials for Mercer County, State of New Jersey. Accessed September 6, 2014.
- Voter Registration Summary – Mercer, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, March 23, 2011. Accessed November 21, 2012.
- "Presidential General Election Results – November 8, 2016 – Mercer County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. Retrieved December 31, 2017.
- "Presidential General Election Results – November 6, 2012 – Mercer County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. March 15, 2013. Retrieved December 23, 2014.
- 2008 Presidential General Election Results: Mercer County, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 23, 2008. Accessed November 21, 2012.
- 2004 Presidential Election: Mercer County, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 13, 2004. Accessed November 21, 2012.
- "Number of Registered Voters and Ballots Cast – November 6, 2012 – General Election Results – Mercer County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. March 15, 2013. Retrieved December 23, 2014.
- "Governor – Mercer County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 1, 2018. Retrieved December 31, 2017.
- "Governor – Mercer County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. January 29, 2014. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- 2009 Governor: Mercer County, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 31, 2009. Accessed November 21, 2012.
- 2005 Governor: Mercer County Archived July 7, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections. Accessed December 31, 2017.
- "Number of Registered Voters and Ballots Cast – November 5, 2013 – General Election Results – Mercer County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. January 31, 2014. Retrieved December 23, 2014.
- Fire Department, City of Trenton. Accessed March 15, 2020. "The Trenton Fire Department traces its roots back to a blacksmith shop at Broad and Front Streets where, on February 7, 1747, a group of volunteers formed the Union Fire Company. The volunteers served the city well for the next 145 years until, on April 4, 1892, the paid department was established."
- Fire Department Facilities, City of Trenton. Accessed March 15, 2020.
- Fire & Emergency Services Apparatus, City of Trenton. Accessed March 15, 2020.
- Fast Facts, Thomas Edison State College. Accessed August 11, 2013.
- The James Kerney Campus, Mercer County Community College. Accessed August 11, 2013.
- Historic Rider, Rider University. Accessed February 12, 2014. "Gradually growing in size and scope through the first half of the 20th century, Rider began its move to a more spacious, suburban campus in 1959, when the first offices and classes moved to a 280-acre tract of land on Route 206 in Lawrence Township, N.J."
- Trenton Board of Education District Policy 0110 - Identification, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed March 15, 2020. "Purpose: The Board of Education exists for the purpose of providing a thorough and efficient system of free public education in grades Pre-Kindergarten through twelve in the Trenton School District. Composition: The Trenton School District is comprised of all the area within the municipal boundaries of the City of Trenton."
- Abbott School Districts, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed March 1, 2020.
- What We Do, New Jersey Schools Development Authority. Accessed March 1, 2020.
- SDA Districts, New Jersey Schools Development Authority. Accessed March 1, 2020.
- New Jersey Boards of Education by District Election Types - 2018 School Election, New Jersey Department of Education, updated February 16, 2018. Accessed January 26, 2020.
- Board of Education, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed March 15, 2020.
- District information for Trenton Public School District, National Center for Education Statistics. Accessed April 1, 2020.
- School Data for the Trenton Public Schools, National Center for Education Statistics. Accessed April 1, 2020.
- Columbus Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Franklin Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Grant Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Gregory Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Harrison Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools, Accessed May 10, 2020.
- P.J. Hill Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Jefferson Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr, Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Mott Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Parker Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Robbins Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Washington Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Wilson Elementary School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Grace A. Dunn Middle School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Hedgepeth-Williams Middle School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Joyce Kilmer Middle School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Luis Munoz Rivera Middle School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Trenton Ninth Grade Academy, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Daylight-Twilight Alternative High School, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Trenton Central High School Chambers Campus, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- Schools, Trenton Public Schools. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- 2017-2018 Charter and Public School Directory, Mercer County, New Jersey. Accessed May 10, 2020.
- New Jersey School Directory for the Trenton Public Schools, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed December 29, 2016.
- Heyboer, Kelly. "How to get your kid a seat in one of N.J.'s hardest-to-get-into high schools", NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, May 2017. Accessed November 18, 2019. "Mercer County has a stand-alone specialized high school for top students: a Health Sciences Academy at the district's Assunpink Center campus. The district also offers a STEM Academy at Mercer County Community College. How to apply: Students can apply online in the fall of their 8th grade year."
- High School Programs, Mercer County Technical Schools. Accessed November 18, 2019.
- Approved Charter Schools, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed February 12, 2014.
- Foster, David. "Trenton charter school officially announces closure as 9th Grade Academy readies move-in", The Trentonian, June 1, 2018. Accessed July 11, 2018. "In a statement sent to The Trentonian on Friday, International Academy of Trenton (IAT) Charter School Board President Larry Chenault 'regretfully' accepted the doomed fate of the school, which spent $17 million to renovate the former Times of Trenton building into a state-of-the-art learning center.... IAT was informed in January by the New Jersey Department of Education (DOE) that the school, which educated 650 students, would be losing its charter at the end of this month for poor student performance and classroom mismanagement."
- School Finder, Roman Catholic Diocese of Trenton. Accessed May 21, 2017.
- About Us, Islamic School of Trenton. Accessed February 12, 2014.
- "Trenton murders hit all-time high", The Signal, January 25, 2006. Accessed June 7, 2015. "With 31 murders, 2005 was the deadliest year in Trenton's history, up from 18 in 2004."
- 12th Annual Safest/Most Dangerous Cities Survey: Top and Bottom 25 Cities Overall. Accessed June 23, 2006.
- 13th Annual Safest (and Most Dangerous) Cities: Top and Bottom 25 Cities Overall Archived June 15, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Morgan Quitno. Accessed October 30, 2006.
- Shea, Kevin. "City sees murder rate increase: Trenton records 25 homicides in 2007, up from 20 in 2006", The Times (Trenton), January 2, 2008. Accessed January 21, 2008. "Trenton had 25 homicides in 2007, up from 20 in 2006."
- Ray, Penny. "2018: Trenton homicides by the numbers", The Trentonian, January 1, 2019. Accessed December 2, 2019. "The capital city concluded 2018 with 21 homicides, which includes the death of 52-year-old Michael Anderson, who was shot on a Wayne Avenue porch during the early morning hours of June 7, 2017."
- Cohen, Noah; and Iati, Marisa. "Homicides dropped by 7 percent in 2017. Here's how many each county had.", NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, January 2018. Accessed December 2, 2019. "The state's capital, Trenton, accounted for 21 of this year's homicides in Mercer County, according to the county prosecutor's office. Ewing, Hamilton, Hopewell and Lawrence each logged one killing this year."
- Zdan, Alex. "Trenton police layoff plan to go into effect today", The Times (Trenton), September 16, 2011. Accessed January 10, 2012. "The 108 police officers slated to be terminated represent one-third of the force. Demotions affecting nearly 30 members will send current lieutenants and sergeants back to the street, depleting supervisor levels and the detective bureaus in an effort to keep patrols close to their current strength."
- Queally, James. "N.J. homicides soared to seven-year high in 2013 after surges in Newark, Trenton", The Star-Ledger, January 1, 2014. Accessed February 12, 2014. "In Trenton, the number of homicides soared to 37, the most in the state capital's recorded history."
- Brown, Keith. "Trenton homicides down, but not by much, in 2014", The Star-Ledger, January 1, 2015. Accessed May 16, 2016. "There were 34 homicides in Trenton in 2014 – a year following an inglorious record-setting 37 homicides in 2013."
- McEvoy, James. "Authorities ID Trenton homicide victim, investigate separate shooting", The Times (Trenton), October 19, 2014. Accessed May 16, 2016. "Sutphin's slaying was the first homicide in Trenton since July 30 when Tyshawn Goodman, 25, of Trenton, and George Jamison, 44, of Pennington, were shot to death in what police believed were separate robberies. The nearly three months of relative peace followed a bloody start in which the city saw 23 homicides in the first seven months of the year."
- Editorial. "Trenton bucks trend as murder rate drops in 2015", The Times (Trenton), January 7, 2016. Accessed May 16, 2016. "It is a sad fact that 17 people were murdered in Trenton last year. But from a purely statistical point of view, that number is cause for celebration in New Jersey's capital city."
- A Short History of Trenton State Prison, InsideOut: Fifty Years Behind the Walls of New Jersey's Trenton State Prison. Accessed March 16, 2012.
- Lundy, F. L.; et al. Manual of the Legislature of New Jersey, Volume 139, p. 97. J.A. Fitzgerald, 1915. Accessed June 12, 2018.
- Mercer County Mileage by Municipality and Jurisdiction, New Jersey Department of Transportation, March 2019. Accessed January 26, 2021.
- U.S. Route 1 Straight Line Diagram, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated May 2018. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- Route 29 Straight Line Diagram, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated July 2014. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- Route 129 Straight Line Diagram, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated March 2018. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- U.S. Route 206 Straight Line Diagram, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated June 2017. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- Route 31 Straight Line Diagram, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated May 2017. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- Route 33 Straight Line Diagram, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated March 2017. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- Trenton Station Renovation, NJ Transit. Accessed March 16, 2012.
- River Line System Map, NJ Transit. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- Trenton, New Jersey, Amtrak. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- McEvoy, James. "Frontier Airlines cancels service from Trenton-Mercer to 5 destinations because of lack of demand", Times of Trenton, January 5, 2015. Accessed January 5, 2015. "As of Tuesday, Frontier Airlines will discontinue service to Nashville, Tenn., St. Louis, Indianapolis, Milwaukee and Cleveland because of lack of demand, Frontier spokesman Todd Lehmacher said in an email. Service to Cleveland ended last month."
- "Mercer County Bus / Rail Connections". Archived from the original on May 22, 2009. Retrieved May 22, 2009.CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link), NJ Transit, backed up by the Internet Archive as of May 22, 2009. Accessed November 20, 2012.
- Mercer County Rider Guide, NJ Transit. Accessed November 27, 2019.
- Mercer County Bus Service, Greater Mercer Transportation Management Association. Accessed December 1, 2019.
- Home page Archived December 22, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, WZBN. Accessed December 7, 2011.
- Charles Conrad Abbott Papers, 1770–1919 (bulk 1874–1916): Finding Aid, Princeton University Library. Accessed January 25, 2011.
- "Mary Joyce Doyle Credited with Revolutionizing Book Lending in Bergen County Dies at 87", The Record (North Jersey), June 29, 2016. Accessed October 30, 2019. "Mary Joyce Doyle, the middle of three daughters, was born and raised in Trenton and educated in Catholic schools."
- Robert B. Duffield, American Institute of Physics. Accessed May 24, 2020. "October 15, 1917 - Birth, Trenton (N.J.)."
- Andrews, Edmund L. "A Salesman for Bush's Tax Plan Who Has Belittled Similar Ideas", The New York Times, February 28, 2003. Accessed March 16, 2012. "Nicholas Gregory Mankiw: Born – Feb. 3, 1958, Trenton"
- George Reynolds, Rutgers University Oral History Archives, October 29, 1999. Accessed June 28, 2019. "I was born in 1917, in Trenton. Soon after that, I guess I was two years old, we moved to Highland Park, New Jersey, and that's where I lived my early life."
- Dr. Joshua Zeitz: Alumni Hall of Fame Class of 1990, Bordentown Regional High School. Accessed February 14, 2020. "Josh Zeitz was born in Trenton and grew up on Prince Street in Bordentown City."
- Donnelley, Paul. Fade to Black: A Book of Movie Obituaries, p. 7. Music Sales Group, 2003. ISBN 9780711995123. Accessed January 5, 2015. "Mrs Rudolph Valentino the First. Born in Trenton, New Jersey, the petite, hazel-eyed brunette began acting aged 18."
- Staff. "Betty Bronson, 17, Gets Peter Pan Role; Sir James Barrie Selects Almost Unknown Film Actress After 100 Tests of Players.", The New York Times, August 16, 1924. Accessed July 11, 2018. "Film Director Herbert Brenon announced tonight the name of the film actress selected to play Peter Pan in the screen version of Barrie's phantasy. She is Betty Bronson, aged 17, born in Trenton, N.J."
- Bennetts, Leslie. "New Face: Roxanne Hart Coming of Age In Loose Ends", The New York Times, July 6, 1979. Accessed July 2, 2018. "She was born in Trenton, the oldest of five children, but moved from Delaware to Colorado to Georgia to Long Island as her father, a biology teacher, took different jobs."
- Iannucci, Lisa. "Spotlight: Richard Kind; Mad about him", SuburbanLife Philadelphia, December 2009. Accessed October 2, 2019. "Born in Trenton, N.J., Kind was in fourth grade when his parents moved him and his younger sister, Joanne, to Yardley, Pa., where he stayed until he graduated from Pennsbury High School in 1974."
- Staff. "Trenton's own Ernie Kovacs to be celebrated Sunday, his 92nd birthday", The Trentonian, January 23, 2011. Accessed February 1, 2011.
- Stone, Sally. "Judith Light: Is best always better?", The Spokesman-Review, October 12, 1993. Accessed February 1, 2011. "Judith Light grew up in Trenton, New Jersey. After her junior year at St. Mary's Hall, a private girls' school, she enrolled in a summer drama program at Carnegie Tech..."
- Abdur-Rahman, Sulaiman. "Former 'Melrose Place' actress Amy Locane-Bovenizer of Hopewell indicted in fatal crash", The Trentonian, December 16, 2010. Accessed February 1, 2011. "Trenton-born TV and film actress Amy Locane-Bovenizer, whose resume includes several big screen gigs with Hollywood A-listers, was indicted Thursday on charges she was boozed up and driving recklessly when she killed a woman in a horrific two-vehicle accident June 27."
- Amy Robinson:Overview Archived June 12, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, MSN. Accessed February 8, 2011.
- Burch, Audra D. S. "Code Blue Best Of Times, Worst Of Times For Black Comics", Chicago Tribune, April 13, 1997. Accessed February 8, 2011. "'I talk about what people are thinking about,' says Sommore, from Trenton, N.J. 'And I use curse words to enrich what I am saying.'"
- About Us Archived January 26, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Treadway Realty. Accessed June 25, 2017. "Former One Life to Live television star and 4 time Emmy nominated talk show host Ty Treadway was born and raised in Trenton, New Jersey."
- Roberts, Sam. "Sammy Williams, Tony Winner in ‘A Chorus Line,’ Dies at 69", The New York Times, March 22, 2018. Accessed July 19, 2019. "Samuel Joseph Williams was born on Nov. 13, 1948, in Trenton to Joseph Williams, a factory worker, and the former Nona Dibella, who worked in a hospital."
- Fox, Margalit. "Helen Boehm, the Princess of Porcelain, Dies at 89", The New York Times, November 19, 2010. Accessed January 5, 2015. "In 1944, she married Edward Marshall Boehm. An experienced livestock breeder, he made realistic clay sculptures of animals as a pastime. Mrs. Boehm encouraged him to pursue his art professionally, and eventually, with a loan from one of her eyeglass clients, they started a porcelain studio in a Trenton basement."
- Blau, Eleanor. "Ruth Donnelly, Comedienne And Character Actor In Films", The New York Times, November 19, 1982. Accessed January 9, 2015. "Born in Trenton, Miss Donnelly, whose father was a newspaper editor, music critic and columnist, began her career at the age of 17 as a chorus girl and shortly afterward began appearing in stage plays, including several productions of George M. Cohan."
- Peter Hujar, Blouin Artinfo. Accessed January 22, 2017. "Born in Trenton, New Jersey, in the autumn of 1934, Peter Hujar was left in the care of his immigrant grandparents as an infant."
- Atkins, Holly. "Welcome to Tangerine, and be careful", St. Petersburg Times, February 18, 2002. Accessed January 25, 2011.
- Guide to the Edward Y. Breese papers 1965–1972, Orbiscascade.org. Accessed January 5, 2015. "Edward Yarde Breese was born in Trenton, New Jersey in 1912."
- Staff. "Princeton Authors", p. 26. Princeton Alumni Weekly, Volume 50. Accessed January 5, 2015. "Born in New York City and reared in Trenton, Mr. Brooks entered Princeton from Kent School in 1938."
- "Russell G. Carter; Newton Author Wrote 50 Books", The Boston Globe, May 9, 1957. Accessed December 8, 2020, via Newspapers.com. "Mr. Carter was born Jan. 1, 1892, Trenton, N.J, the son of John Rogers and Alice (Hughes) Carter."
- Morris, Shaheed M. "City woman's 50-year-old letter part of TLC Kennedy special", The Trentonian, November 16, 2013. Accessed January 15, 2018. "Hirsch was born in Trenton. She graduated from Ewing High School in 1968."
- Wolk, Martin. "Reading the Northwest: Pam Houston saved the ranch, and it saved her in return", The Spokesman-Review, January 19, 2019. Accessed December 2, 2019. "Pam Houston at a glance Born in: Trenton, N.J., 1962 (age 57)"
- Kabatchnik, Amnon. Blood on the Stage, 1975–2000: Milestone Plays of Crime, Mystery, and Detection, p. 139. Scarecrow Press, 2012. ISBN 9780810883550. Accessed September 15, 2018. "William Mastrosimone was born in Trenton, New Jersey in 1947. He attended The Pennington School and received an MFA in playwriting from Mason Gross School of the Arts, part of Rutgers University, where his first play, Devil Take the Hindmost, was produced in 1977, winning the David Library of the American Revolution Award."
- Marsh, Steven P. "Kung Fu Panda director takes on The Little Prince", The Journal News, February 29, 2016. Accessed July 2, 2018. "The two-time Academy Award nominee's journey toward making a big-screen version of The Little Prince – based on Antoine de Saint-Exupéry's beloved 1943 illustrated novella – began more than two decades ago, as the result of a young woman's romantic gesture toward the Trenton, New Jersey, native."
- Staff. "Talking too much for our own good", The Intelligencer, May 15, 2003. Accessed February 8, 2011. "That version of Bob Ryan spent 20 minutes talking about the Palestra, growing up in Trenton, and great writers from the Philadelphia area."
- "Ntozake Shange" Archived July 7, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, Illustrated Women in History. Accessed October 3, 2017. "Shange was born Paulette L. Williams in 1948 in Trenton, New Jersey, where as a child she attended poetry readings with her sister."
- Sharpe, Tom. "Nancy Wood, 1936–2013: Writer, photographer found new 'way of being and seeing' in New Mexico", The Santa Fe New Mexican, March 13, 2013. Accessed October 10, 2016. "Born on June 20, 1936, in Trenton, N.J., to an Irish Catholic family, Wood attended Bucknell University in Lewisburg, Penn."
- Sparkman, Wayne. This Day in Presbyterian History – January 19: Rev. James Francis Armstrong, PCA Historical Center, January 19, 2013. Accessed October 12, 2015.
- "Atlee, Samuel John, (1739–1786)", Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed January 5, 2015. "a Delegate from Pennsylvania; born in Trenton, N.J., in 1739, during the temporary residence of his parents at that place"
- Cadwalader Family Papers, Historical Society of Pennsylvania. Accessed October 12, 2015. "Dr. Thomas's elder son, John Cadwalader (1742–1786), spent his first eight years living in Trenton, before the family returned to Philadelphia."
- "Cadwalader, Lambert, (1742–1823)", Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed January 8, 2015. "Delegate and a Representative from New Jersey; born near Trenton, N.J., in 1742"
- Dr. Thomas Cadwalader (1707–1779) Archived July 8, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, University of Pennsylvania Archives & Records Center. Accessed January 8, 2015. "In addition to his work as a physician, Cadwalader was politically active. In 1746, while a resident of Trenton, he became its chief burgess."
- Dickinson, Philemon, (1739–1809), Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed January 9, 2015.
- Hansen, Brandon. "Great Americans: Molly Pitcher, Woman of the Revolution", The Chewelah Independent, July 4, 2019. Accessed December 3, 2019. "Hays was given the nickname of Molly Pitcher, as the history is still a little bit contested as some say there were other women that also earned the nickname Molly Pitcher at the battle. Mary Ludwig Gays, however, is generally believed to be the original Molly Pitcher although there is a great deal of folklore around the woman. Hays was born in 1744 in Trenton New Jersey and lived to be 87 years old, passing away in 1832."
- McAuliff, Michael. "Alito Bit of GOP Love", Daily News|location=New York, January 10, 2006. Accessed January 25, 2011. "With two rows of his family sitting behind him, Alito recounted his Trenton upbringing, the lives of his immigrant parents, and the culture clash he felt when he went to Princeton University in the late '60s."
- Johnson, Eric A.; and Hermann, Anna. "The Last Flight From Tallinn" Archived August 1, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Foreign Service Journal, May 2007. Accessed August 1, 2019. "Henry Antheil Jr. was born in 1912 in Trenton, N.J., one of four children to Henry William Antheil, owner of a shoe store, and his wife Wilhemine Huse, both Lutheran immigrants from Germany."
- Staff. "Americans Reach Safety In Sweden; 43 Persons, Evacuated From Finnish Capital, Are Taken to Stockholm by Ship U.S. Legation Is Moved Staff, Still on Duty, Takes Up Temporary Quarters About 12 Miles From Helsinki", The New York Times, December 6, 1939. Accessed July 22, 2018. "Henry W. Antheil, clerk, Trenton, N. J."
- John Taylor Bird, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed August 17, 2007.
- James Bishop, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed September 1, 2007.
- Kennedy, Charles Stuart. Interview with Ambassador Peggy Blackford, Association for Diplomatic Studies and Training, November 28, 2016. "Q: Let’s start at the beginning. When and where were you born? BLACKFORD: I was born in Trenton, New Jersey, in 1942."
- John Hart Brewer, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed August 17, 2007.
- Staff. "Ex-Senator Briggs Dead In Trehton; Chairman of Republican State Committee Had Been III for a Year", The New York Times, May 9, 1913. Accessed July 2, 2018. "Trenton, N. J., May 8. – Having suffered for some time with a complication of diseases, although having been confined to his bed for only a week, Frank O. Briggs, until last March United States Senator from New Jersey, died at his West State Street home here tonight at 8:30 o'clock."
- Michele Brown: Chief Executive Officer, Economic Development Authority Archived November 1, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Governor Chris Christie. Accessed January 5, 2015. "A native of Trenton, New Jersey, Ms. Brown received her J.D., magna cum laude, from Georgetown University Law Center and her B.A., magna cum laude, from Drew University."
- James Buchanan, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed August 27, 2007.
- Dullard, John P. Fitzgerald's Legislative Manual of the State of New Jersey, 1922, p. 375. Josephine A. Fitzgerald, 1922. Accessed October 12, 2015. "State Comptroller. Newton Abert Kendall Bugbee, Trenton"
- Saxon, Wolfgang. "Robert J. Burkhardt, 83, Leader Of New Jersey Democrats in 60's", The New York Times, January 5, 2000. Accessed January 5, 2015. "Robert James Burkhardt, a onetime power in the New Jersey Democratic Party who helped organize the Soviet-American summit meeting at Glassboro, N.J., but stumbled in a bribery scandal, died on Dec. 30 at Arden Hill Hospital in Goshen, N.Y. A former resident of Trenton and Central Valley, N.Y., he was 83."
- Bio, TeamChopra.org. Accessed January 8, 2015. "Born the son of immigrants in Trenton, New Jersey, Aneesh Chopra has spent his life focusing on education and innovation."
- Conger, James Lockwood, (1805 - 1876), Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed December 2, 2019. "Conger, James Lockwood, a Representative from Michigan; born in Trenton, N.J., February 18, 1805"
- Biographical Profile for Martin Connor, Vote NY. Accessed January 8, 2015. "He was born in 1945 in Trenton, New Jersey."
- Staff. "Former Rep. Willard S. Curtin Dies At 90 Caption: Republican Represented Bucks And Lehigh Counties, 1957–67.", The Morning Call, February 7, 1996. Accessed January 8, 2015. "Born in Trenton, N.J., he was a son of the late William and Edna (Mountford) Curtin."
- Brown, John Howard. Lamb's Biographical Dictionary of the United States, Volume 2, 1900, page 394. Accessed November 25, 2012.
- Wayne DeAngelo's BiographyPrintTrack This Politician, Project Vote Smart. Accessed January 9, 2015.
- Bohlen, Celestine. "The Nation: David N. Dinkins; An Even Temper In the Tempest of Mayoral Politics", The New York Times, September 17, 1989. Accessed March 16, 2012. "From his childhood, which he spent divided between New York City and Trenton, David Dinkins has kept steady control of his emotions, friends and family members say. When he was 6 years old, his mother left his father in Trenton and moved to New York, taking her two children with her. Mr. Dinkins later returned to Trenton, where he attended elementary and high school."
- Doane, George Washington; and Doane, William Croswell. The Life and Writings of George Washington Doane ...: For Twenty-seven Years Bishop of New Jersey. Containing His Poetical Works, Sermons, and Miscellaneous Writings, Volume 1, p. 11. D. Appleton, 1860. Accessed January 9, 2015. "George Washington Doane was born in Trenton, New Jersey, May 27 A. D. 1799."
- Staff. "F. Donnelly Dead. 21 Years as Mayor. Trenton Leader Resigned in 1932 Because of Health. His Father Mayor 1884–86.", The New York Times, September 26, 1935. Accessed July 2, 2018..
- "Rubin Names BEP Director And Deputy Director", United States Department of the Treasury, press release dated December 7, 1998. Accessed December 2, 2019. "Ferguson received a B.A. in economics from Lafayette College, Easton, PA, and a master's degree in public administration from the University of Southern California. He was born in Trenton, N.J."
- Kennedy, Charles Stuart. Ambassador Richard Funkhouser, Association for Diplomatic Studies and Training, February 2, 1998. Accessed December 2, 2019. "I was born and raised as a young man in Trenton, New Jersey, and, whimsically, I used to look at the "National Geographics" and figure out the farthest place I could get from Trenton, which turned out to be Outer Mongolia, in the country of the yaks, and I resolved that I would get there."
- Myers, William Starr. Prominent Families of New Jersey, Volume 1, p. 24. reprinted by Genealogical Publishing Company, 2000. ISBN 9780806350363. Accessed August 1, 2019. "Hon. Harry Heher - Justice Harry Heher was born March 20, 1889, in Trenton, New Jersey, son of John and Anne (Spelman) Heher."
- Charles Robert Howell, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed September 10, 2007.
- Elijah Cubberley Hutchinson, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed September 7, 2007.
- Kull, Helen. "Ewing Then and Now: A life spent devoted to service", Community News, March 28, 2017. Accessed December 2, 2019. "Marie Louise Hunt Hilson was born in Trenton on Dec. 8, 1882 to Cleaveland and Matilda Emily Hunt."
- Staff. "Former JFK, LBJ aide remembers years in Washington" Archived October 24, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Associated Press, October 23, 2008. Accessed February 1, 2011. "Katzenbach, a native of Philadelphia who grew up in Trenton, NJ, was born into a political family."
- Gray, Jerry. "Television's 'Lottery Guy' Strives to Stay in Senate", The New York Times, September 4, 1992. Accessed November 2, 2017. "Richard Joseph LaRossa Born: July 1, 1946; Trenton. Hometown: Trenton. Education: Notre Dame High School, Trenton"
- Cohen, J. "Leo Levin, 96", Jewish Exponent, December 10, 2015. Accessed August 1, 2019. "Leo Levin loved people, Judaism and the law. The Trenton native, who spent the last 28 years in Merion, taught for 50 years at the University of Pennsylvania Law School, started Lower Merion Synagogue in Bala Cynwyd and always put other people first."
- Joe Holley, "Former Diplomat Sol Linowitz, 91, Dies", The Washington Post, March 18, 2005. Accessed March 20, 2012. "Sol Myron Linowitz was the eldest of four sons born to Joseph and Rose Oglenskye Linowitz, immigrants from a region of Poland under Russian rule. He was born in Trenton, N.J., in a multicultural neighborhood of Jews, Protestants and Catholics, as well as one African American family."
- Manual of the Legislature of New Jersey, Volume 204, Part 2, p. 215. J.A. Fitzgerald., 1991. Accessed April 20, 2020. "Francis J. McManimon, Dem., Hamilton - Senator McManimon was born in Trenton, Sept. 30, 1926."
- Pace, Eric. "Joseph Merlino, 76, Trenton Political Figure", The New York Times, October 9, 1998. Accessed August 1, 2019. "Born in Trenton, he was the son of Pasquale Merlino and the former Margarita Fuccello."
- Staff. "Dayton Oliphant, Ex-Judge, 75, Dies; Headed Court of Errors and Appeals in New Jersey", The New York Times, June 27, 1963. Accessed July 2, 2018. "Born in Trenton, Mr. Oliphant attended the Lawrenceville School and was a memberof the Princeton University class of 2010."
- Justice Anne M. Patterson Archived May 30, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Courts. Accessed June 3, 2018. "Justice Patterson was born in Trenton on April 15, 1959, and raised in Hopewell Township and Princeton."
- David Lane Powers, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed September 9, 2007.
- Johnson, Brent. "Meet N.J.'s newest Assembly member", NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, February 15, 2018. Accessed February 15, 2018. "A two-term Trenton councilwoman is now the newest lawmaker serving in the Statehouse across town.... Reynolds-Jackson is a graduate of Trenton Central High School and has a bachelor's degree in sociology from Trenton State College – now the College of New Jersey – and a master's degree in administration from Central Michigan University."
- Daniel Bailey Ryall, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed September 3, 2007.
- Staff. "Antonin Scalia Associate Justice Nominee", The Miami Herald, June 18, 1986. Accessed August 6, 2009.
- Manual of the Legislature of New Jersey, 1956, p. 381. Accessed August 1, 2019. "Sido L. Ridolfi (Dem., Trenton, N. J.) Senator Ridolfi was born in Trenton, September 28, 1913. He is a graduate of Trenton Senior High School, Princeton University, and Harvard Law School."
- Charles Skelton, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed August 25, 2007.
- Robin Titus' BiographyPrintTrack This Politician, Project Vote Smart. Accessed February 9, 2016.
- Sackett, William Edgar; and Scannell, John James. Scannell's New Jersey First Citizens: Biographies and Portraits of the Notable Living Men and Women of New Jersey with Informing Glimpses Into the State's History and Affairs, Volume 1, p. 511. J. J. Scannell, 1917. Accessed July 13, 2016. "Bennet Van Syckel— Trenton.— Jurist. Born in Bethlehem, Hunterdon Co., April 17, 1830."
- Staff. "Albert C. Wagner Dies at 76; Headed Jersey Prison System", The New York Times, June 20, 1987. Accessed October 17, 2015. "Born in Trenton, Mr. Wagner was a graduate of Villanova University and the University of Pennsylvania, where he received a master's degree."
- Allan Bartholomew Walsh, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed September 6, 2007.
- Fitzgerald's Legislative Manual, 1984, p. 262. J.A. Fitzgerald, 1986. Accessed November 9, 2017. "Karl Weidel, Rep., Clinton – Assemblyman Weidel was born Sept. 27, 1923, in Trenton. He lives at One Charles Way, Clinton."
- Ira Wells Wood, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed September 6, 2007.
- Staff. "Ousted In Jersey Over Food Charges; Barlow Dropped as Procurement Officer After Appeal to Hershey by Edison U.S. Audit Is Started State Quartermaster, Who Also Held a Selective Service Post, Is Silent on Move", The New York Times, February 22, 1942. Accessed July 2, 2018. "Stephen H. Barlow of Trenton, quartermaster general of New Jersey, was summarily removed today as procurement officer of this State for selective service."
- Staff. "Gen. Bluemel Gets DSM; Jersey Officer Commanded Division at Bataan Before Capture", The New York Times, November 10, 1945. Accessed July 2, 2018. "The Army's Distinguished Service Medal was presented at the Presidio today to Brig. Gen. Clifford Bluemel of Trenton, N. J., who commanded the Thirty-first Division in the defense of Bataan before his capture by the Japanese who held him prisoner more than two years."
- Thomas McCall Cadwalader, The Society of the Cincinnati in the State of New Jersey. Accessed December 2, 2019. "Born in Trenton, NJ on 11 Sep 1795 and died at 'Greenwood' in Trenton, NJ on 16 Oct 1873."
- Ensign Frank W. Crilley, USNR (1883–1947), Naval History & Heritage Command. Accessed January 8, 2015. ""Frank William Crilley was born in Trenton, New Jersey, on September 13, 1883."
- Armstrong, Samuel S. "Trenton in the Mexican, Civil, and Spanish–American Wars", Trenton Historical Society. Accessed May 9, 2007. "Samuel Gibbs French was a native of Trenton and graduated from West Point in 1843 with the brevet rank of Second Lieutenant and assigned to the Third U.S. Artillery, July 1, 1843."
- Medal of Honor Recipients — World War II (G-L), United States Army Center of Military History, July 16, 2007. Accessed January 28, 2008.
- Nadel, Logan. "Celebrating Trenton’S Historical Figures: Needham Roberts", Trenton Daily, May 18, 2020. Accessed June 3, 2020. "For the third iteration of Trenton’s Historic Figures, we will be taking a close look at Needham Roberts, a war hero who earned not only the Croix de Guerre medal by the French government, but also the purple heart posthumously in 1996 for his service during World War I. Born in 1901, Roberts grew up on Wilson Street in Trenton, NJ and was the son of a pastor."
- Lamb, David. "General a winner who learned history's lessons", St. Petersburg Times, March 9, 1991. Accessed February 8, 2011. "H. Norman Schwarzkopf Jr. – the H. stands for nothing and he doesn't use the junior – was born in Trenton, NJ, 56 years ago, the son of German immigrants."
- Livingston, Guy. "George Antheil's Childhood in Trenton", Neue Zeitschrift für Musik, September 2001. Accessed January 25, 2011.
- Phillips, Rashad. "MellowHype: Chordaroy Life" Archived March 3, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, HipHopDX, July 15, 2011. Accessed March 30, 2012. "DX: Now as far as the L.A. scene, I read that you are actually from out East. Hodgy Beats: Yeah, I was born in East Lawrence, New Jersey and raised in Trenton until I was eight."
- Carman, ChristianMusic.com. Accessed January 8, 2015. "Carman grew up in a close, fun-loving, musical Italian family in Trenton, New Jersey."
- Kaufman, Gil. "Jay-Z's 'Decoded': The Reviews Are In! Hov 'deserves the same level of respect as any of those great scribes,' one reviewer writes, comparing the MC to iconic poets.", MTV, November 16, 2010. Accessed January 25, 2011.
- Charles Hayward Chapman Obituary Archived January 9, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, ObitsforLife.com. Accessed January 8, 2015. "Born in Trenton, New Jersey Charles was fascinated by the guitar at an early age, and that fascination led him to Berklee College of Music."
- Opdyke, Tom. "Pop Music This 'Boots' Is Made For The Tenor Saxophone", The Morning Call, February 18, 1984. Accessed January 25, 2011.
- Provizer, Norman. "Richie Cole Brings Sax Appeal To Vartan", Rocky Mountain News, April 4, 1996. Accessed March 25, 2012. "On his current CD, Kush: The Music of Dizzy Gillespie, alto saxophonist Richie Cole spends most of his time in the company of a large brass section.... Instead, the Trenton, N.J. native will be in a quartet setting for a live recording on the Vartan Jazz label."
- Staff. "Johnny Coles, 71, Warm Jazz Trumpeter", The New York Times, December 31, 1997. Accessed January 8, 2015."Mr. Coles was born in Trenton, and his family moved to Philadelphia when he was still a child."
- Staff. "Richard Crooks Wins Plaudits On Return; American Tenor Sings Oratorio and Opera Airs Before Throng in Carnegie Hall.", The New York Times, October 27, 1927. Accessed July 2, 2018. "There was a distinct feeling, however, that the stalwart young lyric singer of seven-and-twenty from Trenton, N. J., stood now at a parting of the professional ways, since his promising dramatic essay in Berlin."
- Urciuoli, Brielle. "Sarah Dash of Labelle talks at TCNJ about her Trenton roots", The Times (Trenton), September 24, 2014. Accessed October 28, 2014. "Musician and Trenton native Sarah Dash lectures at The College of New Jersey in Ewing on Wednesday, September 24, 2014."
- Smith, Liz. "The great Nona Hendryx – jamming with Lady Marmalade", Chicago Tribune, July 2, 2014. Accessed May 13, 2016. "That's the great R&B, soul, dance, funk, rock, art rock, hard rock and New Age diva Nona Hendryx. (Born in Trenton, New Jersey, Nona sounds rather British now. It's been a cosmopolitan life.)"
- Staff. "Jim Croce and Maury Muehleisen's musical partnership endures", Inside Jersey, August 16, 2010. Accessed March 16, 2012. "Maury Muehleisen was blessed with many musical gifts. By the time he was a teenager, the Trenton native already was an accomplished pianist. In late 1970, at age 21, Muehleisen released Gingerbreadd, his only solo album, on Capitol Records."
- Staff. "Local celebs need to brush up on Goodwill" Archived July 3, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, 98.4 Capital FM, July 4, 2010. Accessed February 8, 2011. "In addition to Jay-Z and Russell Simmons, rappers Ludacris, Chuck D and Trenton's own Wise Intelligent of the Poor Righteous Teachers will deliver taped messages to attendees."
- Kuperinsky, Amy. "Trenton's DJ Father Shaheed of Poor Righteous Teachers dead at 45", NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, May 28, 2014, updated March 29, 2019. Accessed September 3, 2020. "DJ Father Shaheed, a member of the Trenton hip-hop trio Poor Righteous Teachers born Scott Phillips, died in a motorcycle accident on Memorial Day."
- "Trenton Pianist Bows; Marion Zarzeczna Includes 2 Contemporary Compositions", The New York Times, April 5, 1954. Accessed August 22, 2018. "Marion Zarzeczna, young Trenton pianist with well drilled fingers, gave her first New York recital late yesterday afternoon at Town Hall."
- Gordon, Cormac. "Former Wagner College basketball player Terrance Bailey in good company", Staten Island Advance, February 14, 2013. Accessed October 12, 2015. "It turns out, not surprisingly, that Bailey liked being included with those Hall of Famers a whole lot. 'Wow,' the 47-year-old said after hearing the list over the phone Tuesday night in his Trenton home."
- Thompson, Thomas. "Brash Bo Comes On with a Big Pitch", Life, June 8, 1962. Accessed January 25, 2011.
- Elvin Bethea Archived September 30, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, database Football. Accessed November 26, 2007.
- Mike Bloom, NJSports.com. Accessed August 1, 2019. "Meyer Bloom was born January 14, 1915 in New York City and grew up in Trenton."
- Chass, Murray. "Twins Defeat Yanks for Sweep", The New York Times, May 7, 1971. Accessed October 22, 2017. "Braun, a resident of Trenton who will be 23 years old on Saturday, took two balls before sending a grounder toward center field."
- Staff. "Tal Brody returns to basketball home, A Trenton High star who became a star in Israel leads students on a U.S. exhibition tour.", The Philadelphia Inquirer, October 13, 2006. Accessed January 25, 2011.
- Caldwell, Dave. "Sprinter Turned Driver Is a Quick Study in Acceleration", The New York Times, August 30, 2009. Accessed November 26, 2013. "Brown, a 33-year-old native of Chesterfield, N.J., could become the first African-American to win a major N.H.R.A. championship.... Brown lived in Trenton until he was 6. When his grandfather died, his family moved to his grandmother's 10-acre farm in Chesterfield, in the rural part of Burlington County."
- Wally Campbell, Getty Images. Accessed January 8, 2015. "Wally Campbell of Trenton, New Jersey, had a short racing career that lasted from 1947 through 1954, but his accomplishments were many."
- Case III, George. "Remembering a Trenton dad who made his mark in the big leagues", The Trentonian, July 4, 2010. Accessed January 25, 2011.
- Longman, Jere. "Boxing; 3 Friends Qualify for U.S. Boxing Team", The New York Times, April 19, 1996. Accessed December 4, 2007. "Cauthen, 19, grew up 40 miles north, in Trenton, but he has fought out of Frazier's gym in Philadelphia for nine years."
- Maidenburg, Micah. "Investor aims to buy 3,000 foreclosed Chicago homes", Chicago Real Estate Daily, October 19, 2012. Accessed January 8, 2015. "A native New Yorker, Mr. Cogsville, 47, grew up in Trenton, N.J., before moving south to attend the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, where he was a soccer star, scoring 29 goals over four years, according to an article in the Daily Tar Heel, a student newspaper."
- Gwyn Coogan Archived January 12, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, USA Track & Field. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- Hollis Copeland, Basketball-Reference.com. Accessed January 8, 2015.
- Harry Deane, Baseball-Reference.com. Accessed January 9, 2015.
- Staff. "ECWA Interview with WWE Hall of Famer JJ Dillon", ECWA Pro Wrestling, December 20, 2013. Accessed January 9, 2015. "JJ Dillon: I started as a fan. I was born and raised in Trenton, New Jersey. As a young teenager I discovered wrestling on... I'm giving my age away (laughs)... on a black and white television. It was on one night a week for an hour and a half. And eventually a live event came to my hometown to the armory in Trenton. And when I went to the show and saw all these larger than life characters in action I was hooked."
- Lewis, Brian. "Rutgers hires St Louis' Dan Donigan", New York Post, January 22, 2010. Accessed January 9, 2015. "Donigan is a 43-year-old Trenton native and Steinert (NJ) High School grad."
- Freeman, Rick. "Diamond Reflections: Al Downing misses creativity in the batters' box", The Times (Trenton), August 18, 2010. Accessed March 20, 2012. "Over 33 years since he threw his last major-league pitch and nearly a half-century since he left Trenton to pursue a professional career, Al Downing remains a keen and opinionated observer of the game of baseball."
- John David Easton '55, Princeton Alumni Weekly. Accessed August 1, 2019. "John Easton died of melanoma July 28, 2001, at the Medical Center in Princeton. Born in Trenton, he was a longtime Hopewell Township resident."
- Nick Frascella, Peach Basket Society. Accessed September 10, 2019. "Born: July 6, 1914 Trenton, NJ"
- Bostrom, Don. "Gallagher Leads Phils Past Giants Outfielder's 3-For-3 Night Sparks 2-1 Win", The Morning Call, May 25, 1995. Accessed February 1, 2011. "With Lenny Dykstra nursing his sore lower back for the second straight day, role player Dave Gallagher took over the leading role. All the 34-year-old Trenton native did was go 3-for-3 to raise his average to a nifty .441."
- Avilucea, Isaac. "Trenton on hook for $60K in high-speed chase that injured famed boxer, woman", The Trentonian, January 3, 2018. Accessed December 11, 2018. "While city boxing legend Samuel Goss scored a technical knockout, his daughter also scored a nice chunk of change following a police car chase that injured the two city residents.... Goss, a five-time Golden Gloves champ and former Olympian, is settling his federal lawsuit – which accused several 'John Doe' cops of being 'careless and negligent' in the car chase – for $25,000."
- Staff. "76ers Add Greg Grant's Speed As Team Seeks Zip In Offense The Team's Newest Guard Came From The Cba To Help Replace Vernon Maxwell. He Has A Chance To Stick.", The Philadelphia Inquirer, November 22, 1995. Accessed February 1, 2011. "Grant, a Trenton native, has played with five NBA teams since coming into the league as the Phoenix Suns' second round pick out of Trenton State in 1989."
- Mel Groomes, Pro-Football-Reference.com. Accessed August 1, 2019. "Born: March 6, 1927 in Trenton, NJ"
- Fremon, Suzanne S. "State Has 13 on Olympic Team", The New York Times, August 13, 1972. Accessed November 22, 2017. "Other New Jerseyans on the various Olympic teams are Phillip Grippaldo of Belle ville and Frank Capsouras of River Edge, weight lifters; Robert Sparks of Clark and Thomas Hardiman of Trenton, team‐handball players, and Reginald Jones of Newark a light‐middleweight boxer."
- Jacke Healey, Minor League Baseball. Accessed July 2, 2018. "Birthplace: Trenton, NJ"
- Staff. "Sixers-Nets Talks Stall Over Hinson", The Philadelphia Inquirer, January 15, 1988. Accessed February 1, 2011. "'If it's in New Jersey, I'm close to home,' added Hinson, a native of Trenton."
- D'Allesandro, Dave. "Notebook: Trenton native Dahntay Jones enjoying his best season yet with the Indiana Pacers", The Star-Ledger, November 17, 2009. Accessed February 1, 2011.
- Staff. "Falcons win at Lambeau, take on Vet next", Philadelphia Daily News, January 6, 2003. Accessed February 1, 2011. "Now it's on to Philadelphia, not far from Kerney's hometown of Trenton, to play the Eagles..."
- CFL.ca Player Profile. Accessed December 17, 2007.
- Varsallone, Jim. "Ring of Honor fans enjoy making Cheeseburger a top seller", The Miami Herald, April 30, 2016. Accessed January 4, 2018. "Cheeseburger grew up Brandel in Trenton, N.J. He attended Trenton Catholic Academy in Hamilton, N.J. He played some basketball in school but nothing serious."
- Staff. "Report: Giants' Mckenzie Arrested For Dui", The Sports Network, November 14, 2008. Accessed February 1, 2011. "A Trenton, New Jersey native, McKenzie has played all but three games for the Giants since signing with the club as a free agent prior to the 2005 season."
- Bob Milacki Stats, Baseball-Reference.com. Accessed June 3, 2018.
- Karin Miller, International Tennis Federation. Accessed September 17, 2018. "Birth Place: Trenton, New Jersey, USA"
- Johnson, Greg. "Trenton Central grad Keith Newell returns to Sun National Bank Center with Philadelphia Soul", The Trentonian, June 9, 2016. Accessed August 1, 2019. "The nostalgia washes over Keith Newell as he paces the turf on the floor of Sun National Bank Center, completing a two-hour walkthrough with the Arena Football League’s Philadelphia Soul. Moments later, the Trenton native speaks to a trio of reporters and reminisces about his days around these parts and this venue."
- Myles Powell, Seton Hall Pirates men's basketball. Accessed August 6, 2019. "Attended Medford Tech, Trenton Catholic, and most recently South Kent School... birthday is July 7 and was born in Trenton, N.J."
- Sherman, Steve. "Soccer: Popularity aside, a new skill is mastered in Bristol", Bucks Local News, August 22, 2012. Accessed November 2, 2017. "'You can't just stand there flat-footed,' said Robinson, a former Trenton resident and three-time All-American at Adelphi University (1990) who graduated from Notre Dame High School in 1986."
- Staff. "Miller, Rodman highlight Hall of Fame finalists", Toronto Sun, November 30, 2010. Accessed February 8, 2011. "A native of Trenton, New Jersey, Rodman was a controversial presence both on and off the court despite winning five NBA titles (1988–89 with Detroit; 1996–98 with Chicago)."
- Hageny, John Christian. "Hockey: Where are they now? Call Lawrenceville's Sanguinetti a Hurricane", The Star-Ledger, February 24, 2013. Accessed February 8, 2018. "Bobby Sanguinetti was born in Trenton, grew up a New York Rangers fan and even wore number 22 for a time in his career in honor of his favorite player, Brian Leetch, while skating at Lawrenceville."
- Harris, Beth. "Dutch treat: Schoutens earns 2nd Olympic speedskating spot" Archived January 26, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Herald, January 4, 2018. Accessed January 25, 2018. "Schoutens, born in Trenton, New Jersey, to Dutch parents, won the 3,000 on Tuesday to qualify for her first Olympics."
- Lee, Edward. "Special Season For Ravens' Stills; Reserve Linebacker, Dominant On Special Teams, Calls Campaign 'Highlight Of My Career'", The Baltimore Sun, December 9, 2006. Accessed February 8, 2011. "A native of Trenton, NJ, Stills repeated the fourth and seventh grades and sat out his first year at West Virginia after being ruled academically."
- Parker, L.A.. "The former South Carolina University star via Trenton Catholic Academy requested a rebounder then showed the genesis of her nickname.", Trentonian for trentonian.com, February 26, 2019.
- Alphonso Taylor, JustSportsStats.com. Accessed August 1, 2019. "Born: September 7, 1969 Trenton, NJ"
- Vince Thompson, Pro-Football-Reference.com. Accessed July 15, 2019. "Born: February 21, 1957 (Age: 62-144d) in Trenton, NJ"
- Lamb, Bill. Mike Tiernan, Society for American Baseball Research. Accessed June 12, 2018. "Michael Joseph Tiernan was born in Trenton, New Jersey, on January 21, 1867, the youngest of three boys born to Irish Catholic immigrants."
- Dantouma Toure, TopDrawerSoccer.com. Accessed July 20, 2020. "High School: Trenton Central; Region: New Jersey; City: Trenton; State: New Jersey"
- Attner, Paul. "A work of heart: much of Eagles cornerback Troy Vincent's hometown of Trenton, N.J., is in disrepair. But his plentiful, passionate and personal work to rebuild and revitalize the community is beginning to show results and makes him No. 1 on TSN's annual list of Good Guys in pro sports", The Sporting News, July 7, 2003. Accessed May 21, 2017. "Troy Vincent is walking through the Wilbur section of Trenton, N.J. He grew up in Wilbur when survival was a daily 10-round fight. It's worse now."
- Charlie Weis Archived March 9, 2005, at the Wayback Machine, New England Patriots. Accessed August 18, 2007.
- "Former All-American Cager, Werkman, Is Now Coaching", Asbury Park Press, July 22, 1973. Accessed November 9, 2017. "Nick Werkman, Seton Hall University's last All-America basketball player, is now the varsity baseball and basketball coach at Stockton State College. He was born in Trenton, where he started playing CYO basketball when he was 10 years old."
- Wright, T. M. The intelligent man's guide to flying saucers, p. 211. A. S. Barnes, 1968. Accessed January 5, 2015. "Finally, there is Orfeo Angelucci, an Italian immigrant raised in Trenton, New Jersey."
- Stout, David. "Trenton Man Faces Charges in the Slayings of 4 Women", The New York Times, August 9, 1996. Accessed December 2, 2019. "Not much was known about Mr. Balaam. The police said he had been born in Trenton, was unemployed and lived at 421 Stuyvesant Avenue, where he was arrested about 2:30 P.M."
- Smythe, Christie; Dolmetsch, Chris; and Larson, Erik. "Giuliani Law Partner Named Top New York Federal Prosecutor", Bloomberg News, January 4, 2018. Accessed January 7, 2018. "A native of Trenton, New Jersey, where his father was a real estate developer, Berman graduated from the University of Pennsylvania in 1981 and its Wharton School."
- King, Elspeth. "Obituary: Jude Burkhauser", The Independent, October 27, 1998. Accessed January 5, 2015. "Jude Burkhauser, artist and curator: born Trenton, New Jersey 10 September 1947; died 19 September 1998."
- "Biggest Yacht Built For American Woman; Mrs. R.M. Cadwalader's Craft Is 407 Feet 10 Inches Long and Displaces 5,600 Tons.", The New York Times, January 27, 1931, Accessed October 27, 2019. "Mrs. Cadwalader was formerly Miss Emily Roebling of Trenton, N. J."
- "The Alumni Trustees", p. 800. Princeton Alumni Weekly, Volume 1. Accessed January 8, 2015. "John Lambert Cadwalader '56 was born in Trenton, N. J., in 1836."
- Husted, Bill. "Husted: Independence Institute's Jon Caldara on Trump, conservatism and 'seeing the universe honestly' (Slideshow)", Denver Business Journal, January 25, 2016. Accessed August 31, 2016. "Jon Caldara, 51, is president of the Independence Institute, Denver's right-wing think tank. He spreads the word Sunday nights on KHOW – and he's happy to talk the talk over a beer at the Avenue Grill. He was born in Trenton, NJ – moved with the family to Colorado at 6."
- Saffron, Inga. "Bernard Cywinski, paterfamilias of Philadelphia architecture", The Philadelphia Inquirer, March 6, 2011. Accessed January 8, 2015. "To look at Mr. Cywinski, who grew up in Trenton, you would never guess he could be such a warm, gregarious personality."
- Kelly, Jacques. "Mathias J. DeVito, former Rouse Co. leader, dies", The Baltimore Sun, July 29, 2019. Accessed August 1, 2019. "Born in Trenton, N.J., he was the son of Charles DeVito, a paperhanger, and his wife, Margaret."
- Kleinberg, Eliot. "The Last Flight of Matt Duke", The Palm Beach Post, September 4, 2015, updated August 29, 2016. Accessed December 2, 2019. "Matthew Edward Duke wasn't even Matt Duke. He was born Matthew Ducko in 1915 in Trenton, N.J., one of four children of European immigrants."
- Kandell, Jonathan (September 29, 2017). "Can This Man Return AIG to Glory?". Institutional Investor. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
A working single mother, she then took 5-month-old Brian to Trenton, New Jersey, where she had a sister and raised him.
- Harrington Emerson Papers, 1848–1931, Penn State University. Accessed October 19, 2013. "Emerson was born on August 2, 1853 in Trenton, New Jersey."
- Shultz, Alex. "Why Am I So Tired All the Time? What science says about perpetual sleepiness—and what you can do about it.", GQ, November 1, 2018. Accessed December 2, 2019. "Al Herpin of Trenton, New Jersey, died on January 3, 1947. He was 94. Herpin spent a large chunk of his adult life making a peculiar claim: that he never slept."
- via Associated Press. "Bishop Edward Kmiec Installed As Leader of Catholic Diocese", WBFO. Accessed December 2, 2019. "A native of Trenton, N.J., Kmiec said he was drawn to the priesthood during his days as an altar boy."
- Fletcher, Juliet. "There's No Place Like Home: After two years in New Hope, a Tin Man finds the heart of the gallery scene in Philly." Archived July 4, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Philadelphia City Paper, November 27 – December 3, 2002. Accessed March 20, 2012. "Partly why this Trenton expat moved his base of operations to Philadelphia from New York, 'where it costs four times what it does here to run a business month to month,' was to give artists – particularly those very New York or West Coast-oriented – a wider spread of support."
- Strausbaugh, John. "Street Art That's Finding A New Address", The New York Times, March 7, 2010. Accessed July 2, 2018. "Mr. LeVine came to the movement the same way his artists did. He grew up in Trenton and earned a degree in sculpture, but he was less attracted to fine art than he was to underground comics, punk and hip-hop, 'anything subculture and edgy.' With a loan from his parents, he opened his first small art gallery in New Hope, Pa., in 2001."
- Manufacturers' Association Bulletin. Manufacturers' Association of New Jersey. 1922. p. 6.
Of the original partners John Astbury and Richard Millington formed in 1873 a partnership with Thomas Maddock, and with this co-partnership was born the sanitary pottery business in this country.
- Hein, Leonard W. "J. Lee Nicholson: pioneer cost accountant", Accounting Review (1959): 106–111. Accessed January 8, 2015. "Major Nicholson was born in Trenton, New Jersey, in 1863, but spent his early years in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania."
- Baldwin, Tom. "Where did Pike peak? Colo. explorer got start in New Jersey", Courier-Post, August 25, 2008. Accessed September 19, 2008. "Nineteenth century Jersey explorer Zebulon Pike was born in Lamberton, now a part of south Trenton, but gave his name to Colorado's 14,000-foot (4,300 m) Pikes Peak."
- Bianco, Anthony. "Joe Plumeri: The Apostle of Life Insurance", Business Week, March 30, 1998. Accessed February 12, 2014. "That would be the blue-collar precincts of North Trenton, N.J., just 15 miles from here. The cool-walking demonstration ended, Plumeri explains how he stumbled into a career on Wall Street by taking a menial job at a brokerage house that he had mistaken for a law firm."
- CEO Plumeri. Business Week. May 6, 2008. Retrieved July 15, 2010.
- Wosh, Peter J. Wosh, Covenant House: Journey of a Faith-Based Charity, pp. 13–35. University of Pennsylvania Press, 2005. ISBN 9780812238310. Accessed January 17, 2018.
- Staff. "Frank D. Schroth, 89, Publisher Of The Brooklyn Eagle, Is Dead; Acclaimed for His Service", The New York Times, June 11, 1974. Accessed July 11, 2018. "Following the closing of The Eagle in March of 1955, after a seven‐week strike by the New York Newspaper Guild, Mr. Schroth retired and made his home in Trenton."
- Weber, Bruce. "Thomas N. Schroth, Influential Washington Editor, Is Dead at 88", The New York Times, August 4, 2009. Accessed March 16, 2012. "Thomas Nolan Schroth was born in Trenton on Dec. 21, 1920, the son of The Brooklyn Eagle's publisher, Frank D. Schroth."
- Smith, Lanny; and Capps, Linnea. "An interview with Dr. Vic Sidel", Social Medicine, Volume 7, Number 3, October 2013. Accessed February 1, 2018. "Graduates went on to Trenton Central High School, which had a class size of 3000. My main recollection of high school was graduation.... In my speech I talked about a $10,000 home, which in 1949 was an impossible dream."
- Staff. "GM's history of CEOs – Robert C. Stempel", Los Angeles Times. Accessed February 8, 2011. "Stempel was born July 15, 1933, in Trenton, N.J."
- "Thompson, Margaret E., 1911–1992", American Numismatic Society. Accessed June 12, 2018. "Margaret Thompson was born in 1911 in Trenton, New Jersey and received her bachelor of arts from Radcliffe College in 1931."
- Bloom, Susan. "Artist vs. tyranny Agudath Israel hosts program on Arthur Szyk, 'advocate for humanity'", New Jersey Jewish News, March 4, 2015. Accessed August 1, 2019. "Ungar: Though I’ve lived in California for many years, I grew up in Trenton and still have family in New Jersey."
- Hagenmayer, S. Joseph. "Episcopal Bishop Albert W. Van Duzer", The Philadelphia Inquirer, November 30, 1999. Accessed November 8, 2015. "A longtime New Jersey resident, he lived in Moorestown for five years, Medford for 10 years, Trenton for 20 years, and Merchantville for 20 years."
- About Ken Wolski, Ladybud. Accessed February 9, 2016. "Born in Trenton, Ken Wolski obtained a BA in Philosophy and a Masters in Public Administration (MPA) from Rutgers University."
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Trenton, New Jersey. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Trenton. |
| Wikisource has the text of a 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article about Trenton, New Jersey. |
- City of Trenton website
- Trenton Historical Society
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Trenton, New Jersey
- US Census Data for Trenton, NJ
| Preceded by Annapolis, Maryland |
Capital of the United States of America 1784–1785 |
Succeeded by New York City |





